| BESTERRA CO., LTD (1433) |
|
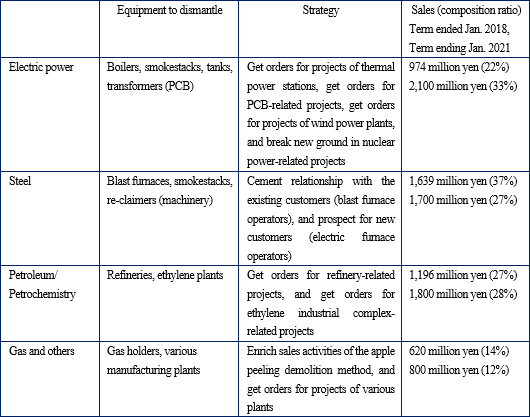
||||||||
Company |
BESTERRA CO., LTD |
||
Code No. |
1433 |
||
Exchange |
Tokyo Stock Exchange, First Section |
||
Industry |
Construction business |
||
President |
Yoshihide Yoshino |
||
Address |
Kiba Park Bldg, 3-2-6 Hirano, Koto-ku, Tokyo, Japan |
||
Year-end |
January |
||
URL |
|||
* The share price is as of the end of September 11. The number of shares issued was obtained by subtracting the number of treasury shares from the number of outstanding shares as of the end of the latest quarter. ROE and BPS are results at the end of the previous fiscal year.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
*The forecasted values were provided by the company.
*From the term ending Jan. 2019, consolidated performance will be posted, and net income means profit attributable to owners of parent (hereinafter called "net income.") * Stock split 1:4 in May 2015, 1:2 in February 2016. 1:3 in February 2017 (EPS has been revised retrospectively) This Bridge Report reviews on the outlook of BESTERRA for the first half of the fiscal year January 2019 and its business plans from fiscal year January 2019. |
| Key Points |
 |
| Company Overview |
|
Code of conduct
We will fulfill our responsibilities as professionals. We constantly develop new technologies, "put a higher priority on safety than anything else," and offer our services to clients while increasing assurance under the motto "Swifter, more affordable, and safer." 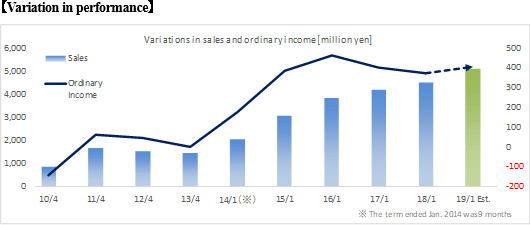 The company sticks to fabless management, in which it does not own necessary heavy machinery or engineers for dismantlement (so that they can handle any kinds of equipment of plants that have complex structures). 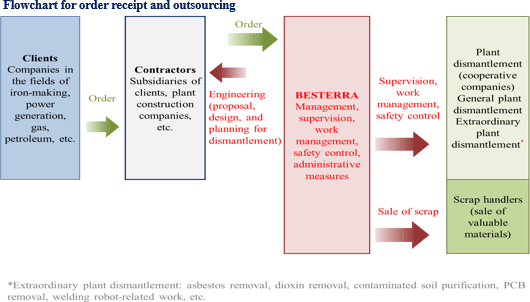 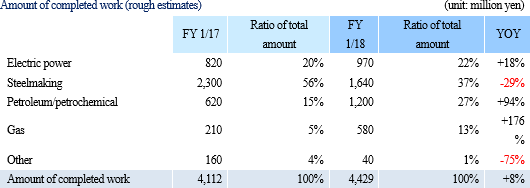 *Concerning 2 revenue recognition methods and seasonality of revenue recognition.
