Bridge Report:(6250)YAMABIKO the Fiscal Year December 2019
 President Yoshiaki Nagao | YAMABIKO CORPORATION(6250) |
 |
Company Information
Market | TSE 1st Section |
Industry | Machinery (Manufacturing) |
President | Yoshiaki Nagao |
HQ Address | 1-7-2, Suehiro-cho, Ome-shi, Tokyo, Japan |
Year-end | End of December |
Homepage |
Stock Information
Share Price | Shares Outstanding | Total market cap | ROE Act. | Trading Unit | |
688yen | 44,108,428 shares | 30,346 million yen | 7.6% | 100 shares | |
DPS Est. | Dividend yield Est. | EPS Est. | PER Est. | BPS Act. | PBR Act. |
35.00yen | 5.1% | 106.15yen | 6.5 times | 1,356.54yen | 0.5 times |
* The share price is the closing price on March 19. Each number was taken from the financial report of FY 12/19.
Earnings Trend
Fiscal Year | Sales | Operating Income | Ordinary Income | Net Income | EPS | DPS |
March 2017 Act. | 111,945 | 7,620 | 7,288 | 2,374 | 57.46 | 25.00 |
December 2017 Act. | 102,948 | 6,283 | 6,823 | 4,930 | 119.33 | 35.00 |
December 2018 Act. | 118,049 | 6,290 | 5,957 | 4,188 | 101.39 | 40.00 |
December 2019 Act. | 120,922 | 6,203 | 5,917 | 4,164 | 100.46 | 35.00 |
December 2020 Est. | 124,000 | 6,300 | 6,100 | 4,400 | 106.15 | 35.00 |
*The forecast was made by the company. Unit: Million yen or yen. Net income is profit attributable to owners of the parent. Hereinafter the same shall apply. FY December 2017 was a 9-month one. The DPS of 40 yen for FY December 2018 includes the 5yen dividend for commemorating the company‘s 10th anniversary.
This report introduces YAMABIKO CORPORATION’s earnings results for the Fiscal Year ended December 2019, Medium-term Management Plan and so on.
Table of Contents
Key Points
1.Company Overview
2.Fiscal Year ended December 2019 Earnings Results
3.Fiscal Year ending December 2020 Earnings Forecasts
4.Medium-term Management Plan 2022
5.Conclusions
<Reference:Concerning corporate governance>
Key Points
- The sales for the term ended December 2019 were 120.9 billion yen, up 2.4% year on year. In Japan, the sales of industrial machinery grew considerably, and the sales of outdoor power equipment and agricultural machinery were solid. Outside Japan, outdoor power equipment sold well in the Americas. Outside Japan other than the Americas, sales volume increased in Western Europe, but the performance in Russia, Asia, and Australia was sluggish. Overseas sales declined due to the effect of exchange rates. Operating income was 6.2 billion yen, down 1.4% year on year. Sales volume increased and the company strived to improve cost ratio, but profit dropped due to the augmentation of SG&A expenses and the effect of exchange rates.
- For the term ending December 2020, sales are estimated to be 124 billion yen, up 2.5% year on year. In Japan, it is estimated that there will be recoil from the rush demand before the consumption tax hike in the previous year, but overseas sales are projected to increase mainly in North America, and overall sales are forecasted to rise. Operating income is estimated to be 6.3 billion yen, up 1.6% year on year. The decline due to the augmentation of SG&A expenses and the yen appreciation against the dollar will be offset by the increase in sales volume, the improvement in cost ratio, etc. The assumed exchange rates are 1 U.S. dollar = 107 Japanese yen (109 Japanese yen in the previous term) and 1 euro = 118 Japanese yen (123 Japanese yen in the previous term). The dividend is to be 35 yen/share, unchanged from the previous term. The estimated payout ratio is 33.0%.
- The company announced a new Mid-term Management Plan. Based on the premise of the yen appreciation, they plan to increase sales by 10.8% and CAGR by 3.5% from the term ended December 2019.
- The largest driver is outdoor power equipment. Its performance in the U.S. market, where domestic demand is strong , is especially the key. By releasing highly functional products, etc., the company aims to expand its business and share in the professional market. In Japan, the sales of industrial machinery increased significantly in the previous term, but are estimated to decline, so it is forecasted that total sales will be on a plateau, but outdoor power equipment will perform well.
- The external environment has uncertainties due to Covid-19, etc., but we would like to pay attention to the progress of measures for achieving the plan in each segment inside and outside Japan.
1. Company Overview
YAMABIKO CORPORATION develops, manufactures and sells outdoor power equipment (e.g. trimmers, chain saws etc.), agricultural machinery (e.g. pest control equipment, sloop mower), industrial machinery (e.g. generators, welders etc.) in Japan and overseas. The overseas sales occupy about 60% of their total sales. In terms of manufacturing and selling outdoor power equipment, the company not only has the top share in Japan but also a large share in the US. Its strength is owning unique production technology, a variety of product line-ups, and an excellent technical support system.
1-1 Corporate history
YAMABIKO CORPORATION started as a joint holding company established in December 2008 through a merger between KIORITZ CORPORATION (listed in the first section of the Tokyo, Osaka and Nagoya Stock Exchanges), which dealt with agricultural machinery in Japan and outdoor power equipment overseas, and Shindaiwa Corporation (listed in the second section of the Tokyo Stock Exchange), which dealt with outdoor power equipment and industrial machinery globally. In October 2009, YAMABIKO CORPORATION established its current business entity by merging both KIORITZ and Shindaiwa.
KIORITZ CORPORATION was established in 1947 in Tokyo and originally called KIORITZ AGRICULTURAL EQUIPMENT CORPORATION. It has been a leading company in both agricultural equipment business through which they developed “Japan’s first speed sprayers” and outdoor power equipment business through which they developed “Japan’s first motorized backpack trimmers” and “the world’s first handheld power blowers”. Furthermore, since its establishment, it has been focusing on self-development of engines for outdoor power equipment. The accumulative number of engines produced in 2008, before the merger, was about 40 million.
Shindaiwa Corporation was established in 1952 in Hiroshima and was originally called Asamoto Precision Manufacturer. It not only developed “Japan’s first electric chain saws” for the outdoor power equipment business, but also manufactured and sold engine generators and engine welders for the industrial machinery business. Its strength was high technological development capabilities, as can be seen in the development of the world’s first mixed fuel 4-cycle engine.
In the late 1990s, with growing concern about global warming caused by greenhouse effect gas, and as engine’s emission gas control became stricter in the Western countries, especially in the US, research and development expenses increased to comply with the new regulations. In the 2000s, the medium and small-sized companies that could not afford these expenses went through rapid industry restructuring on a global scale in the outdoor power equipment industry.
Moreover, the business environment became further uncertain due to a flood of cheaper products from newly emerging countries and diversification of customers’ needs.
Under these circumstances, the two companies concluded a business and capital alliance agreement in May 2007 on the premise of future business integration in order to strengthen the vitality to survive and win the intensifying competition.
In December 2008, YAMABIKO CORPORATION was established as a joint holding company to achieve better efficiency and expansion for all its businesses including development, manufacturing, logistics, sales and management. In October 2009, YAMABIKO CORPORATION conducted an absorption-type merger of KIORITZ and Shindaiwa and became the current business entity.
