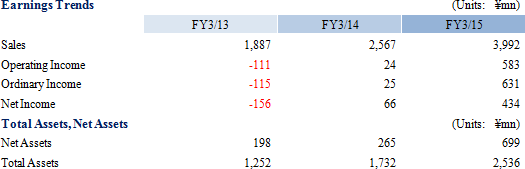
| Ferrotec Corporation (6890) |
|
||||||||
Company |
Ferrotec Corporation |
||
Code No. |
6890 |
||
Exchange |
JASDAQ |
||
Industry |
Electric Equipment (Manufacturing) |
||
President |
Akira Yamamura |
||
HQ Address |
Nihonbashi Plaza Building, Nihonbashi 2-3-4, Chuo-ku, Tokyo |
||
Year-end |
March |
||
URL |
|||
* Share price as of closing on December 7, 2015. Number of shares issued at the end of the most recent quarter excluding treasury shares.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
* Estimates are those of the Company. From the current fiscal year, the definition for net income has been changed to net income attributable to parent company shareholders (Abbreviated as parent net income).
|
| Key Points |
 |
| Company Overview |
|
Ferrotec was born as a company with highly unique technologies including thermoelectric modules with uses in thermal elements and vacuum technologies that respond to magnetic fluids that were born from the NASA space program in the 1980s. Over the course of its 30-year history of operations, the Company has developed a wide range of diverse technologies with applications in the automobile, electronics, next generation energy and other industries. And as a transnational company, Ferrotec deploys its businesses in Japan, Europe, the Americas, China, and Asia, and boasts of marketing, development, manufacturing, sales, and management capabilities in various countries and regions. <Corporate Philosophy and Code of Conduct>
Corporate Philosophy
Bringing Satisfaction to Customers
Caring About the Environment Providing Dreams and Vitality to the World Code of Conduct
Based on a global point of view, we always plan to harmonize with the global society, and act sincerely with a firm corporate philosophy and social common sense, not to mention observing the laws and ordinances of each country, as a company which supplies products and services which contributes to the life of people related to communities and others around the world.Ferrotec Group's aim is to offer high quality products and service, mainly to the "New Energy Industry" and "Electronic industry," and be trusted by customers and satisfy them, by providing price competitive products and service. Ferrotec Group considers to positively promote activities, which take into consideration of world environment, as one of our most important management task, and adapt to the latest environment control request in order. In Addition, we aim to develop material, products, and etc., which can be utilized in the "New Energy Industry" so that we can contribute to solve the world environment problem. Ferrotec Group will contribute to the society through manufacturing, utilizing our original technology, and continuously be a company which has expectations to grow, for people, such as, our customers, stockholders, employees, clients, communities, and stakeholders. As for company activities, we aim to act with social common sense, such as, observing the laws and ordinances, social order, and international rules. <Business Segments>
Ferrotec's operations can be divided between the equipment related business segment, where vacuum seals, quartz, and other ceramic products used in semiconductor, FPD, and LED related manufacturing equipment are manufactured, the electronic device business segment, where chiefly thermoelectric module application products are made, and the photovoltaic business segment, where silicon crystal, PV wafers, and crucibles used in crystal manufacturing devices are produced. In fiscal year March 2015, sales of the equipment related, electronic device, and photovoltaic related business segments accounted for 45.0%, 16.4% and 30.4% of total sales, respectively, while saw blades, equipment part cleaning, machine tool, and other products not included in reported segments accounted for 8.3%.
