| Nakamura Choukou Co., Ltd. (6166) |
|
||||||||
Company |
Nakamura Choukou Co., Ltd. |
||
Code No. |
6166 |
||
Exchange |
TSE Mothers |
||
Industry |
Machinery (manufacturing) |
||
President |
Makoto Inoue |
||
Address |
27-27 Tsuruta-cho, Nishi-ku, Sakai-shi, Osaka prefecture |
||
Year-end |
End of March |
||
URL |
|||
* The share price is the closing price on December 5. Number of shares issued on the latest earning summary.
ROE and BPS are the values at the end of March 2017. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
* The values for the term ending Mar. 2018 were estimated by the Company.
Net income is profit attributable to the stock owners of the parent Company. Hereinafter the same applies. This report introduces Nakamura Choukou Co., Ltd.'s first half of fiscal year March 2018 earnings results and others. |
| Key Points |
 |
| Company Overview |
|
Wafers (*)
A wafer is a flat functional part that is produced by thinly slicing ingots of electronic materials. It is made of various materials by purpose such as silicon, sapphire, SiC (silicon carbide) and GaN (gallium nitride). Silicon wafers are often used for IC chips and solar cells. Slicing business (*2) Business transferred to Nakacho Device Technology Corporation (an equity method affiliated company) in September 2013. Diamond nozzles (*)
A nozzle with sintered diamond at the tip, which is used for mounting electronic components on a print circuit board. By using diamond, the lifespan of the nozzle, holding capacity of the electronic component, image recognition efficiency and mounting efficiency are improved.  In the first half of the 2000s, solar power generation was adopted as a national policy and popularized mainly through subsidies, and for a period of time, the expansion rate of the solar panel market was sluggish. In contrast, the adoption rate nowadays is accelerated again not only as a national policy but also due to the soaring installation rate from the perspective of economic rationality, such as a decline of power generation costs. 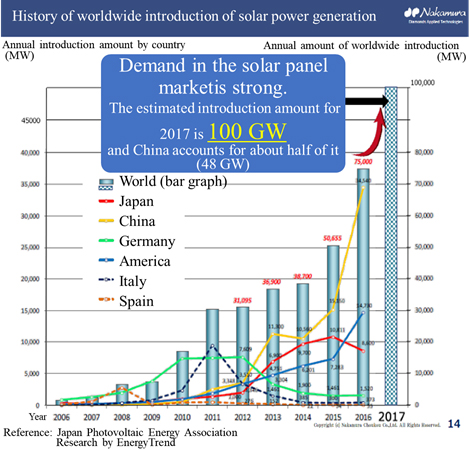 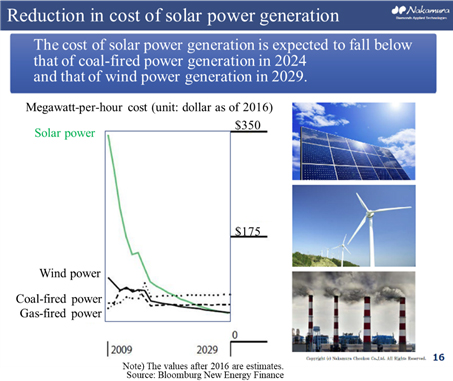 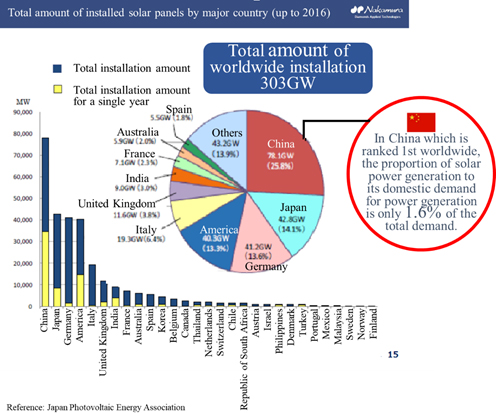 Japanese companies, including Asahi Diamond Industries Co., Ltd. (6140, first section of Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE)) and the Company, globally had the largest market share of diamond wires; however, Chinese manufacturers have been rising lately and, seemingly, their total market share has exceeded that of Japanese companies.  1. Segment
Nakamura Choukou's businesses consist of the three segments: Peripheral Business of Electronic Material Slicing, High-precision Equipment, and Chemical Fiber Spinning Nozzle Businesses.