The company name “YAMABIKO” derives from the mountain god, “Yamabiko”. Its corporate philosophy is to “create the bridge that bonds people and nature with the future”. This expresses the company’s willingness to contribute to the conservation and improvement of the nature and environment.
1-2 Corporate philosophy, etc.
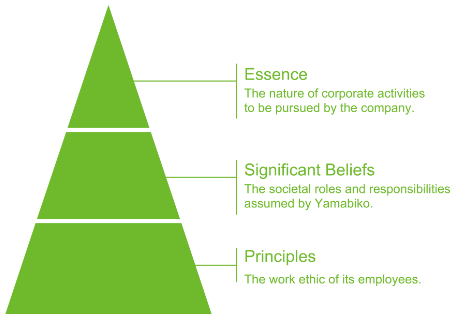
YAMABIKO Group’s corporate philosophy is formed from three elements: “Essence”, “Purpose of Existence” and “Code of Conduct”.
“Essence”, which incorporates both “Purpose of Existence” and “Code of Conduct”, expresses in a single word what YAMABIKO Group aims to be as a company, and the essence of its corporate activities.
“Purpose of Existence” sets out the role and responsibilities of YAMABIKO Group in society and makes a commitment to this.
“Code of Conduct” defines the attitude of each YAMABIKO Group employee in relation to their work.
(From the Company’s website)
<Essence>
*Create the bridge that bonds people and nature with the future. |
<Significant Beliefs>
*Offer the best products and service in the world. *Support people and companies committed to sustaining nature and the environment. *Lead the industry through the creation of new markets and customers, ultimately resulting in growth for tomorrow. *Provide a sense of fulfillment for all persons affiliated with YAMABIKO CORPORATION. |
<Principles>
*Observe change and anticipate the future. *Combine fact with theory. *Break the status quo through innovation and creativity. *Think and act with the spirit and vitality of a globally competitive company. *Conduct oneself with sincerity and grace. |
In addition, the company established 14 detailed measures that augment the Code of Conduct to facilitate the implementation of business activities in accordance with the corporate philosophy.
President Nagao disseminates messages that are based on “Essence”, “Purpose of Existence” and “Code of Conduct” at various occasions. They are also making daily efforts so that the corporate philosophy would lead to each employee’s actual activities in each workplace.
* Profile of President Yoshiaki Nagao
President Yoshiaki Nagao was born in February 1953 (Age 66). Since his childhood, he enjoyed “creation” such as building plastic models. When he was in the middle school, his interest grew in automobiles, especially those made in the US. He majored in “combustion engineering” in graduate school, where he studied engines. He began working at KIORITZ CORPORATION in April 1978.
At KIORITZ, he worked at the research department. He was involved with research and development of various engines, especially chain saws engines, under the corporate culture that supported the employees’ spirit to find and work on the issues of their interest. Instead of focusing on his research only in the lab, he went out to the mountains and interviewed woodsmen who were the users of their products to hear opinions and identify the demands in detail.
After working in the technology area for most of his time at KIORITZ, he was appointed as President and CEO of ECHO Incorporated, an affiliate of KIORITZ in the US in February 2006. His focus at ECHO Incorporated was to observe the actual situation of the emission gas control regulations in the US, to find measures to meet the regulations, and to enhance the users’ satisfaction. During the merger process of KIORITZ and Shindaiwa, he facilitated fast and drastic organization of the local sales routes. He recalled, “It was an important step to diversify my work”.
After the establishment of YAMABIKO CORPORATION, he managed to implement smooth integration as a board director / managing officer / industrial machinery division officer in Hiroshima where the head plant of Shindaiwa Corporation was located. In June 2011, he was appointed CEO and President of YAMABIKO CORPORATION.
1-3 Market environment
Although no detailed statistics about the outdoor power equipment market is available, it is known that the largest market is in North America including the US, followed by Europe. In Japan, about 1 million outdoor power equipment/tools are sold per year. The indicators that may impact the company’s trend in the earnings include “number of housing start”, “commodity price”, and “crude oil price” for the overseas market and “rice price” for the Japanese market.
The company recognizes that there are two global manufacturers of outdoor power equipment in Europe (Germany and Sweden).
1-4 Business contents
1. Segment
YAMABIKO Group operates businesses in three sectors: Outdoor power equipment, Agricultural machinery and Industrial machinery. These three segments are reported.
(Developed by us based on YAMABIKO CORPORATION’s financial report.)
“Outdoor power equipment business”
YAMABIKO CORPORATION manufactures and sells handheld or backpack-style forestry and landscape maintenance machinery powered by small internal combustion engines. The main products include chain saws, trimmers, power blowers, hedge trimmers, etc.
In Nov. 2014, the company acquired “Belrobotics SA,” a Belgian venture company, which develops, manufactures, and sells robotic mowers for professional use. (In Jan. 2017, Belrobotics SA was renamed “Yamabiko Europe SA” for the purpose of enhancing sales in Europe.)
Based on the accumulated experiences and know-how and excellent development capabilities that meet the customers’ needs, YAMABIKO CORPORATION continues to produce high performance, highly durable and high-quality engines.
<Chain saws>
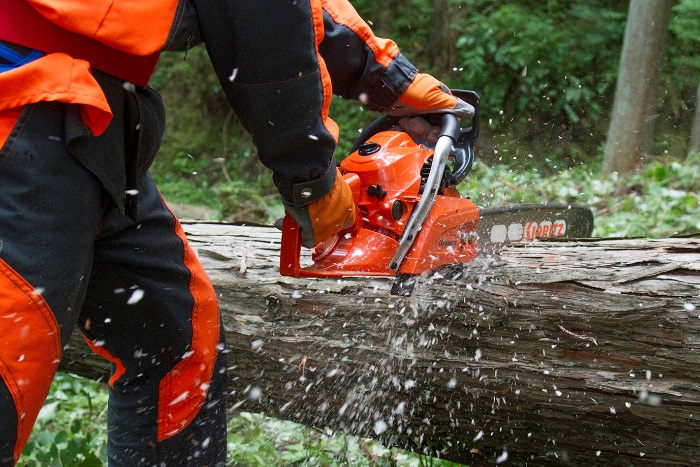 | <Trimmers>
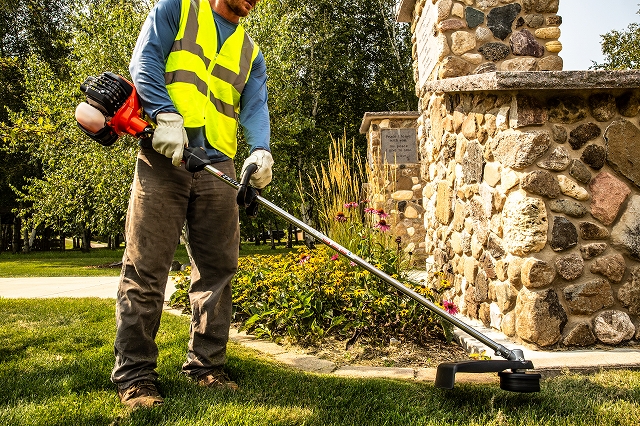 |
<Power blowers>
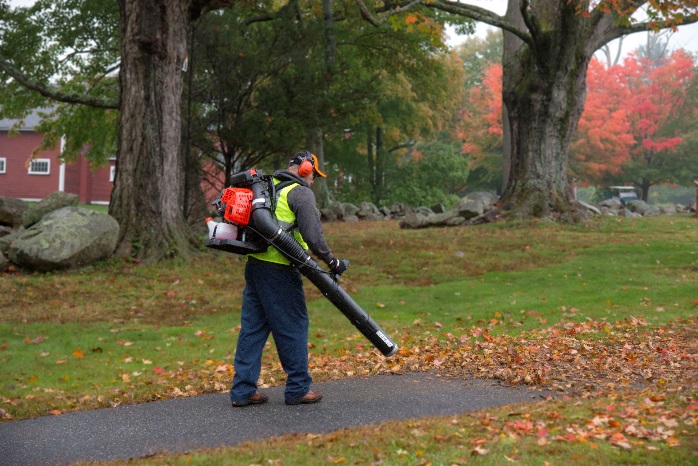 |
|
(Gasoline engine system)
The engines for outdoor power equipment such as chain saws and trimmers are mainly 2-stroke gasoline engines. As described later, the company’s excellent capability to develop engines is one of their most important features/strengths.