 Equipment related Business
Ferrotec provides total engineering services in the equipment related business segment, including the manufacture and sale of equipment parts for solar power, semiconductor, FPD and LED applications, consumable products used in manufacturing, spare parts and equipment cleaning services (50% share in China). The main product of vacuum seals boasts of top market shares in the world, and is a functional part that insulates the interior of manufacturing equipment from gas and dust contamination while supporting rotating action of the above mentioned equipment. These vacuum seals use magnetic fluids (Fluids that respond to magnetic fields), which has been a core technology of Ferrotec since its founding. Because of instability in these applications arising from their link with corporate capital investments cycles, the Company focuses its marketing efforts upon expanding sales to applications for which demand is more stable, including transportation equipment, precision robots, and general industry usages. In addition, Ferrotec has also focused its efforts upon assuming consigned manufacture of vacuum chambers that use vacuum seals and gate valves (Both use vacuum related equipment).Quartz crucibles and ceramic products are critical elements in the process of semiconductor manufacturing. Quartz products are able to resist high temperature conditions that exist in the semiconductor manufacturing process, and are a high purity silica glass product that protects semiconductors from undergoing chemical reaction by preventing it from activating with gas. Ferrotec boasts of a high share of products purchased by LED manufacturers, in addition to high share of quartz crucibles (Photovoltaic related business) used in the photovoltaic cell manufacturing process. This technology is also being used to cultivate high purity crucibles for use in semiconductor applications. The Company boasts of semiconductor manufacturing equipment manufacturers as their main clients in Japan and overseas that purchase ceramic products, which are Ferrotec's core material and technology. At the same time, semiconductor inspection jigs for machinable ceramics and fine ceramics used in semiconductor manufacturing equipment are two main products in this realm. In addition, Ferrotec has achieved output of 300,000 units per month of 6-inch wafer processing (Ingot slicing) for discrete semiconductor applications, and its contributions in the realm of small-diameter wafer processing are becoming significant. Electronic Device Business
Thermal element "thermoelectric modules" are products that can instantly raise or lower temperatures to a highly precise degree and are a core product of this business. Thermoelectric modules are used primarily in heated automobile seats, and also in a wide range of other applications including genetic analysis equipment, optical communications, and consumer electronics. Ferrotec is also devoting efforts to cultivating new markets and expanding the range of applications for this product by improving product quality, introducing automated manufacturing lines to reduce costs, and developing new products that are high in functionality. Sales of magnetic fluids, including applications currently being developed for use in fishing reels (Waterproofing internal seals) and speakers for 4K televisions, are also conducted in this segment.
Photovoltaic Related Business
Ferrotec entered the photovoltaic related business in 2005, and has manufactured and sold silicon crystal manufacturing equipment, consumable products including quartz crucibles, and silicon products used in photovoltaic applications. Based upon the current needs of the market, the Company is conducting manufacture and sales of silicon use multiple crystal square tanks (Manufactured using quartz processing technologies), single crystal crucibles manufactured when making ingots, and consigned manufacturing of silicon crystal ingots and wafers used in photovoltaic substrates. With regards to consumable products like crucibles, Ferrotec boasts of a high market share due to its wide ranging lineup of products and ability to manufacture customized products.