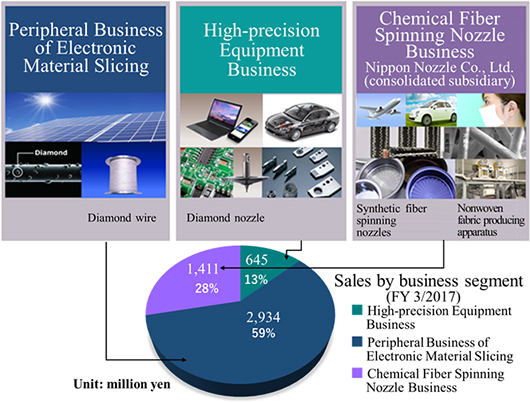 (1) Peripheral Business of Electronic Material Slicing
The development, manufacturing, and distribution of diamond wire which is used in the slicing silicon ingot during the manufacturing process of solar cells.
① What is Diamond wire?
Nakamura Choukou's diamond wire is used in the slicing process in manufacturing silicon wafers, which are used for the main part of a solar battery panel, that is, a solar cell.◎ Manufacturing Process of Silicon Wafer A "diamond wire" is a tool used to thinly slice rectangular silicon ingots that are pre-cut to the dimensions of each wafer. It is a threadlike slicing tool made of a thin piano wire with diamond granules firmly attached and is thinner than a human hair. The ingots are sliced by the diamond wires juxtaposed at short intervals and rotating at high speed over the guide rollers on a slicer. 2000 to 3000 silicon wafers are produced in 3 to 4 hours. The wafers are then cleaned and quality-inspected, treated to turn into cells, and incorporated into solar panel modules. 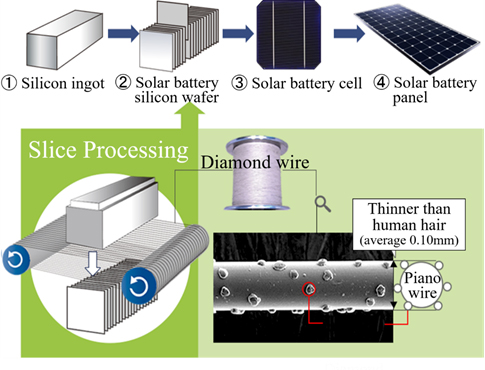 ②Diamond Wire Overview
There are two methods of slicing silicon wafers; "loose grain method" and "fixed grain method (using diamond wires)."
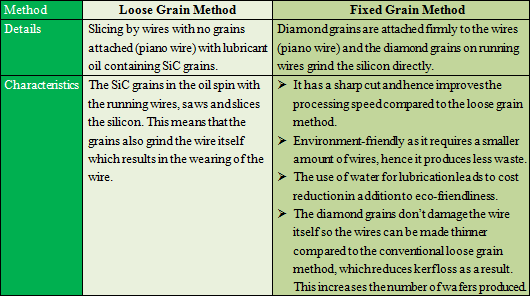 *kerf loss
Amount of the waste silicon when slicing. Kerf loss means material waste, so it must be kept minimum in order to reduce the manufacturing cost of solar battery panels. 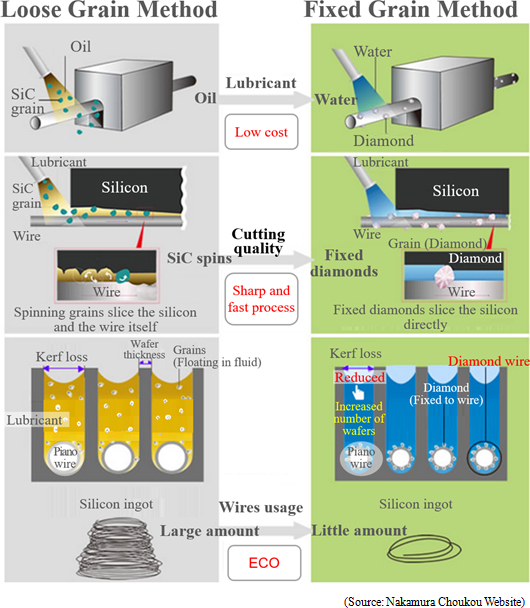 Nakamura Choukou had thinned the diamond wire to Φ (*) 80 μm from the conventional standard of Φ100 μm and continues to create Φ70 μm and Φ60 μm diamond wires. (*) Φ
A symbol to indicate the diameter. Phi. (2) High-precision Equipment Business
Conduct the development, manufacturing and sale of high-precision equipment made of hard and brittle materials with high abrasion resistance such as diamond, cemented carbide and ceramic. The main products are diamond parts used in the engineering machines for manufacturing automobile parts and bearings and diamond nozzles, which are used in industrial machines for mounting electronic parts onto LCD television sets, smartphones, tablets, etc. In addition to high-precision parts and equipment, the Company develops, manufactures and sells the cleaning machines for nozzles of the machines, etc. (3) Chemical Fiber Spinning Nozzle Business
The designing, manufacturing and sale of chemical fiber spinning nozzles, the peripheral parts and nozzles and devices for nonwoven fabric.Nakamura Choukou started the domestic manufacturing of nozzles for chemical fibers (for production of rayon) and has been operating the business as a chemical fiber spinning nozzle manufacturer since its establishment in 1930. The spinning nozzle is a core manufacturing part which determines the quality of nonwoven and carbon fibers. The manufacturing of the nozzles requires delicate technologies in micro punching process and in the production of the devices, where Nakamura Choukou has provided for the market's needs with the technologies accumulated for many years in the same specialized industry. *The unique business model with the slicing business