Brief information concerning the company’s engines is provided below because knowing the gasoline engine system and characteristics of each engine type helps to understand the business of the company,
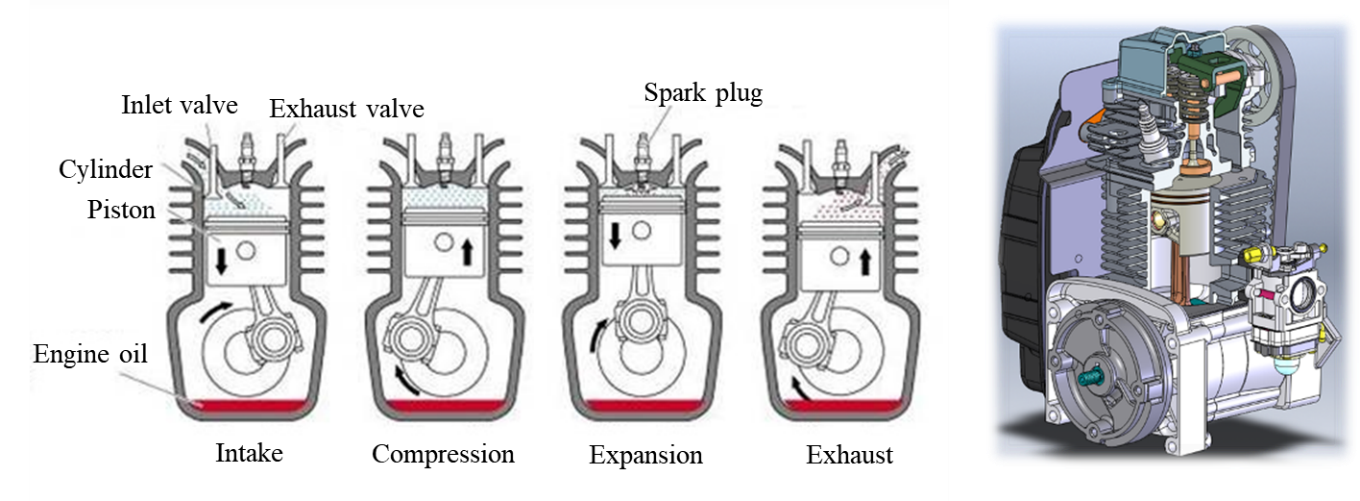
Basically, a gasoline engine generates power by moving the piston down with the combustion of gasoline through the following 4 steps.
Step | Overview |
1. Intake | The air-fuel mixture is sucked in a cylinder. |
2. Compression | The air-fuel mixture in the cylinder is compressed as the piston moves up. |
3. Expansion | When the air-fuel mixture is compressed the most, a spark will be generated to ignite. Expansion from burning pushes the piston down. |
4. Exhaust | The burned gas is discharged to outside. |
Reciprocating motion of the piston is converted into revolution by a crankshaft. The rotating motion turns the rotating shaft of axel of a car or revolving shaft of chain saws.
The gasoline engine is largely categorized in two types (2-stroke engine and 4-stroke engine), depending on the number of reciprocating motions by piston to complete “1 cycle” of the 4 steps.
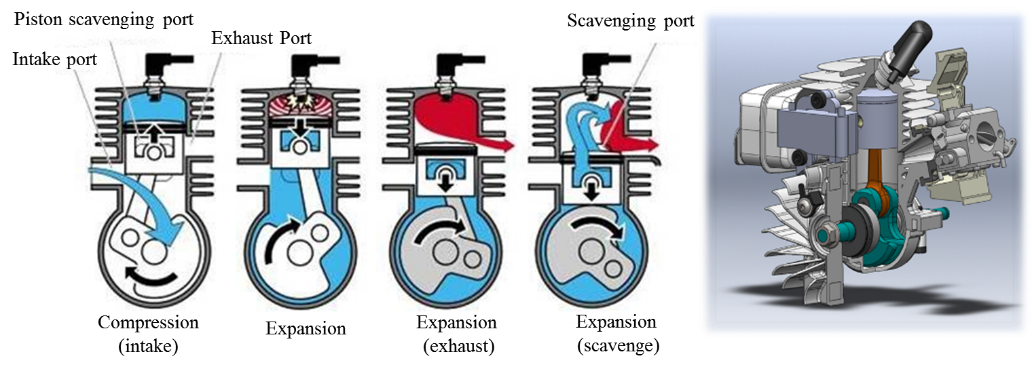
“2-stroke engine”
One power cycle is completed by 2-stroke. In other words, a power is generated by “1 piston reciprocating motion, 1 crankshaft revolution”.
First stroke (piston moving up): “Intake” and “compression” of air-fuel mixture occurs.
Second stroke (piston moving down): Piston moves down due to the “expansion” of air-fuel mixture and “exhaust” occurs later.
“4-stroke engine”
One power cycle is completed by 4-stroke. A power is generated by “2 piston reciprocating motions, 2 crankshaft revolutions”.
First stroke (piston moving down): “Intake” of air-fuel mixture occurs.
Second stroke (piston moving up): “Compression” of air-fuel mixture occurs.
Third stroke (piston moving down): Piston rapidly moves down as a result of “expansion”.
Fourth stroke (piston moving up): Combusted gas is “exhausted”.
The advantage of the 4-stroke engine is the easy control of intake and exhaust. However, its structure is complicated compared to a 2-stroke engine, because the intake/exhaust valves of a 4-stroke engine are installed at the cylinder head, while intake and exhaust of a 2-stroke engine occur at the port that is located on the body of the cylinder. Because of this structure, the weight of a 4-stroke engine is heavier than a 2-stroke engine.
On the other hand, a 2-stroke engine has a larger ratio of burning engine oil and fuel in order to make smooth piston motion and blow-by of air-fuel mixture. This means it releases more harmful substances in the exhaust gas as compared with a 4-stroke engine. However, because of its simple structure and smaller number of parts, the 2-stroke engine can be smaller and lighter. The overhaul is also easier for the same reasons. Therefore, a 2-stroke engine is the most appropriate engine for outdoor power equipment.
“Agricultural machinery business”
YAMABIKO CORPORATION manufactures and sells pest control equipment for Japan and agricultural harvesting equipment for North America.
Its major products include pest control equipment (speed sprayers, mounted equipment for cropland pest control, power sprayers), sloop mower, soy and potato harvesters, etc.