|
| First Half of Fiscal Year March 2016 Earnings Results |
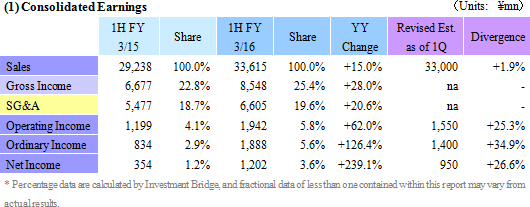 Sales, Operating Income Grow by 15.0%, 62.0% Year-On-Year
Sales rose by 15.0% year-on-year to ¥33.615 billion. While sales of the photovoltaic related business declined by 13.9% year-on-year due to weak demand for silicon crystal manufacturing equipment and consumables, sales of the electronic device business rose by 55.3% year-on-year on the back of increases in demand for thermoelectric modules from automobile seat automated heating and consumer and industrial equipment applications. In addition, equipment related business sales rose by 19.6% year-on-year on the back of growth in sales of vacuum seals and materials products used in semiconductor manufacturing processes.With regards to profits, gross income rose by 28.0% year-on-year due to the positive influence of the weaker yen and to improvements in profitability of the equipment related and electronic device businesses arising from increases in capacity utilization rates. While sales, general and administrative expenses rose by a large margin due to higher expenses of overseas subsidiaries in yen terms due to the weaker yen and the booking of doubtful account reserves (¥322 million), operating income was still able to rise by a large margin of 62.0% year-on-year to ¥1.942 billion. While an extraordinary loss of ¥54 million associated with the disposal of assets due to the renovation of the main plant was booked, improvement in foreign exchange translation gains (Improved from a loss of ¥106 million in the previous first half to a profit of ¥243 million in the current term) and a decline in the effective tax rate allowed net income to rise by 3.3 times year-on-year to ¥1.202 billion. The average exchange rate during the term for the dollar and Chinese yuan were ¥120.48 and ¥19.36, respectively (Compared with ¥102.23 and ¥16.56, respectively in the previous term). 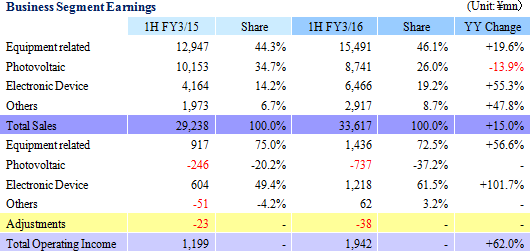 At the same time, demand for silicon crystal manufacturing equipment, quartz crucibles, square tanks and other consumable products trended weakly in the photovoltaic related business. Furthermore, withdrawal from the multiple crystal wafer processing business also contributed to weaker sales of nearly all products. With regards to profitability, the shift of production to the Yinchuan Plant, withdrawal from unprofitable businesses and implementation of impairment accounting for facilities undertaken during the previous term allowed this business to realize a profit at the gross income level during the first half. However, the booking of doubtful account reserves and valuation losses on materials and product inventories compounded the declining trend in sales and contributed to an expansion in the loss at the operating level to ¥372 million. Positive effects of measures implemented during the previous term are expected to materially surface during the second half of the current term. 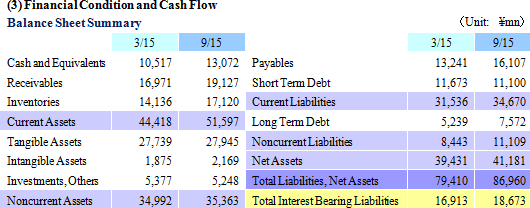 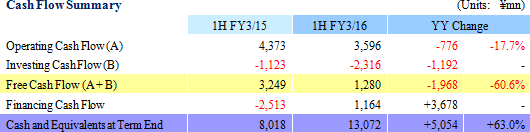 (4) Conversion of Admap Inc. into a Subsidiary
On July 1, 2015, Ferrotec acquired 66% of the shares of Admap Inc. (Headquartered in Tamano City, Okayama Prefecture, President Yasuaki Matsuda) from Mitsui Engineering & Shipbuilding Co., Ltd. (Headquartered in Chuo-ku, Tokyo; President: Takao Tanaka) (Maintains ownership of the remaining 34% of share) and turned the company into its consolidated subsidiary. Admap boasts of its own unique CVD-SiC technologies and provides high quality CVD-SiC structural parts. SiC (Silicon Carbide) is a compound that combines one part each of silicon and carbon. And while it is found commonly in meteorites, it is almost non-existent naturally on earth. CVD-SiC is SiC manufactured through the chemical vapor deposition process (CVD).