As mentioned above, the affiliated Company "Suminoe Nakacho Device Technology Corporation" slices silicon ingots using Nakamura Choukou's diamond wires, manufactures and sales silicon wafers for solar cells. Suminoe Nakacho Device Technology provides Nakamura Choukou with the results of mass production tests as feedback. Nakamura Choukou then works on the improvement of the diamond wire based on the feedback. By combining the "technologies of diamond wire manufacturing" and "technologies of diamond wire usage" to create a synergy effect, the Company has made it possible to support its clients (silicon wafers manufacturers) in different technological perspectives and gain trust from them, which in turn has made its market expansion advantageous. This kind of business model is unique and makes Nakamura Choukou Group stand out. 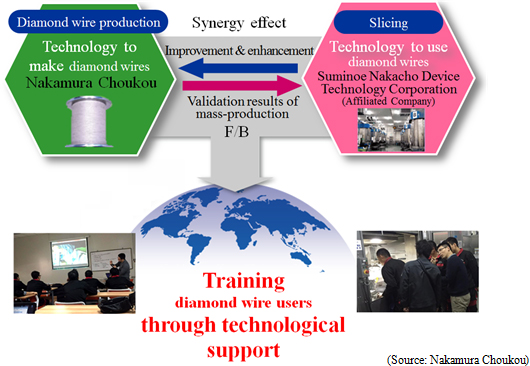 |
| First Half of Fiscal Year March 2018 Earnings Results |
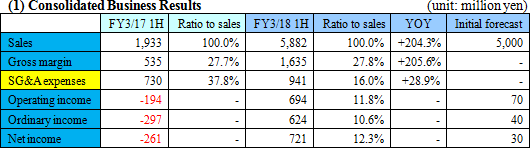 Sales increased considerably, resulting in a return to profitability
The sales were 5,882 million yen, increasing by about three times year on year. As a shift to the fixed abrasive grain method in which diamond wires are used has been driven in the market of polycrystalline silicon wafers, the amount of orders for diamond wires, the Company's major product, exceeded the estimate on a continuous basis. Although competition existed, the price remained robust thanks not only to the escalating demand but also the great trust in the products of the Company. In addition to the increase in sales, the effect of cost reduction enabled the Company to regain profitability in operating income and other incomes. The Company made upward revisions twice in August and November 2017, achieving business results that considerably exceeded the initial forecast. 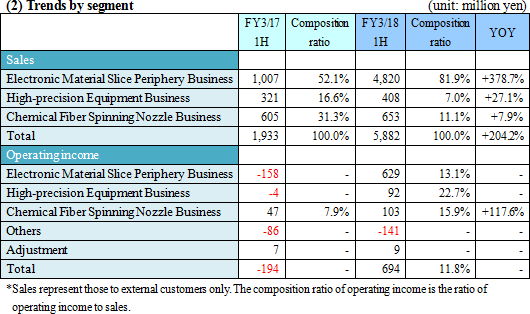 Sales increased, resulting in a return to profitability. Diamond wires, the Company's core product, gained in popularity on a rapid basis newly in the market of polycrystalline silicon wafers, in addition to the monocrystalline silicon wafer market which has been the conventional supply market. Furthermore, the amount of orders received and the sales volume exceeded those of the second quarter of the previous term thanks to the increasing production amount achieved through a number of factors, including the start of a full-scale operation of Okinawa Factory. The Company returned to profitability thanks not only to the effect of the sales growth but also to certain results in the cost reduction measures which the Company launched in the previous term. The quantity of orders for the wafer slicing process placed by Panasonic, one of the Company's major customers, declined considerably. <High-precision Equipment Business> Sales increased, resulting in a return to profitability. Sales of nozzles for mounters and wear-resistant components for machine tools showed a healthy growth as, in addition to the rise in smartphone-related investment in China, demand for semiconductors and automobile-related demand increased. The Company focused on prospecting for new customers. <Chemical Fiber Spinning Nozzle Business> Sales and profit grew. Sales of a variety of nozzles rose healthily both in and outside of Japan. Automation of part of the process boosted the profitability. 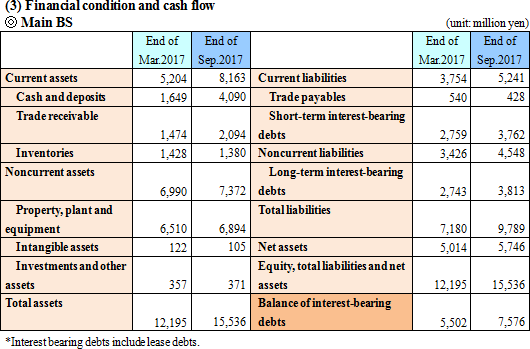 Net assets were 5,746 million yen, up 731 million yen from the end of the previous term, due to the growing retained earnings. Consequently, the equity ratio was 37.0%, down 4.1 points from the end of the previous term. 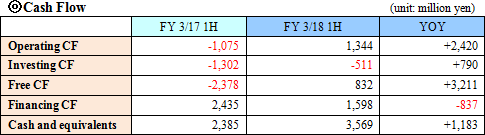 On the other hand, purchase of property, plant and equipment was less than those in the second quarter of the previous term, decreasing the deficit of investing CF. Consequently, Free CF became positive. Proceeds from issuance of common shares in the second quarter of the previous term became zero this term, and financing CF rose at a lower rate. The cash position improved. (4) Topics