YAMABIKO CORPORATION’s technological strengths in this business segment are KIORITZ’s blowing, spraying, and pumping technology as well as technology to create small and light equipment. These technological capabilities have been built up over many years at KIORITZ.
<Mounted equipment for cropland pest control>
 | <Speed sprayers>
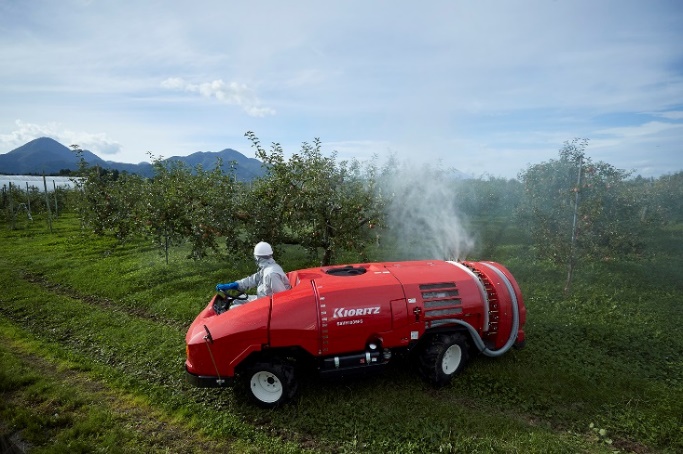 |
<Sloop mowers>
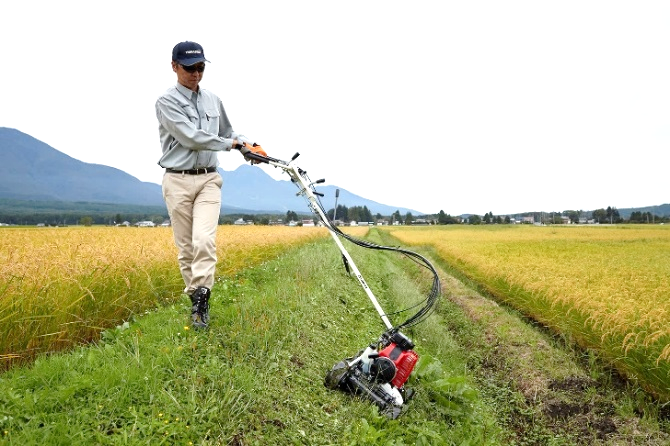 |
|
“Industrial machinery business”
YAMABIKO CORPORATION manufactures and sells equipment for construction, civil engineering and iron works.
Its major products include generators, welders, lighting equipment, cutting machines and high-pressure washers.
Technological strengths in this business segment are established by the R&D knowledge accumulated since YAMABIKO CORPORATION started business as Shindaiwa, and such strengths can be found in alternator designing capability improved by their efforts for alternative current motor development, as well as technologies for electronic control and noise prevention.
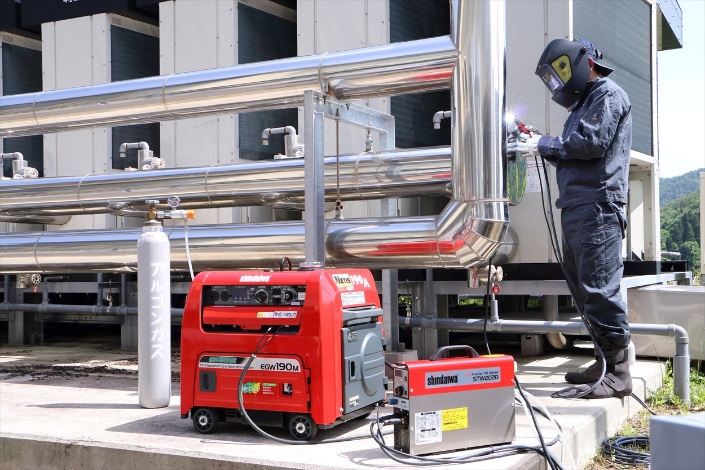
<Generators>
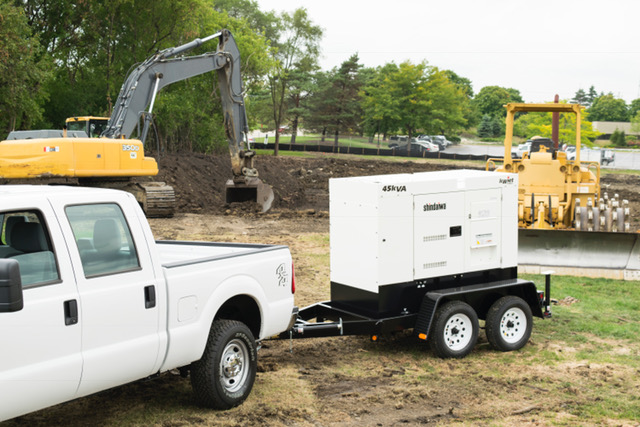 | <Welders>
 |
“Others”
The company manufactures and sells accessories and the parts for after purchasing service for various machines and equipment.
The profitability in this segment is the highest among all segments.
<Maintenance kit>
 | <Nylon trimmer line>
 | <Fuel/Oil>
 |
2. Brand
YAMABIKO CORPORATION was established based on the integration of two companies. The products of both companies are well recognized both in Japan and overseas for many years. Therefore, YAMABIKO CORPORATION maintains the brand names as KIORITZ, Shindaiwa, and ECHO.
YAMABIKO CORPORATION is proactively investing in marketing activities as well as exploring new sales routes to enhance its brand values.

3. Development structure
Each business segment is working on development with a focus on the following priority issues.
Business | Priority issues for development |
Outdoor power equipment | *To comply with exhaust gas regulations at the global level *To comply with fuel permeability regulations in North America *To comply with noise and vibration regulations in Europe *To create smaller and lighter equipment with low noise, low fuel consumption and high durability *To improve safety |
Agricultural machinery | *To achieve reduction of drift, proper quantity of spraying, high performance, and easy operation |
Industrial machinery | *To create smaller and lighter machinery with low noise, high performance, high function, and low fuel consumption |
The exhaust gas regulations are expected to be further tightened in the future. Therefore, addressing them is of paramount importance.
In addition, the company is conducting research on control technology in the field of electronic control.
4. Production structure
The company has 3 plants (Yokosuka, Morioka, and Hiroshima) and 4 production related subsidiaries in Japan and a total of 10 production related subsidiaries in the USA, Belgium, China and Vietnam.
5. Sales route and sales methods
The company supplies its products in over 90 countries for about 28,000 stores.
More than 60% of the sales are from overseas sales.
<Domestic market>
Seven sales subsidiaries, which were separated mainly by region, were merged into YAMABIKO JAPAN CO., LTD. in April 2017, with the aim of allocating management resources in a more efficient manner, strengthening sales capabilities, and improving customer services through a unified management system and integral operation of business assets.
YAMABIKO JAPAN CO., LTD sells the products to distributors, ZEN-NOH (National Federation of Agricultural Cooperative Associations), home improvement retailers, and construction machinery rental companies, etc. Through them, the products are supplied to the end users including farmers/foresters, companies in the construction, civil engineering and iron industries and landscapers.
The company presents their products in exhibitions in collaboration with dealers and distributors and facilitates sales through demonstration and test drive.
Furthermore, the company accompanies dealers to visit end users to understand their needs and utilize the information for product development.