There are 2 revenue recognition methods for construction contracts: 1) a completed-contract (CC) method in which revenue is recorded at the end of the construction, and 2) a percentage-of-completion (PC) method in which revenue is recorded as construction progresses. For the projects from which valuable materials, such as scrap, are generated through plant dismantlement, the company basically applies the PC method to large-scale projects whose contract amount exceeds 50 million yen and whose period exceeds 3 months (from the term ended Jan. 2018), and the CC method to other projects. Meanwhile, the timing of revenue recording (completion of construction) using the CC method is often influenced by facility investment plans of the clients. In case of the company, the revenue is often recorded during the first quarter (February to April) and the fourth quarter (November to January) (seasonality of revenue recognition). With this method, however, changes of quarterly results may mislead investors,Therefore, the company is expanding the scope of application of the PC method step by step, and makes continuous efforts to smooth revenue.
|
| Medium-term Management Plan (from the term ending Jan. 2019 to the term ending Jan. 2021) |
 Profit structure reform, Personnel structure reform, Pursuit of 3D business values, M&A strategy Reform of the earnings structure
The company will expand the number and scale of projects for which it receives orders, enrich demolition methods, and strengthen its sales capabilities.
Expansion of the number and scale of projects for which the company receives orders
As described below, the company will go ahead with individual strategies by setting targets for each of the fields of electric power, steel, petroleum and petrochemistry, and gas and others:
 The company targets its business in the thermal power generation field which carries heavier environmental burdens. The company will make the most of its extensive experiences and business results in dismantling boilers, smokestacks, and tanks, and its advantageous patented demolition methods in order to take in demand for demolition. <Steel Industry> While blast furnace manufacturers produce three-fourths of crude steel and the other one fourth is produced by electric furnace manufacturers and metal rolling manufacturers, the company has made transactions with all the blast furnace manufacturers, electric furnace manufacturers, and metal rolling manufacturers. The blast furnaces (coke ovens) built during the high economic growth period will come up for repair in the next 10 years, and besides, each blast furnace manufacturer is integrating their respective production bases and enhancing the equipment there with the aim of increasing price competitiveness. The company will focus on making a proposal for demolition works using the 3D technology, as well as take in demand for demolition through numerous strengths, including the patented demolition techniques, and the safe and efficient demolition works the company has cultivated. <Petroleum/Petrochemical Industry> Japan has 22 refineries in 14 regions; however, demand is falling due to the population decrease, popularization of fuel-efficient vehicles, and fuel change. The petroleum and petrochemical industry, therefore, is being forced to take action, such as corporate restructuring and equipment reduction, and the government is encouraging reorganization through the Sophisticated Method of Energy Supply Structures and the Industrial Competitiveness Enhancement Act. In addition, 15 petrochemical complexes in nine regions in Japan are pushed aside by overseas competitors in terms of cost competitiveness and size, and they are forced to go through corporate restructuring and downsizing of facilities. The company will take in demand for demolition, using its advantageous experiences in demolition of not only refineries and ethylene plants, but also plant equipment which is a downstream business. Specifically, the company will open offices in the bay area, which is the so-called "Pacific belt zone," with a focus on proposing and marketing its unique demolition techniques. Enrichment of demolition methods