◎Funds were raised from the stock market for making capital investment and accelerating the new business.The Company decided to issue 300,000 shares (with the stock dilution rate of 6.41%) in order to raise funds of about 1.4 billion yen (estimate) by granting the 5th share option whose scheduled allottee is FVC-EVO Growth Platform Fund Ltd., SPC. FVC-EVO Growth Platform Fund Ltd., SPC is an investment fund established jointly by Future Venture Capital Co., Ltd. (8462, JASDAQ) and EVOLUTION FINANCIAL GROUP. The fundraising method employed this time is called "commit issue," in which Nakamura Choukou determines in advance the scheduled number of common shares subject to the share option (300,000 shares) and the scheduled allottee will surely exercise all of the share option based on the volume weighted average price on the price calculation date during an execution period within, in principle, 27 price calculation days from the transaction day following the day when the share option was granted. This method makes it possible for Nakamura Choukou to raise funds without fail. The intended uses of the funds so raised are as follows: ① Capital investment of about 1.2 billion yen for increasing the production volume of diamond wires with the aim of expanding the market share Using 1.6 billion yen, consisting of 1.2 billion yen mentioned above and about 400 million yen which includes its own money and bank loans, the Company will modify production equipment (make the production speed higher) and introduce new equipment with the aim of boosting its productivity nearly twice as high as that at the beginning of this term by the end of June 2018. ② Investment of 200 million yen for accelerating the new business The Company will take a stake in PeptiStar Inc., which is a joint venture company established in September 2017 by PeptiDream Inc. (4587, first section of TSE), Shionogi & Co., Ltd. (4507, first section of TSE), and Sekisui Chemical Co., Ltd. (4202, first section of TSE), aiming for research and development, manufacturing, and sale of special peptide drug substances. In addition to these three companies, several companies, including Nakamura Choukou, plan to participate with the aim of building a low-cost and stable supply system of high-quality special peptide drug substances by concentrating multifarious kinds of advanced technology through an all-Japan team structure. Nakamura Choukou is striving to launch a life science business as a new business whose core technology is the "microreactor system." The conventional so-called "batch type" technology used for manufacturing chemicals produces the required chemicals by mixing, heating and cooling a variety of materials. While the technology can synthesize a large volume all at once, there are a number of issues, such as difficulty in uniformly mixing materials, dangerousness, consumption of a massive amount of energy in large-scale facilities, and production of an enormous quantity of wastes. In contrast, in the flow synthesis technology, chemicals are produced in a device called a microreactor with fine flow paths of dozens to hundreds of micrometers, in which the flow paths join together, materials are mixed, heated and cooled, and divided in a flow, and ideal chemical reaction occurs. Its great advantages include energy conservation and safety, and therefore, social demand for the technology is rapidly growing. The Company continues to carry out research and development of the technology related to the microreactor with the aim of entering the market as early as possible. It plans to contribute to establishment of a stable supply system of special peptide drug substances by PeptiStar, by making the best of the microreactor-related technology through the investment this time and playing a role in developing more efficient equipment for manufacturing special peptide drug substances. |