<North American market>
ECHO Incorporated Group, one of the company’s subsidiaries, sells the products to The Home Depot (*) and other distributors, through which the products are supplied to the end users such as landscapers, homeowners, farmers/foresters, and companies in the construction/civil engineering industry.
*The Home Depot: The Home Depot, Inc. is the world’s largest home improvement retailer and construction products and services. It was established in 1978. Sales in 2018 were US$108.2 billion and net income was US$11.1 billion. It has over 2,200 stores in the US, Canada and Mexico. It is listed on the New York Stock Exchange. (Excerpted from the company’s website)
The Home Depot classifies their products into GOOD, BETTER and BEST in accordance with the quality. It is only YAMABIKO CORPORATION that supplies the high-quality BEST products to The Home Depot. This is one of the proofs that the company’s products are highly reputed in the North American market.
In the Central and South American market, ECHO Incorporated, one of the company’s subsidiaries, sells the products to the distributors of each country, and made their products supplied to the end users through dealers.
Yamabiko Europe SA in Europe and ECHO MACHINERY (SHENZHEN) Co., Ltd. in China, both of which are subsidiaries of Yamabiko, sell products to distributors in their respective countries
Asia and other areas, YAMABIKO CORPORATION sells the products to the distributors in each country.
The overseas dealers display the products by brand, and salesperson conducts person-to-person sales while understanding the needs of the end users.
The home improvement retailer also displays the products by type and price. The end users purchase the products based on the needs, budget and image they have from advertisement, etc.
1-5 Characteristics and strengths
①Unique production and technological capabilities and vertically integrated production
The most important characteristics and strengths of the company are the “unique production and technological capabilities and vertically integrated production capabilities”.
Their mainstay 2-stroke engines that are mounted to the outdoor power equipment are manufactured by an integrated production system solely by the company from development, procurement of aluminum, molding, parts production, processing to assembly, which is said to be unique anywhere in the world. The power sources for the products of agricultural machinery and industrial machinery are also engines, but they are mostly procured externally.
The company have solved various issues with their unique technologies including iron plating and electric discharge processing. This results in the quality improvement and production capacity improvement of the company.
Specifically, the company has established the following technologies.
<Example 1: Iron plating>
Plating is a surface covering method in which the surface of a metal is covered by a thin layer of another metal. For engine production, inside of the cylinder should be plated to avoid abrasion caused by friction with a piston.
The conventional method is to use chrome plating from durability and cost perspectives. However, chrome plating gives negative impact on the environment. Its production efficiency is also low. Therefore, there was an increasing demand for different materials for plating.
The company has been working on “iron plating” since 1978 to reduce environmental load.
Initially, they could produce only hundreds per day. However, as a result of improved productivity, enhanced plating precision, and reduction of environmental load, the company now has the iron plating technology that does not require finish processing. Their technology has drastically smaller environmental load. Furthermore, their daily production capacity increased significantly, reaching thousands.
The company holds 5 patents related to iron plating.
<Example 2: Electric discharge processing>
As described above, a 2-stroke engine requires a smaller number of parts and has a simpler structure as compared to a 4-stroke engine. Therefore, it is most suitable for the “handheld” and “backpack-style” outdoor power equipment. However, it releases some fuel mixed gas. In order to respond to the increasingly strict exhaust gas regulations globally, the company was faced with a challenge to control the flow of the fuel mixed gas for efficient burning.
In order to achieve it, the company explored the production methods to modify the internal shape of the cylinder (by installing a wall between the fuel mixed gas passage and internal shape of the cylinder).
A “wall” can be created by die-casting (*), but it requires a horizontal hole to lead the fuel mixed gas to a combustion chamber. With die-casting, it was impossible to create a horizontal hole. It was also difficult to carry out machining due to small space in the chamber.
The company came up with the idea of using “electric discharge processing (*)” to create a form while taking advantage of die-casting.
Although electric discharge processing enabled to create complicated forms, it was costly due to long processing time and high electrode consumption. The company conducted research on processing conditions for a large volume production and developed designs of special electrode form. As a result, it succeeded in producing a large volume of products, by shortening processing time, saving personnel, lowering the cost of electrode and enhancing efficiency.
Having obtained three patents related to electrode processing, the company has established the unique technology that cannot be imitated by other companies.
(*) Die-casting
Die-casting is one of the metal mold casting methods. By injecting melted metal in a metallic mold, a large amount of casting with high precision can be produced within a short period of time. It enables to create a thin product at low cost.
(*) Electric discharge processing
Electric discharge processing is a machine processing method to remove a part of the surface of a non-processed workpiece through repeated electrode discharge at short cycles between electrode and the non-processed workpiece. It enables to cut out complicated outline on extremely hard steel.
With “advanced capabilities for creation” such as the above-mentioned technologies, the Company not only complies with exhaust gas regulations but also responds to various needs including weight reduction, enhancing durability and cost reduction. It succeeded in developing and mass-producing “a light weight and highly durable 2-stroke engine that meets the exhaust gas regulations”.
While many companies in the world are forced to leave the industry because they cannot address these issues, YAMABIKO CORPORATION continues to make further development as a leading manufacturer.
②Unique research and development capabilities for each business segment
The company’s capability to address environmental issues is high. The company possesses one of the highest number of US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)-accredited engines in the world.
Furthermore, not only for outdoor power equipment, the company also has unique research and development capabilities for the agricultural machinery and industrial machinery. Based on the technological capacities that have been accumulated by KIORITZ and Shindaiwa for many years, the company is further brushing up the capabilities.
③Extensive product lineup and expansion of sales network and domestic services network
The company has an extensive lineup of products that meet various needs of the customers in each of the three business segments.
It also currently supplies the products to about 28,000 stores in more than 90 countries across the world.
As a result of merging KIORITZ and Shindaiwa, YAMABIKO CORPORATION’s product lineup and sales network were further expanded.
With the aim of improving the satisfaction level of diversifying users, the company established “Yamabiko Service Shop” inside Japan in 2013, and is operating service systems for maintenance, repair a failure, etc., which are not offered by competitors, throughout Japan. The number of affiliated shops is 342 as of Mar.2020.
④Excellent technical support system
The company also provides excellent technical support in order to enhance credibility of the products and strengthen the relationships with distributors and dealers.
In addition to offering about 40 service schools annually both in Japan and abroad, in 2018, the company started to provide a new e-learning course using its originally developed teaching materials targeted at overseas distributors in an attempt to enhance their repair skills and deepen their understanding of the mechanism of the engines.
Furthermore, the European subsidiaries of the company recently organize road show-style education and training sessions for nurturing trainers at distributors, and lecture classes designed for distributors’ salespersons, endeavoring to further fortify its service capabilities.
⑤High product share
By demonstrating the above-mentioned characteristics and strengths (1-5-1) to (1-5-4) in an integrated manner, the company is becoming highly competitive at a global level. For the outdoor power equipment business, the company has the top market share (more than 30%) in Japan and is ranked high in North America, the largest market.