The company will keep on proposing competitive patent-based dismantlement methods including the cost competitive "Apple peeling demolition method" and the "Ringo☆Star" (dismantling of tanks), unique fireless method (power related equipment such as transformers), and the windmill dismantling method (wind power generation) that is pending for international patent, and it is making efforts to put them into practical use. <"Apple peeling demolition method" and fusing robot "Ringo☆Star"> The "apple peeling demolition method" is a method of dismantling a large spherical tank, such as gas holders and oil tanks, by cutting it in spirals from the center of the ceiling of the enclosure part. The cut part spirals down to the ground gradually under the force of the earth's gravity (natural energy). The method enjoys superiority in a work period, cost, and safety, and has considerable competitive advantages, realizing "greater promptness, higher cost efficiency, and added safety." Furthermore, the company offers a robot for the fusing process, "Ring☆Star," which automates the "apple peeling demolition method." <Environment-related methods> The company has cultivated experiences and business results of a multitude of environment-related demolition works, using the "fireless methods" which do not require the use of fire. For example, although polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are considered as a toxic substance and therefore totally abolished today, it had been used for many years in transformers and condensers because of its excellent thermal stability and chemical stability (electric insulation characteristics). In many cases, transformers and condensers are disposed of in conjunction with plant demolition works; however, because PCBs gasify when they are treated at the high temperature, posing a risk of inhaling the gas so generated, any firearms (such as gas cutting machines) cannot be used in demolition and withdrawal involving PCBs. The company is skillful at fireless and quasi-fireless methods using saber saws (which cut off objects with their saw blades moving in a reciprocating manner) that can cut off objects thicker than the thickness, which, in the industry, had been considered impossible to cut, through numerous devices, including measures against seizure of motors and recycling of blades. <Windmill demolition works> According to the material presented by the company, the wind power generation volume worldwide is 486,790 MW (by about 340,000 onshore power generation plants and about 4,000 offshore ones) with an annual growth rate of about 20%. In Japan, the number of wind power generation plants stood at 2,225 as of the end of 2017, expanding by about 90 every year. Meanwhile, as the useful life is approximately 15 to 20 years, and the windmills for power generation established in the early stage are reaching the application limit. Moreover, not a few plants need to be dismantled due to damage or fatal failure caused by thunderbolts or typhoons. Windmills for power generation are generally dismantled by building scaffolds outside the support columns. As some windmills have been built in mountain districts and on the sea, demolition of them is highly difficult. The company has invented windmill demolition methods that do not require scaffolds, and are filing a patent as the "knocking-down method for dismantling windmills for power generation (international patent)," "knocking-down method for dismantling towering structures using their bases," and "method for dismantling tower-shaped equipment for wind power generation (international patent)." Safety of workers can be improved dramatically and the work period can be shortened by using these patent-based methods. 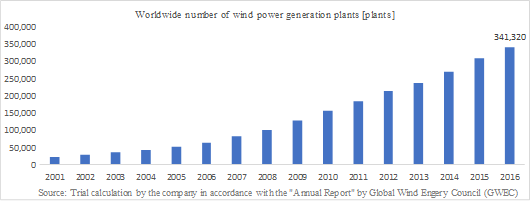 Enhancement of sales capabilities
The company will increase the ratio of demolition works ordered based on prime contracts and enrich sales bases. Currently, the ratio of works as a primary subcontractor entrusted by prime contractors is high. It, therefore, will increase the number of orders received directly from customers and the proportion of prime contract-based works, with the aim of improving earnings ratio. Specifically, the company will enrich advertising media, such as the website, promotional materials, and other various media, as well as present its products and services at exhibitions. Furthermore, the company will also examine possibilities of establishing bases in the Keihin region and the industrial district in Sendai to expand orders for stock-type projects (e.g. continuous orders on customer group units and on-site). As of the end of the fiscal year ended January 2018, the business bases are the Tokyo head office (3,561 million yen in sales in the fiscal year ended January 2018), JFE Chiba Port Office (Chiba city, Chiba prefecture, 550 million yen), Chiba office (Ichihara city, Chiba prefecture, 221 million yen), and West Japan office (Fukuyama city, Hiroshima prefecture, 164 million yen).