 The two main methods of manufacturing SiC include the "sintering method" that forms compound by sintering powdered materials, and the "chemical vapor deposition" method that forms compound from silicon and carbon gas. Admap is able to form highly fine and pure SiC using only the CVD process, and this ability is one of its unique strengths. Manufacture of CVD-SiC products allows for thin and light weight products that are free from impurities to be made with few particulate matters being born. These CVD-SiC products can also be used in high speed applications and reused multiple times after cleaning. Admap is expected to strengthen its research and development activities in the realms of aeronautics and aerospace (Turbines, mirrors), automobile (Power semiconductors), energy (Nuclear power related), information technology (Semiconductor manufacturing equipment part use) and other realms. 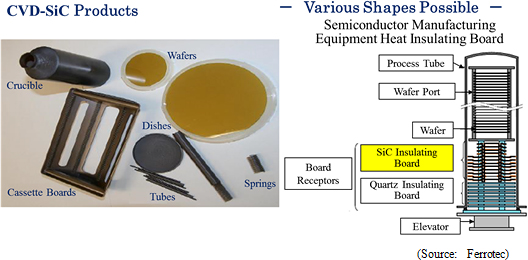 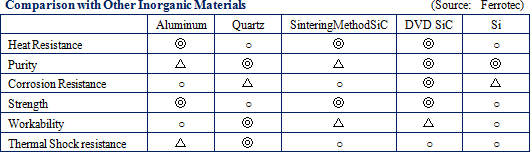 |
| Fiscal Year March 2016 Earnings Estimates |
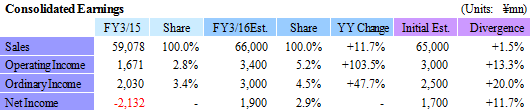 Sales, Operating Income Expected to Rise by 11.7%, 103.5%
In light of the first half earnings performance, Ferrotec revised its full year earnings estimates upwards. However, the upward revision to the second half earnings estimates for sales, and operating and ordinary incomes was maintained to a small margin given the uncertainties surrounding capital investments for the semiconductor industry. At the same time, sales of the photovoltaic related business are expected to turn to positive growth, allowing all business segments to see higher sales.The full year estimates call for a doubling of operating income, and a 47.7% year-on-year increase in ordinary income without any foreign exchange gains included in these assumptions. The full-year foreign exchange rate assumptions are ¥120.00 per United States Dollar (¥106.46 in the previous term), and ¥19.50 per Chinese Yuan (¥17.26 in the previous term). Capital investments and depreciation in the full year are expected to amount to ¥3.3 and ¥4.2 billion, respectively (¥3.375 and ¥3.964 billion, respectively during FY3/15). A dividend of ¥8 per share is expected to be paid at the end of the fiscal year. 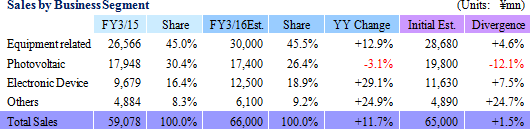 |
| Trends and Outlook by Business Segment |
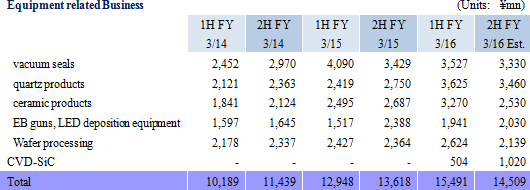 Quartz products supplied on an OEM basis to major United States and Japanese clients grew during the first half (OEM supplies during the first half accounted for 64% of total quartz product sales). And while output capacity was expanded, customers' demands for short delivery times caused the production facilities to operate at full capacity. During the second half, OEM orders for products from major United States clients are expected to remain brisk, but the peaking out of foundry operating rates and orders from Japanese clients are expected to trend weakly. Ferrotec expects to strengthen its marketing of next generation silicon parts. Demand for machinable ceramics "photoveel" semiconductor inspection jigs for memory (NAND Flash) applications rose, along with increases in orders from Korean and Taiwanese clients for new smartphone and logic applications within the ceramic product division during the first half. At the same time, fine ceramics used in semiconductor manufacturing equipment parts saw particularly strong demand from certain clients for new equipment in line with their capital investment and miniaturization applications. And while demand for "photoveels" for semiconductor applications is expected to slow during the second half, foundry related demand from logic and new model smartphone applications is expected to increase. Due to postponement of capital investments to expand output capacity and for miniaturization by major semiconductor manufacturers, orders for fine ceramics has slowed since fall. The share of exports of CVD-SiC products is high, with exports to China, North America, Taiwan and Europe accounting for 38%, 36%, 3% and 1%, respectively, with 22% sold within Japan. Sales to major United States clients trended favorably, but sales to major Japanese clients slowed from the second quarter onwards. Sales to Asia declined. During the second half, demand from major United States clients is expected to continue to trend favorably, with a recovery in demand from within Japan and Asia starting during the fourth quarter (October to December, due to the December fiscal year end of subsidiaries). Efforts will be implemented to expand sales channels and pursue synergies with the parent company Ferrotec in order to cultivate demand from applications aside from the semiconductor realm. In addition, orders for in-house branded wafer processing from Taiwan and China grew, and OEM production for new customers cultivated in Europe has been started. However, declines in both near term orders and pricing have contributed to a cautious outlook during the second half. EB gun and LED deposition equipment benefitted from strong demand for EB guns from smartphone communications chip related applications. Furthermore, this strong demand is expected to continue during the second half. Demand for LED deposition equipment from automobile applications is also expected to continue to trend strongly. 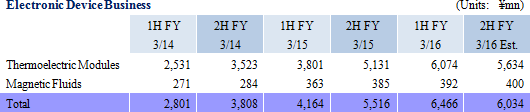 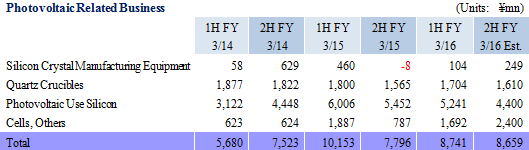 |