1-6 Return on Equity (ROE) Analysis
| FY 3/12 | FY 3/13 | FY 3/14 | FY 3/15 | FY 3/16 | FY 3/17 | FY 12/17 | FY 12/18 | FY 12/19 |
ROE (%) | 7.9 | 8.7 | 14.5 | 12.4 | 10.4 | 5.1 | 9.9 | 7.9 | 7.6 |
Net income margin [%] | 2.27 | 2.72 | 4.48 | 4.67 | 4.15 | 2.12 | 4.79 | 3.55 | 3.44 |
Total asset turnover [times] | 1.14 | 1.13 | 1.28 | 1.18 | 1.21 | 1.20 | 1.05 | 1.18 | 1.18 |
Leverage [times] | 3.04 | 2.85 | 2.52 | 2.26 | 2.08 | 2.00 | 1.98 | 1.91 | 1.84 |
The estimated net income margin for this term is 3.55%, which surpass the previous term. Although leverage is showing a downward trend, the company is expected to continuously achieve a ROE of around 8%.
2. Fiscal Year ended December 2019 Earnings Results
2-1 Consolidated Business Results
| FY 12/ 18 | Ratio to sales | FY 12/ 19 | Ratio to sales | YoY | Difference from the initial forecast |
Sales | 118,049 | 100.0% | 120,922 | 100.0% | +2.4% | -3.3% |
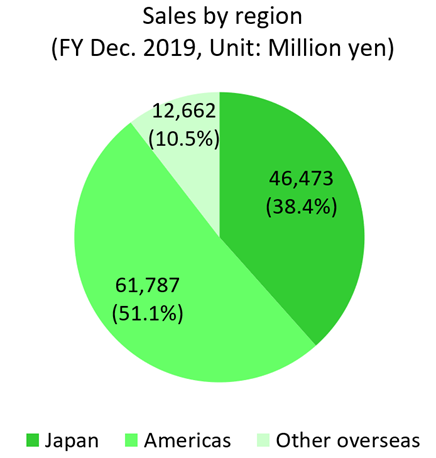
Domestic | 42,943 | 36.4% | 46,473 | 38.4% | +8.2% | - |
Oversea | 75,105 | 63.6% | 74,449 | 61.6% | -0.9% | - |
Americas | 61,418 | 52.0% | 61,787 | 51.1% | +0.6% | - |
Others overseas | 13,687 | 11.6% | 12,662 | 10.5% | -7.5% | - |
Gross profit | 33,266 | 28.2% | 33,994 | 28.1% | +2.2% | -1.5% |
SG&A | 26,976 | 22.9% | 27,791 | 23.0% | +3.0% | -0.7% |
Operating Income | 6,290 | 5.3% | 6,203 | 5.1% | -1.4% | -4.6% |
Ordinary Income | 5,957 | 5.0% | 5,917 | 4.9% | -0.7% | -6.1% |
Net Income | 4,188 | 3.5% | 4,164 | 3.4% | -0.6% | -7.5% |
*Unit: million yen. Net income means profit attributable to owners of parent.
Domestic sales were strong, though overseas sales declined due to the effect of exchange rates. Sales increased, but profits decreased.
The sales were 120.9 billion yen, up 2.4% year on year. In Japan, the sales of industrial machinery grew considerably, and the sales of outdoor power equipment and agricultural machinery were solid. Outside Japan, outdoor power equipment sold well in the Americas. Outside Japan other than the Americas, sales volume increased in Western Europe, but the performance in Russia, Asia, and Australia was sluggish. Overseas sales declined due to the effects of exchange rates. Operating income was 6.2 billion yen, down 1.4% year on year. Sales volume increased and the company strived to improve cost ratio, but profit dropped due to the augmentation of SG&A expenses and the effects of exchange rates.
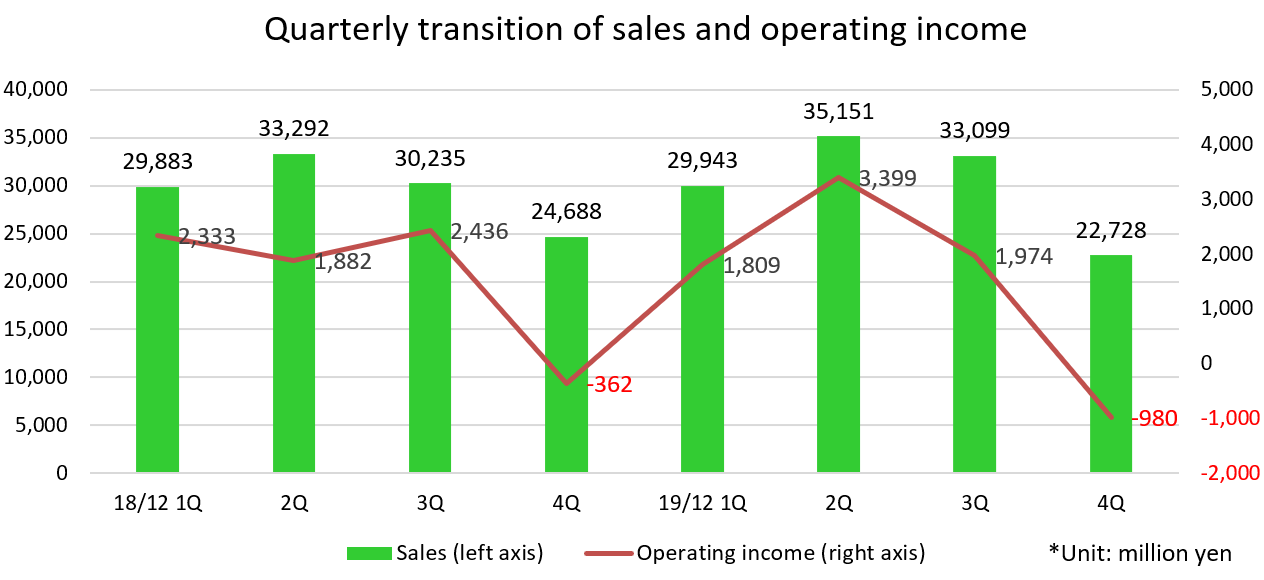
Quarterly sales and profit decreased from the previous term and from the same period of the previous term. The main factor is the recoil from the rush demand before the consumption tax hike.