Reform of the human resources structure
The company, which specializes in executing and managing demolition works, needs to allocate a supervisor in each work site. Although it is essential to increase the number of dismantlement supervisors for a sustainable growth, the number of skilled construction workers falls short chronically; therefore, the company will introduce the complete five-day workweek system and endeavor to establish human resources development programs, with the aim of enhancing recruitment and development of human resources.In introducing the five-day workweek system, the company will strengthen "work shift (time) management by the management" and "work site (labor) rotation" to improve the quality of work with a more relaxed working style. Meanwhile, to establish human resource development programs, based on the assessment of the actual situation of the dismantlement supervisors, the company will establish and operate human resource systems that focus on the individual worker's working style by introducing a dismantlement work expert course and a management course and improving the program to promote acquisition of qualifications. Furthermore, it will promote a "human resource development program" as a system aimed at passing the skills and knowledge down to less-experienced workers. 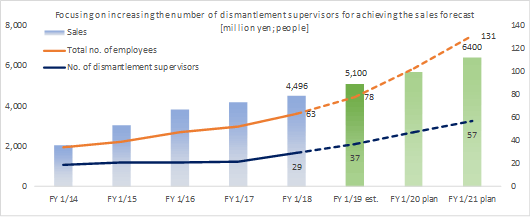 Pursuit of the value of the 3D business
The company will take advantage of the 3D technology as value added to the plant demolition business by providing the 3D measurement and data services along with demolition works (strengthening 3D demolition simulation) and offering on-site 3D data utilization support (introducing remote support). In addition, it will combine the 3D measurement technology with the technology of controlling the demolition planning robot manipulator in order to enter the field of decommissioning of nuclear power plants.As part of enhancing 3D demolition simulation, the company offers the 3D measurement service at the time of submission of estimates for projects of large-scale equipment, and the service of planning demolition works incidental to equipment repair. Three-dimensional laser measurement enables not only highly accurate demolition planning and production of estimates for a shorter period of time, but also implementation and provision of replacement of heavy machinery and equipment, and intervention simulations with three-dimensional CAD at the time of demolition works following equipment repair. Furthermore, the company will introduce remote support and establish a structure of remotely supporting on-site use of 3D data from the headquarters (conventionally, for using 3D data on site, it has been required to station workers with expertise in the 3D technology at customers' offices due to mastery of software and limits of computer specifications). Moreover, the company will break new ground in the field of nuclear power plant decommissioning by integrating the 3D technology and robotics. The company, ahead of any other companies, has put a remote demolition robot (Ringo☆Star) into practical use in plant demolition. It will strive to create an autonomous and remote demolition technology in which various 3D data obtained by robots developed through the integration of robotics and the 3D technology are utilized for dismantling nuclear power plants whose operation has been ceased. M&A strategy
Keeping in mind the maximization of business scale and development of innovative new services, in the highly relevant field such as design, Cloud and robots, in the plant dismantlement business, the field of the personnel service business, and the field of 3D measurement, BIM, and CIM, the company will proactively establish business alliances and carry out M&A deals. In March 2018, it acquired Hiro Engineering Co., Ltd., which is engaged in technical support (human resources services) for machinery, electrical instrumentation, control, system and design, as a consolidated subsidiary. It also established a business collaboration agreement with Hitachi Plant Construction, Ltd. in July to enhance competitiveness in the business related to dismantlement of nuclear reactors and with DAI-ICHI CUTTER KOGYO in September for the plant equipment dismantlement business.
|
| First Half of Fiscal Year January 2019 Earnings Results |
|
The main business of Hiro Engineering Co., Ltd. is to dispatch engineers for machinery, electricity, control, systems, design, etc. mostly in the fields of aviation, space, plants, and industrial equipment. When BESTERRA conducted 3D measurement of a nuclear power plant, Hiro Engineering dispatched competent personnel and gave technical support. BESTERRA plans to utilize the advanced technologies and staffing skills and knowledge of Hiro Engineering Co., Ltd. for improving the quality of services and securing engineers. 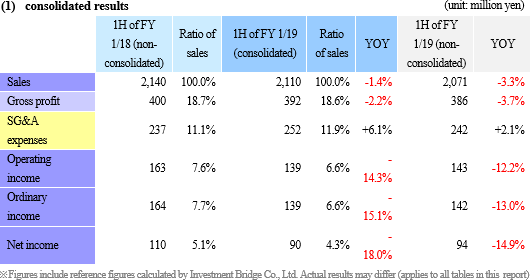 Sales and operating income declined 1.4% and 14.3% respectively from non-consolidated results in the same period last year.