| Fiscal Year March 2018 Earnings Estimates |
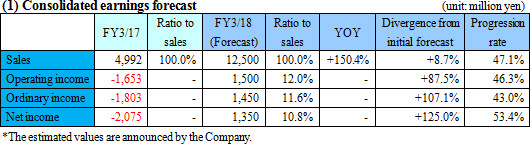 Rapid recovery is expected.
A rapid recovery in business performance was expected at the beginning of this term and the speed of recovery is becoming faster than the expected rate. Sales are expected to mark the record high of 12.5 billion yen, up 150.4% from the previous term. Following the abrupt shift to "fixed abrasive grains" in the polycrystalline silicon wafer market, demand for diamond wires will continue to grow. Furthermore, as the selling price is expected to remain stable on the back of the expanding market scale and the Company's quality superiority, it is projected that operating income and other incomes will significantly rebound and become positive. The dividend amount is to be zero. (2) Immediate situation and outlook
As mentioned above, a shift to "fixed abrasive grains" in the polycrystalline silicon wafer market is advancing on a rapid basis. It is anticipated that 90% of the Company's major customers will have shifted to production of wafers using the fixed abrasive grain method by 2018. ◎Outlook for second half In addition, the Company has earned an impeccable reputation for its wires with small fluctuations in quality that is achieved by the technology it has cultivated for a long period of time as a tool manufacturer, which has clearly demonstrated its "superiority in cost performance." Furthermore, another advantage of the Company is that Chinese competitors do not have much room for setting lower prices as the cost of materials, such as wires and diamond abrasive grains, has increased. Under these favorable circumstances, the Company is taking the following actions for enhancing its productivity and reducing costs: First of all, it will complete the equipment modification for increasing its capacity within this year, due to which the sales amount in the third quarter is estimated to decline temporarily; however, the Company expects that sales will grow toward the fourth quarter. Meanwhile, the progress with reduction in material costs is made as planned thanks to cooperation on prices by material manufacturers and a decline in the amount of waste material (the disposal volume) following the productivity improvement. The Company will pursue speeding up as well as continue improvement toward a further decrease in the material disposal rate. ◎Sales strategies
As a business strategy for sale of diamond wires, first of all, the Company will secure the market share by selectively incorporating the rapidly growing demand. It will make a new capital investment in the existing factories by the end of June 2018 based on the aforementioned funds. In addition, it will devote its limited productivity to priority customers. At the same time, the Company considers that to produce finer wires is a key to winning the competition. Clients that have installed high-performance slicing equipment and used Φ70μm wires have a good environment for using fine wires where Φ60μm wires can be used readily. Furthermore, the technological support utilizing the experience at the consolidated subsidiary, "Suminoe Nakacho Device Technology Corporation," is another