2-2 Trends by Segment
| FY 12/ 18 | Ratio to sales | FY 12/ 19 | Ratio to sales | YoY |
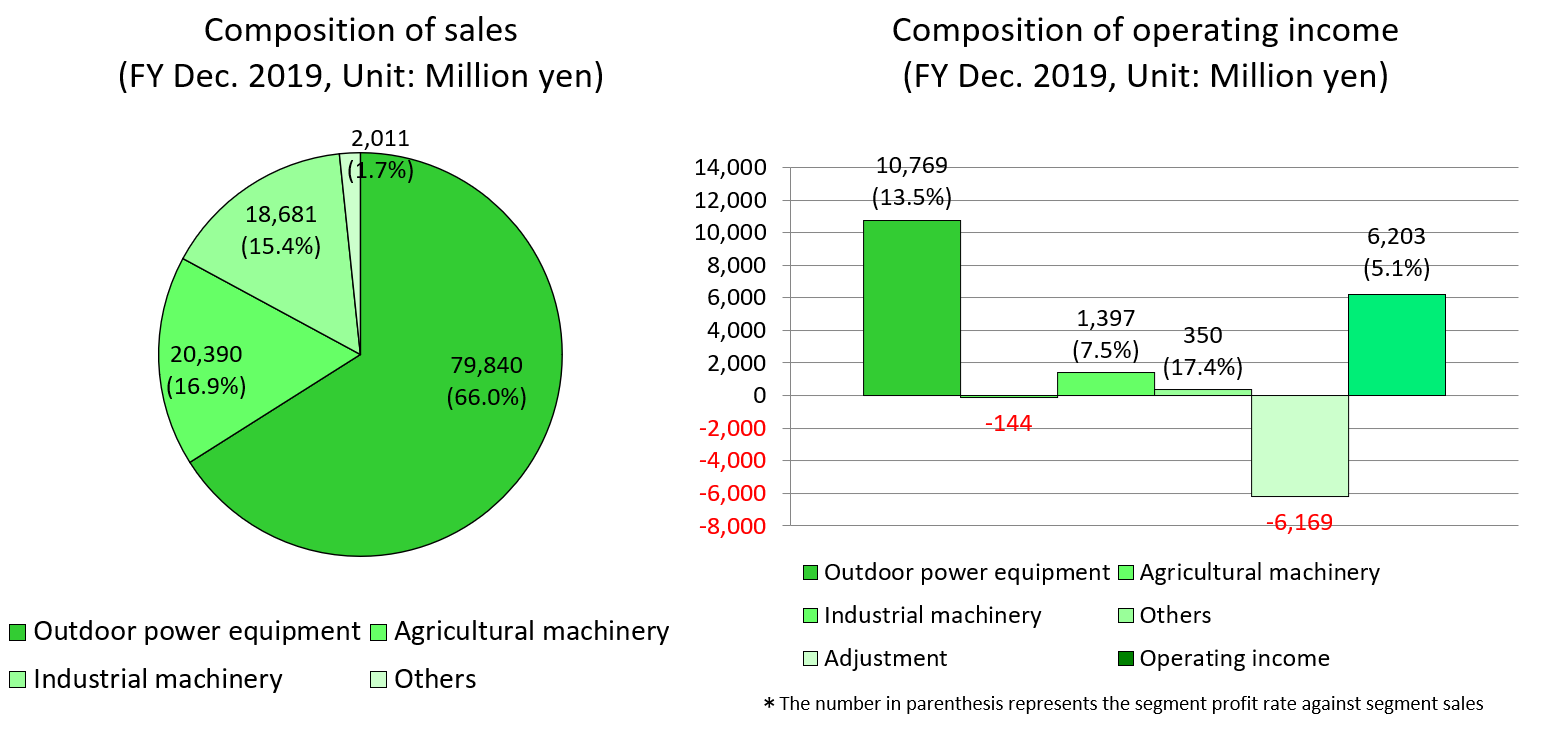
Outdoor power equipment | 79,231 | 67.1% | 79,840 | 66.0% | +0.8% |
Agricultural machinery | 21,206 | 18.0% | 20,390 | 16.9% | -3.9% |
Industrial machinery | 15,248 | 12.9% | 18,681 | 15.4% | +22.5% |
Others | 2,362 | 2.0% | 2,011 | 1.7% | -14.9% |
Sales | 118,049 | 100.0% | 120,922 | 100.0% | +2.4% |
Outdoor power equipment | 11,204 | 14.1% | 10,769 | 13.5% | -3.9% |
Agricultural machinery | -100 | - | -144 | - | - |
Industrial machinery | 756 | 5.0% | 1,397 | 7.5% | +84.8% |
Others | 399 | 16.9% | 350 | 17.4% | -12.2% |
Adjusted amount | -5,969 | - | -6,169 | - | - |
Operating income | 6,290 | 5.3% | 6,203 | 5.1% | -1.4% |
*Unit: million yen. The composition ratio for operating income means the ratio of operating income to sales.
◎ Outdoor power equipment
| FY 12/ 19 | YoY |
Sales | 79,840 | +0.8% |
Japan | 13,621 | +2.4% |
Overseas | 66,219 | +0.4% |
*Unit: million yen
(Japan)
The sales of trimmers, which are core products, recovered as demand increased after the rainy season, and the sales of chain saws mainly for home centers increased. In the fourth quarter (Oct. to Dec.), sales grew thanks to the recovery of sales of spare parts, despite the recoil from the rush demand before the consumption tax hike.
(Overseas)
In North America, which is the major market of the company, the sales of trimmers and power blowers mainly for professionals increased, but the sales growth in the yen in the Americas was slight, due to the downturn of the economy in Latin America, the yen appreciation, against the dollar etc.
In Western Europe, robotic mowers newly launched in the previous year contributed to sales through a whole year. The performance in Asia, too, was healthy, but the sales in Australia and Russia were stagnant, and the yen appreciation against the euro significantly affected business performance. Therefore, the sales in foreign countries, excluding the Americas, decreased. Overseas sales in total were almost the same as in the previous year.
◎Agricultural machinery
| FY 12/ 19 | YoY |
Sales | 20,390 | -3.9% |
Japan | 15,604 | +0.2% |
Overseas | 4,785 | -15.0% |
*Unit: million yen
(Japan)
The sales of mainly large-sized machines, such as speed sprayers and power sprayers, increased until the third quarter, thanks to the launch of new products and the rush demand before the consumption tax hike, but annual sales were almost unchanged from the previous year, due to the recoil from the rush demand, etc.
(Overseas)
In the Americas, sales declined due to the lingering slump in commodity (grain) prices, the trade dispute between the U.S. and China, etc. The sales of mounted equipment for cropland pest control launched in China in the previous year decreased, due to the weakening of demand in the wake of the revision to the subsidy policy.
◎Industrial machinery
| FY 12/ 19 | YoY |
Sales | 18,681 | +22.5% |
Japan | 15,246 | +29.6% |
Overseas | 3,434 | -1.5% |
*Unit: million yen
(Japan)
The sales of power generators, which are the mainstay, increased significantly, thanks to the sustained strong demand for developing infrastructure, preventing and mitigating disasters, and promoting national resilience. The sales of welders grew, as the demand for construction was robust, and led to a considerable increase in domestic sales.
(Overseas)
The performance in Australia, Asia, etc. was solid, but the sales of generators decreased in North America. Consequently, overseas sales declined.
◎Others
| FY 12/ 19 | YoY |
Sales | 2,011 | -14.9% |
Japan | 2,001 | -13.1% |
Overseas | 9 | -83.5% |
*Unit: million yen
Sales declined due to the slowdown of sales of snowplows, etc.
2-3 Financial standing and cash flows
◎Main Balance Sheet
| End of December 2018 | End of December 2019 |
| End of December 2018 | End of December 2019 |
Current Assets | 67,637 | 71,270 | Current liabilities | 36,578 | 33,852 |
Cash | 4,641 | 6,262 | Payables | 19,439 | 20,922 |
Receivables | 25,228 | 25,693 | ST Interest Bearing Liabilities | 10,696 | 5,550 |
Inventories | 35,650 | 37,335 | Noncurrent liabilities | 9,156 | 12,706 |
Noncurrent Assets | 31,676 | 31,575 | LT Interest Bearing Liabilities | 5,756 | 9,837 |
Tangible Assets | 24,994 | 24,208 | Total Liabilities | 45,735 | 46,559 |
Intangible Assets | 896 | 668 | Net Assets | 53,577 | 56,285 |
Investment, Others | 5,784 | 6,697 | Shareholders’ Equity | 52,108 | 54,771 |
Total assets | 99,313 | 102,845 | Total liabilities and net assets | 99,313 | 102,845 |
*Unit: million yen. Trade payables include electronically recorded accounts payable.