Net sales decreased 1.4% from non-consolidated sales in the same period last year to 2,101 million yen. Among them, revenue from completed dismantlement projects decreased 3.3% to 2,034 million yen. Although the plant dismantlement business is doing well, the completion of a project was delayed to the second half based on the customer's request to carry out additional works. By industry, sales in the electricity and gas industries showed growth and sales in the steelmaking industry also increased with a project to dismantle blast furnaces. However, sales in the petroleum and chemistry industries declined greatly because most of dismantlement works of ethylene production equipment had already been completed. Operating income decreased 14.3% from non-consolidated sales in the same period last year to 139 million yen. While sales are temporarily sluggish due to the delay in completion of a project as stated in the above, personnel expenses (which are recorded in cost of sales) increased because of the efforts to develop dismantlement supervisors. As a result, gross profit margin was 18.6%, down 0.1 point. Selling, general and administrative expenses increased 6.1% year on year because of posting of head office relocation expenses as well as strategic business investments such as R&D investments related to 3D measurement and advertising (exhibition) aimed at increasing original contract works. The company is planning to increase the number of dismantlement supervisors by eight for the full term. As of the first half settlement announcement day (September 7, 2018), the number of supervisors is 32, increased by three. It will continue to actively recruit people to achieve the plan. In addition, in preparation for the scale expansion and staff increase accompanying the progress of the medium-term management plan, it moved its head office in August 2018. Orders for dismantlement works decreased 55.7% year on year to 1,163 million yen in reaction to a long-term large-scale project (1,240 million yen) that took place in the same period last year. Due to this factor and steady progress of the work, backlog of orders at the end of the first half decreased 52.4% to 1,346 million yen. In the second half, it is anticipated that orders will grow mainly in the steelmaking and electric power industries, and orders for dismantlement work in the full year are expected to increase from the previous term. 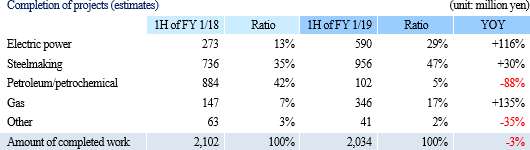 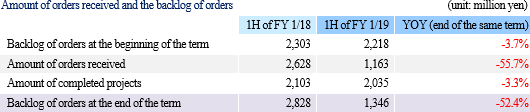 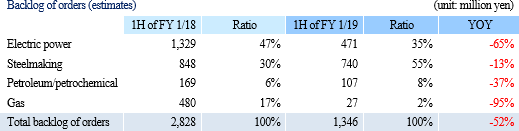 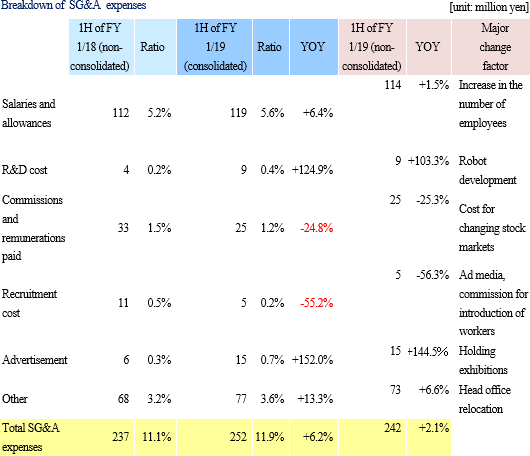 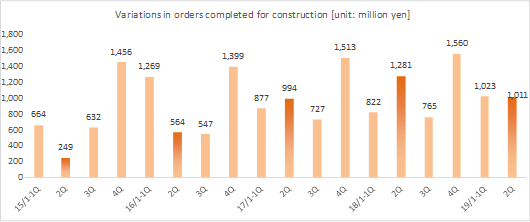 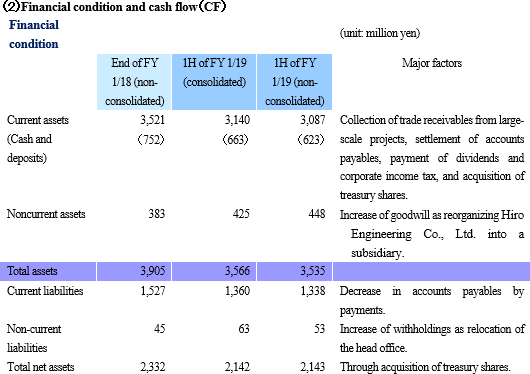 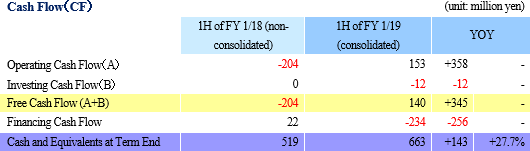 (3) Business alliance with Hitachi Plant Construction, Ltd. for a nuclear power plant dismastment project