great strength of the Company, allowing it to possess a significant advantage for selling Φ60μm wires. Seemingly, it will be difficult for Chinese companies to catch up with the Company for the time being if the Company successfully puts into practical use and commercializes Φ60μm wires whose shipment, though in small quantity, has been already started; therefore, the Company would like to reach the level at which people say that "it is Nakamura Choukou when it comes to Φ60μm wires." In addition, the Company will propel research into finer wires of Φ50μm. |
| Conclusions |
 |
| <Reference 1: Regarding Business Strategies> |
|
(1) Regarding the sale of diamond wires
To sell ahead for diamond wires, the Company set the following 3 major strategies:① To distribute more diamond wires in the market of polycrystalline silicon wafers ② To sell Φ60μm wires with high added value ③ To expand production output and reduce costs through technological innovation ① To distribute more diamond wires in the market of polycrystalline silicon wafers
The most prioritized strategy. It has been said that diamond wires are mainly for processing monocrystalline silicon wafers and not suited for processing polycrystalline silicon wafers, but the technology for processing the surface of a wafer has been spread, and especially in China, equipment has been upgraded for handling diamond wires, rapidly increasing the number of facilities that can adopt diamond wires. From now on, it is expected that the demand for diamond wires for polycrystalline silicon wafers will grow more than estimated. This trend is very favorable to the Company, which is highly evaluated by clients. ② To sell Φ60μm wires with high added value
In the market of monocrystalline silicon wafers, where ingots are expensive, thinner wafers provide higher cost advantage. The clients that installed high-performance slicing equipment have a good environment for the use of fine wires where Φ60μm wires can be used readily. The diamond wires of Nakamura Choukou are favorable for thinning, and the technological support utilizing the experience at the consolidated subsidiary Suminoe Nakacho Device Technology Corporation is a great strength of the Company. Accordingly, the Company possesses significant advantage for selling Φ60μm wires. ③ To expand production output and reduce costs through technological innovation
Nakamura Choukou aims to multiply production speed while maintaining high quality, and expand production output by increasing equipment utilization rate through the considerable reduction in downtime. The Company will also reduce costs by decreasing material cost through the curtailment of the amount of wastes and input and by curbing fixed cost through factory operation acceleration and manpower saving. As for clients, the Company will prioritize leading wafer manufacturers that emphasize quality, and clients that has an advantageous environment for transactions, such as a tax-exempt district and a region outside China, and are expected to do sustainable transactions. In addition, the Company will increase the ratio of transactions with polycrystalline manufacturers, and promote the sales of little-known Φ60μm wires to monocrystalline manufacturers, to choose a usage environment in which the strengths of the Company can be utilized. (2) Regarding new development business and R&D theme
In order to build a new earning pillar following diamond wires, the Company has strived to early commence two new businesses, and finally has decided to shift from R&D to the business operation stage.