| Important Issues: Vice President and Executive Officer of Business Management He Xian Han |
|
Photovoltaic Related Business
While the loss in the photovoltaic related business expanded during the first half, the potential for a recovery is slowly starting to emerge. The transfer of production to the Yinchuan Plant, which is highly cost competitive, was completed in May 2015, and a recovery in the photovoltaic cell related investments has begun to appear, timely coinciding with the Chinese Government's announcement of its plans to increase the output capacity of photovoltaic cell panels from 15 to 18 gigawatts. Therefore, Ferrotec will leverage the cost competitive strength of its Yinchuan Plant to cultivate demand. At the same time, a full scale recovery in demand for quartz crucibles, photovoltaic cell use silicon, cells and other products is anticipated from the coming fiscal year. (In the realm of photovoltaic cell use silicon, currently about 2.00 million processed single crystal silicon wafer products are supplied, but the start of supplies to major United States clients during 2016 is expected to boost the total number to 10.00 million.) With the various subsidiaries having already entered their fourth quarter because their fiscal years end in December, near-term profitability of the photovoltaic related business is showing a notable recovery.In addition, Ferrotec is implementing efforts to cultivate uses of quartz crucibles in semiconductor applications. Currently, evaluations of small to medium diameter crucibles is being conducted, and provision of larger diameters such as 28 and 32 inch crucibles is also being considered. Consequently, a new melting furnace is expected to begin operations within the current term. The Company will leverage its silicon crystal manufacturing equipment technologies in extending furnaces for 8 inch ingots and silicon parts. Electronic Devices Business
General-use thermoelectric modules used in communications, automobile, consumer electronics and other various applications has grown to become a ¥10.0 billion division within the electronic devices business. Consequently, electricity-generating thermoelectric modules will also be cultivated to make it the second cornerstone of this business. Electricity-generating thermoelectric modules can be divided into three operating ranges of low, medium and high temperatures, and Ferrotec will focus upon low operating range products. A strategic partnership has been formed with the Chinese Academy of Sciences for the promotion of joint research and development with a target of achieving sales of between ¥3.0 to ¥4.0 billion over the next three years (Market for low-temperature electricity-generating thermoelectric modules is estimated to amount to ¥10.0 billion). Ferrotec will also promote measures to create high value-added electricity-generating thermoelectric modules units. Specifically, units combining fan, heat sink, and electricity generating thermoelectric modules will be developed as part of Ferrotec's efforts to cultivate this ¥10.0 billion market.In addition, sales of high power device substrates will also be expanded. High power device substrates are used in IGPT (insulated gate bipolar transistor) chips to control electricity. During the past three years, Ferrotec products have passed audits of six Japanese manufacturers and shipments have begun to increase. Audits of products have nearly been completed by six manufacturers in Korea as well, and sample shipments have been started to one of the five major manufacturers in Europe (Audits are expected to be conducted in January, with shipments expected to begin in May 2016.) In China, where they already have 50% market share, Ferrotec expects to form a cooperative agreement with a Chinese chip manufacturer, to which it already provides substrates, for the sale of these products. High power device substrates are expected to achieve ¥5.0 billion in sales (Eventually to achieve ¥10.0 billion). Combined sales of the above mentioned products is expected to amount to between ¥28.0 to ¥29.0 billion (Electronic device business sales of ¥12.5 billion expected in FY3/16) with high profit margins. Equipment Device Business