On July 6, 2018, the company signed a business alliance agreement with Hitachi Plant Construction, Ltd. (a wholly owned subsidiary of Hitachi, Ltd.) with the aim of strengthening competitiveness of the nuclear power plant dismantlement business.Hitachi Plant Construction, Ltd. is a plant construction company of the Hitachi group. In the field of nuclear power, it is engaged in the construction and preventive maintenance services of nuclear power plants with a focus on boiling water reactors and other major facilities, and it has high expertise in nuclear power generation and radiation. It also handles dismantlement of plants, etc., and its strength is the construction technology using large band saw equipment, etc. BESTERRA is expecting to combine its unique dismantlement technology with the proven performance and experience on dismantlement of nuclear power plants of Hitachi Plant Construction, Ltd., and bring in dismantlement projects of nuclear power plants that are expected to increase in the future. Through this business alliance, BESTERRA can capture the sales capabilities and customer base of Hitachi Plant Construction, Ltd. along with expertise on nuclear power generation and radiation and skills and knowledge of on-site management. There are 60 nuclear reactors in 19 locations in Japan, 22 of which have already been decided to decommission. As the review of conformity to the new regulation standard progresses, the number of nuclear reactors to be decommissioned is expected to increase, and expansion of the dismantlement business is expected. However, dismantlement work of nuclear power plants is very complicated, as an efficient dismantlement method is required while preventing radiation exposure. To decommission a nuclear power plant, it is necessary to first disassemble the peripheral equipment of the plant. Dismantlement of peripheral equipment is expected to begin gradually, and the business alliance effect with Hitachi Plant Construction, Ltd. will be visible soon. 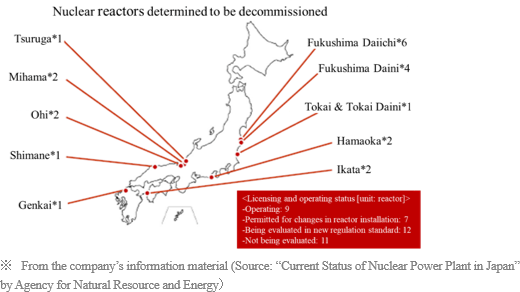 |
| Fiscal Year January 2019 Earnings Estimates |
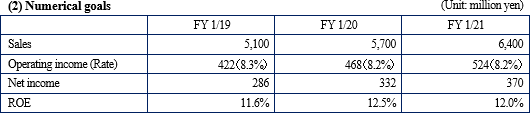
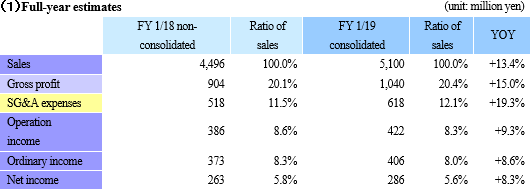 There is no change in the full-year forecasts. Sales are expected to grow 13.4% year on year, and operating income is expected to increase 9.3% year on year.