① Life science business
Commercialization of Microreactor system development.The conventional technology called the "batch type," which is used for producing the required chemical goods, produces chemical goods by mixing, heating, and cooling various materials. It can synthesize a large amount of products at the same time, but there are many problems such as the difficulty in mixing materials homogeneously, danger, the consumption of an enormous amount of energy at a large-scale facility, and the discharge of a large amount of wastes. Meanwhile, the flow synthesis technology induces ideal chemical reactions in a microreactor, which has narrow flow channels with a width of tens or hundreds of micrometers that merge so that materials are mixed, heated, cooled, and separated, and produces chemical goods. This technology has the remarkable merits: energy saving and safety, and social demand for it is growing rapidly. In detail, Nakamura Choukou initiated the joint development of autonomous automatic synthesis device, which would streamline the creation of pharmaceutical products, with the Biomedical Research Division of the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST). The creation of pharmaceutical products requires a great deal of time and labor at the stage of fundamental research, including the synthesis of hundreds of thousands of chemical compounds. This degrades the competitiveness of pharmaceutical manufacturers and increases medication cost considerably. This project is aimed at solving these issues by developing "autonomous automatic searching device," which can operate automatically to analyze, design, and synthesize candidate pharmaceutical products 24 hours a day, 365 days a year. The "autonomous automatic searching device," which they are setting out to develop, would create candidate pharmaceutical products at an overwhelming rate, and contribute to the shortening of the development period of a new drug and the strengthening of international competitiveness. In Sep. 2016, Nakamura Choukou established "Flow Synthesis Laboratory" as a new foothold, strengthening its development system. At the first stage, the Company will undertake the synthesis and research of chemical products from pharmaceutical companies and public institutions, starting the business of entrusted synthesis and research. At the second stage, the Company aims to create a medication venture by accumulating the knowledge of drug discovery. 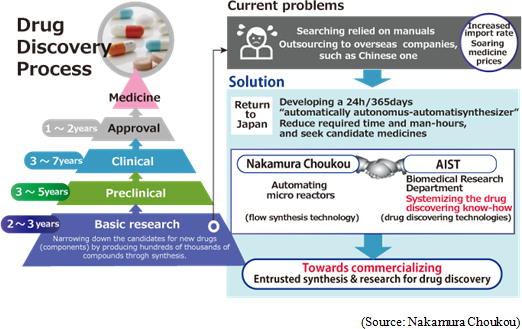 ② Material science business
Commercialization of nano-size zeolite.Zeolite is composed of mainly silica (silicon dioxide) and alumina (aluminum oxide), and characterized by a microporous molecular structure, and has a large surface area equivalent to over one tennis court per gram. Because of this property, zeolite possesses the functions of "adsorption," "ion exchange," and "catalyst," and is used broadly in the chemical field, as a catalyst for purifying the exhaust gas from automobiles; in the environmental field, as an adsorbent for radioactive cesium; and in the daily-life field, as an antibacterial agent for masks, and others. Micron-size particles are currently distributed, but when the particle size reaches the nano level, the above basic functions will improve drastically, and they will be used for new purposes. However, the conventional method for producing nano-sized particles takes a lot of cost, and concrete market evaluation did not progress. In these circumstances, Nakamura Choukou commenced the development of an innovative process for producing nano-sized zeolite by utilizing the nano-technology nurtured by the Company for many years in parallel with the life science business and the "Crushing and Recrystallizing Process" technology owned by Tokyo University, and then succeeded in producing "nano-sized zeolite," whose particle size is one millionth of ordinary zeolite, at low cost. (This "Crushing and Recrystallizing Process" is patent-pending.) In Apr. 2016, the Company started pre-mass production, displayed the products at exhibitions in Japan and China, and received a lot of inquiries. In Aug. 2016, the collaborative research between Nakamura Choukou and Tokyo University titled "Method for producing fine zeolite and Particle size control technology" was adopted as Stage III (NexTEP-A type), one of "A-STEP," which is the program for supporting the optimization of research results offered by Japan Science and Technology Agency. A-STEP is a program for supporting technological transfer targeted at the R&D phase based on research progress regarding science and technology for putting into practice the technology developed by universities, public institutes, and so on, which are important for the national economy. Multiple supports are offered according to the characteristics of phases, including the initial phase of R&D for practical application, in which candidate seeds are found from the research