Growth in earnings of Admap is expected to be a driver of overall growth for the equipment related business. The potential sales of CVD-SiC manufactured by Admap is estimated to amount to ¥10.0 billion (Total sales of the equipment related business is estimated to amount to ¥30.0 billion in FY3/16). Admap will expand the applications of its products from semiconductors to nuclear power generation, aeronautics and aerospace. Furthermore, Admap participates in a CVD-SiC national project led by the Japanese Government. Moreover, silicon parts hold strong business potential. Demand not only for CVD-SiC but other silicon parts as well is expected to expand on the back of the growing trend for miniaturization of semiconductors. Ferrotec's photovoltaic related business is in a strong position to capitalize on this trend due to its ability to supply small and large diameter products made in-house to pulling furnaces used in silicon manufacturing. Negotiations for ceramic products and other materials are currently being promoted with semiconductor manufacturing equipment manufacturers in the United States.Ferrotec is also cultivating new uses for its ceramic products outside of the realm of semiconductors. The potential for business growth in the United States is large with potential clients boasting of sales of over ¥20.0 billion. At the same time, the Company is currently conducting efforts to commercialize 8-inch discrete use wafers in addition to its 5- and 6-inch wafers. Measures are currently being implemented in the semiconductor realm within China to realize the "Made in China Plan 2025", which entails a goal of acquiring 50% market share of the semiconductor and semiconductor materials market in China by 2020. And while demand for 5- and 6-inch wafers is stable, demand for 8- and 12-inch wafers are expected to grow largely on the back of the implementation of this "Made in China Plan 2025." Demand for applications in communications realm for low-cost 8-inch wafers is expected to grow strongly (Currently, 100% of 8-inch wafers are imported into China). By cultivating 8-inch wafers for communication applications, Ferrotec seeks to expand its discrete wafer division to ¥15.0 billion (Sales of discrete wafers in FY3/16 is expected to amount to slightly over ¥4.7 billion). Demand for equipment cleaning is expected to grow arising from the "Made in China Plan 2025" and the subsequent outlook for increases in the number of semiconductor plants. Currently, the cleaning business has been started at three plants operating in Shanghai, Tianjin and Szechuan (Operations just started in December), and three more plants are expected to be newly established to bring the total number of cleaning plants to six and to cover most parts of China. Ferrotec boasts of a 60% share of the semiconductor equipment cleaning market, and it is the only company with the technology necessary to clean miniaturization manufacturing equipment. Furthermore, the most up-to-date trends in the semiconductor manufacturing industry can also be observed through this cleaning business. The above mentioned measures are being implemented to achieve Ferrotec's goal of ¥100.0 billion in sales and 10% operating margin. But as a near-term goal, the Company will endeavor to achieve 8% operating margin. And in his closing comments, Vice President He Xian Han highlighted that "the support of investors is necessary to achieve these goals." |
| Conclusions |
|
A large increase in profits is anticipated during the current term. And while uncertainties continue to cloud the business environment for semiconductor related applications, the risk of a shortfall in earnings appears to be low given Ferrotec's conservative outlook and assumptions for the second half. Furthermore, the potential for earnings to grow a step further in the coming term is supported by the outlook for a recovery in the photovoltaic related business. Therefore, the success of the above mentioned measures should be closely watched. Disclaimer
This report is intended solely for information purposes, and is not intended as a solicitation to invest in the shares of this company. The information and opinions contained within this report are based on data made publicly available by the Company, and comes from sources that we judge to be reliable. However we cannot guarantee the accuracy or completeness of the data. This report is not a guarantee of the accuracy, completeness or validity of said information and or opinions, nor do we bear any responsibility for the same. All rights pertaining to this report belong to Investment Bridge Co., Ltd., which may change the contents thereof at any time without prior notice. All investment decisions are the responsibility of the individual and should be made only after proper consideration.
|