There is no change in the full-year forecasts, as the company stated that "the business is progressing as planned." In the second half, sales from the delayed dismantlement project will be posted, and orders that decreased in the first half in reaction to a long-term large-scale project of the same period last year will recover mainly in the steelmaking and electric power industries. As a result, full-year sales are expected to be 5.1 billion yen, up 13.4% year on year. The impact of a large-scale challenging project will be gone, and the cost of sales ratio is also expected to improve by 0.3 points. Gross profit will increase 15.0% year on year. This will absorb upfront investments including investment in human resources (increase in the number of employees) and R&D investments in the 3D measurement business. Operating income is expected to increase 9.3% year on year to 422 million yen. The company plans to pay a term-end dividend of 10 yen/share, and the annual dividend will be 15 yen/share combined with the dividend at the end of the first half (projected dividend rate: 43.8%). (2) Business alliance with DAI-ICHI CUTTER KOGYO (First Section of the TSE:1716)
On September 7, 2018, the company signed a business alliance agreement with DAI-ICHI CUTTER KOGYO. As a specialized construction company, DAI-ICHI CUTTER KOGYO operates a cutting and drilling work business with a unique diamond method and a water jet method, and it meets demolition, maintenance and repair needs of social infrastructure such as bridges, roads and buildings.While BESTERRA has strengths in the metal field, DAI-ICHI CUTTER KOGYO has strengths in the field of ceramics and cement, and two companies have been in a cooperative relationship. With this tie-up, by mutually utilizing business resources such as human resources and engineering, the company is expecting to obtain more projects to dismantle large-scale plant facilities as well as expand orders for very complicated dismantlement projects such as the one with Hitachi Plant Construction, Ltd. |
| Conclusions |
|
Plant dismantlement works and other construction works often have additional works requested by customers. After completion of the initial work, clearing tasks are needed, and the entire project will not be completed and sales cannot be posted unless these tasks are taken care of. Under these circumstances, in the first half, the company posted personnel expenses, research and development expenses, advertisement expenses, and head office relocation expenses as originally planned. Even though the scale of projects is becoming larger due to improved creditworthiness, etc., the entire business performance is still greatly affected by the fluctuation of one project at its current business size. Although it will be resolved with the expansion of business, in the meantime, it is better to focus on qualitative progress rather than quantitative progress in the light of these facts. Having "dismantlement supervisors" is one of the challenges, and the company is struggling to secure experienced staff, but recruitment of new graduates and recent graduates requiring a training period of 2 to 3 years is making progress. In the previous term, it acquired seven additional dismantlement supervisors, and during this term, it is planning to have additional eight supervisors. It seems that the bottleneck will be resolved gradually after the fiscal year ending January 2020, and the cost ratio due to personal cost factors is expected to improve. Furthermore, in addition to making Hiro Engineering Co., Ltd. which is engaged in engineering human resource services, a subsidiary, the company made it possible to mutually utilize construction technology and human resources through the business alliance with DAI-ICHI CUTTER KOGYO in September. In July, it also established a business collaboration agreement with Hitachi Plant Construction, Ltd. and made a steady step towards a dismantlement business of nuclear reactors, which has significance as a social contribution. |
| <Reference: Regarding Corporate Governance> |
 ◎ Corporate Governance Report
Update date: Apr. 26, 2018
Basic Policy
In order to promote sound business administration and win social trust sufficiently, our company recognizes corporate governance as the most important issue, puts importance on the improvement of the soundness, transparency, and fairness of business administration, and complies with laws and regulations thoroughly, and all executives operate business while keeping in mind that "the violation of laws or regulations would lead to management responsibility." In detail, our company disseminates and executes business pursuant to laws, regulations, and in-company rules thoroughly, by developing appropriate systems for making decisions about business administration, fulfilling duties, supervising work, conducting internal control, etc. It is also important to reform management systems for "achieving appropriate share price" and "increasing share price sustainably" to emphasize shareholders and strengthen the function to check business administration, to establish global-level corporate governance. The results of such efforts would win the trust of society, increase corporate value, and satisfy shareholders. <Disclosure Based on the Principles of the Corporate Governance Code (Excerpts)>