results of universities, etc. from the business viewpoint, the possibilities of seeds are examined, and brought out; the intermediate phase, in which the feasibility of obvious seeds is checked; and the late phase, in which enterprises take the initiative in developing products for corporate and conducting demonstrative tests. This is composed of the three stages: Stage I, Stage II, and Stage III. The objective of Stage III (NexTEP-A type), which adopts the research of Nakamura Choukou, has a purpose to "support enterprises in large-scale development using seeds based on the research results of universities which have risk for development, and to actualize a business based on the research results of universities by promoting practical application." The Company thinks that the above decision will facilitate the collaborative research. It is also expected that it will mitigate the risk caused by the financial burden of the collaborative research, because an R&D subsidy will be granted (if the development is successful, it will be repaid in annual payments. If not, 10% will be repaid). From now on, the Company will accelerate the development for actualizing a business based on the collaboration among industry, government, and academia, by conducting public relations activities, early creation of markets, establishing a low-cost medium-output production system, and so on. 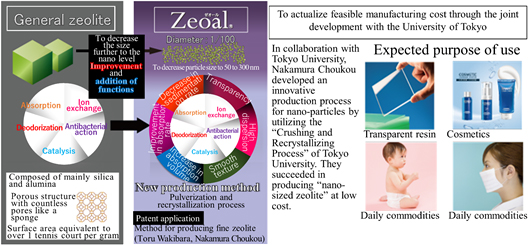 ③ New R&D theme: Development of regenerative medical devices
The Company started "Development of regenerative medical devices," as a new R&D project after Microreactor system and nano-sized zeolite. In Mar. 2017, it was announced that Nakamura Choukou and its consolidated subsidiary, Nippon Nozzle Co., Ltd., signed a contract for collaborative research with Doshisha University, for the purpose of developing regenerative medical devices. Purpose
In each field of cardiovascular, digestive, and respiratory surgeries, and transplantation, the replacement surgery with artificial items utilizing the technology of regenerative medicine is attracting attention as the next-generation strategy for surgical treatment, and it is said that the number of people who require such treatment exceeds 10 million in the world. Professor Akio Hagiwara of Regenerative Medicine Laboratory, Department of Medical Life Systems, Faculty of Life and Medical Sciences, Doshisha University engages in the research into regenerative medicine, in order to conduct the second surgery for correcting the size and functions of artificial items according to the growth of patients and solve the problems with conventional artificial items that need to be replaced after the functional degradation through long-time use. Nakamura Choukou and Nippon Nozzle decided to proceed with the joint research into regenerative medical devices by utilizing their possessed manufacturing technologies. If the development of regenerative medical devices is fulfilled in accordance with the contract for collaborative research, it may be possible to alleviate the physical and mental burdens due to repeated surgeries, which is raising great expectations. Roles of Nakamura Choukou and Nippon Nozzle
Through this joint research, Nakamura Choukou and Nippon Nozzle aim to develop a compact that has a continuous structure with bio-absorbable polymers and a scaffolding material that has a complex mechanism including non-woven and braided fabric structures, by utilizing the possessed technologies for precise processing and chemical fabrics, and put into practice regenerative medical devices, which are taken down and absorbed by the living body and emerge as the congenital own cellular tissue.
|
| <Reference 2: Regarding Corporate Governance> |
 ◎ Corporate Governance Report
Last updated: submitted on July 3, 2017<Reasons for Non-compliance with the Principles of the Corporate Governance Code (Excerpts)> The Company mentioned that "our company implements all of the basic principles of the corporate governance code as a company listed on the Mothers." Disclaimer
This report is intended solely for information purposes, and is not intended as a solicitation for investment. The information and opinions contained within this report are made by our company based on data made publicly available, and the information within this report comes from sources that we judge to be reliable. However we cannot wholly guarantee the accuracy or completeness of the data. This report is not a guarantee of the accuracy, completeness or validity of said information and opinions, nor do we bear any responsibility for the same. All rights pertaining to this report belong to Investment Bridge Co., Ltd., which may change the contents thereof at any time without prior notice. All investment decisions are the responsibility of the individual and should be made only after proper consideration.Copyright (C) 2017 Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. |