Our company may obtain and hold shares of our partner companies and other companies when we determined that relevant shareholdings will contribute to medium- and long-term increase in our corporate value from the perspectives of maintenance and enhancement of long-term and stable transaction relations with partner companies and expansion of our business by strengthening such relations. In meetings of the Board of Directors, our company regularly examines if shares held in a manner described in the foregoing (i.e., strategically held shares) will improve our corporate value and checks the aim and rationality of relevant shareholdings based on the examination. Our company will properly exercise the voting rights by making comprehensive judgment from the perspective of improvement of our corporate value. Each year, our company conducts the survey of transactions with the executives, the employee shareholding association, and major shareholders in order to confirm whether or not any transactions among parties concerned were carried out. In addition, our company has developed an instruction manual on production of financial reports, and in the event that our company makes transactions with the executives, the employee shareholding association, major shareholders, or any other parties, thorough discussion about the necessity of relevant transactions will be held by the internal audit department, management department, the Board of Directors, and the board of auditors in order to avoid any loss imposed by such transactions on interest of our company or common interests of shareholders. (i) The company's management philosophy, management strategies and business plan We disclose our management philosophy, management strategies and business plan on our website. (ii) Basic views and principles concerning corporate governance The basic concept and basic policy regarding our corporate governance are as described in "1. Basic principles on corporate governance and capital structure, corporate attributes and other basic information" in this report. (iii) Board policies and procedures in determining the remuneration of the directors and auditors The remuneration of the directors shall be determined at the Board of Directors, taking into consideration the company's performance, business environment, duties, standards, consistency with treatment of employees, etc. within the range of the remuneration amount resolved at the shareholders meeting. The remuneration of the corporate auditors is determined by consultation at the Board of Corporate Auditors. (iv) Policies and procedures in the nomination of candidates for directors and corporate auditors In appointing management executives and nominating candidates for directors and corporate auditors, candidates are the ones who have appropriate extensive experience, high insight and high level of expertise suitable for executives or directors/corporate auditors of the company, and we make decisions at the Board of Directors. (v) Individual reasons for nomination and appointment of management executives Regarding the appointment of directors and corporate auditors, the reasons for nomination are described in the Notice of Convocation of Ordinary General Meeting of Shareholders. Regarding requests from shareholders for dialogue (interviews), our company believes that we should express a positive attitude within a reasonable scope in order to contribute to sustainable growth and medium- and long-term improvement of the corporate value of our company. Aiming to promote constructive dialogue with shareholders, with the planning department designated as a department in charge of IR activities, our company holds financial results briefings targeted at financial institutions and investors semiannually and discloses corporate information as needed on our website and through the system of optional disclosure offered by Tokyo Stock Exchange. Disclaimer
This report is intended solely for information purposes, and is not intended as a solicitation for investment. The information and opinions contained within this report are made by our company based on data made publicly available, and the information within this report comes from sources that we judge to be reliable. However we cannot wholly guarantee the accuracy or completeness of the data. This report is not a guarantee of the accuracy, completeness or validity of said information and opinions, nor do we bear any responsibility for the same. All rights pertaining to this report belong to Investment Bridge Co., Ltd., which may change the contents thereof at any time without prior notice. All investment decisions are the responsibility of the individual and should be made only after proper consideration.Copyright(C) 2018 Investment Bridge Co.,Ltd. All Rights Reserved. |