Current assets increased 3.6 billion yen from the end of the previous term, due to the growth of cash & deposits, inventories, etc. Noncurrent assets were almost unchanged, and total assets grew 3.5 billion yen to 102.8 billion yen.
Total liabilities augmented 800 million yen to 46.5 billion yen, due to the rise in accounts payable, etc.
Net assets rose 2.7 billion yen to 56.2 billion yen, due to the increase in retained earnings, etc.
As a result, capital-to-asset ratio rose 0.8% from the end of the previous term to 54.7%.
The balance of short and long-term loans payable was 15.3 billion yen, down 1 billion yen from the end of the previous term.
◎Cash Flow
| FY 12/ 18 | FY 12/ 19 | Increase/decrease |
Operating Cash Flow | 4,433 | 7,654 | +3,221 |
Investing Cash Flow | -3,172 | -3,083 | +89 |
Free Cash Flow | 1,261 | 4,571 | +3,310 |
Financing Cash Flow | -2,254 | -2,889 | -635 |
Term End Cash and Equivalents | 4,641 | 6,262 | +1,621 |
*Unit: million yen
The surplus of operating CF and free CF expanded, due to the augmentation of accounts payable, etc.
The deficit of financing CF expanded, due to the decline in short-term interest-bearing debts, etc.
The cash position improved.
3. Fiscal Year ending December 2020 Earnings Forecasts
3-1 Full-year earnings forecasts
| FY 12/ 19 | Ratio to sales | FY 12/ 20 Est. | Ratio to sales | YoY |
Sales | 120,922 | 100.0% | 124,000 | 100.0% | +2.5% |
Gross profit | 33,994 | 28.1% | 34,800 | 28.1% | +2.4% |
SG&A | 27,791 | 23.0% | 28,500 | 23.0% | +2.6% |
Operating Income | 6,203 | 5.1% | 6,300 | 5.1% | +1.6% |
Ordinary Income | 5,917 | 4.9% | 6,100 | 4.9% | +3.1% |
Net Income | 4,164 | 3.4% | 4,400 | 3.5% | +5.7% |
*Unit: Million yen. The forecast was those released by the company.
Sales and profits are estimated to rise
Sales are estimated to be 124 billion yen, up 2.5% year on year. In Japan, it is estimated that there will be recoil from the rush demand before the consumption tax hike in the previous year, but overseas sales are projected to increase mainly in North America, and overall sales are forecasted to rise. Operating income is estimated to be 6.3 billion yen, up 1.6% year on year. The decline due to the augmentation of SG&A expenses and the yen appreciation against the dollar will be offset by the increase in sales volume, the improvement in cost ratio, etc. The assumed exchange rates are 1 U.S. dollar = 107 Japanese yen (109 Japanese yen in the previous term) and 1 euro = 118 Japanese yen (123 Japanese yen in the previous term).
The dividend is to be 35 yen/share, unchanged from the previous term. The estimated payout ratio is 33.0%.
4. Medium-term Management Plan 2022
The review of the Mid-term Management Plan 2019, which ended in the previous term, and the policies and intensive measures set in the Mid-term Management Plan 2022, which will start this term, are as follows.
(1) Review of the Mid-term Management Plan 2019
Sales exceeded 120 billion yen, indicating that the company has grown sustainably, but neither sales nor profit reached the performance goal due to the change in the external environment, and the delays in various measures of the comany, etc.
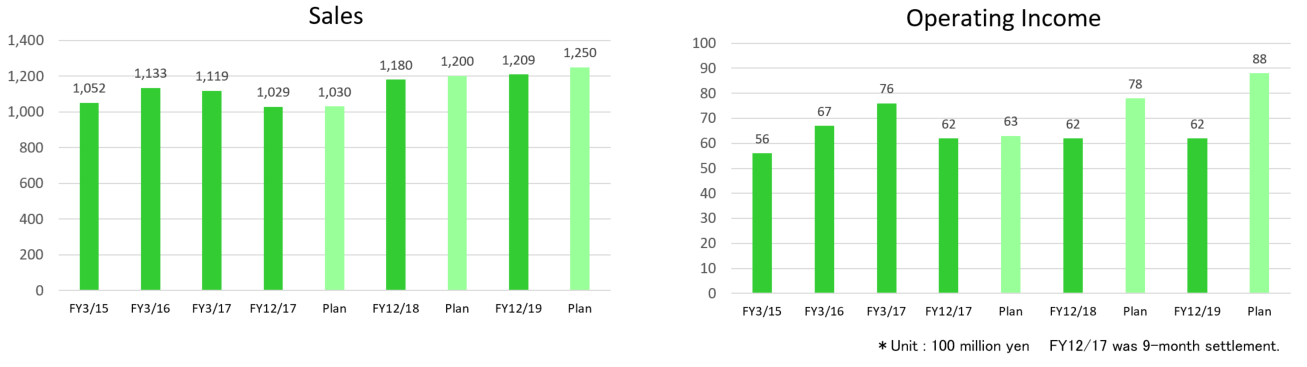
One of the reasons why the results were below the performance goal is that the company failed to reduce costs as planned due to the skyrocketing materials and labor cost caused by the yen appreciation and the trade dispute between the U.S. and China.
The results and overview of each business segment are as follows.
Segment | Results and overview |
Outdoor power equipment | (Japan) Sales were on a plateau.
(Overseas) In North America, the company achieved self-susutaining growth, increasing sales. In Europe, the distribution stock augmented. |
Agricultural machinery | (Japan) The sales of labor-saving products, such as sloop mowers grew.
(Overseas) The sales in China nosedived. The sales in the U.S. were sluggish, due to the downturn of commodity (grain) prices. |
Industrial machinery | (Japan) Sales exceeded the estimate, as the company met national policies and special demand. |
(2) Policies and intensive measures set in the Mid-term Management Plan 2022
① Basic policy
The basic policy set in the previous Mid-term Management Plan will be continued.
We will contribute to the development of society with our strong management foundation and sustainable growth, giving happiness to everyone connected to Yamabiko. |
|
We will enhance our corporate value by creating innovative products and expanding manufacturing, sales, and services globally, while also adapting to the diverse set of values of everyone connected to Yamabiko. |
② Goals and strategies in each segment
As to the major market environment, the demand for engine products is expected to remain strong in the professional market for outdoor power equipment where long-lasting products that can tolerate heavy loads are demanded, the company will shift to the professional market further.
As for agricultural machinery and industrial machinery, the Japanese agricultural and construction industries are seeing the shortage of manpower and the aging of workers, so labor-saving and energy-saving products are in demand.
◎Outdoor power equipment business
The priority measures are (1) to develop engine products ahead of the strict environmental regulations, (2) to monetize the robot business, and (3) to augment the lineup of DC products.
*Efforts to each region
Market | Target sales | Policy |
North America | 61.7 billion yen (+16.7%) | Expansion of product sales for professionals and promotion of digital marketing activities To maximize sales through various measures |
Europe | 9.8 billion yen (+19.2%) | |
Japan | 14.5 billion yen (+6.5%) | To engage in expansion of product sales based on the large market share and utilizing the robust sales network |
*The parenthesis represents the growth rate from the term ended Dec. 2019.
(North America)
The company will enhance marketing strategies targeted at professionals, strive to grow sustainably, expand its presence in the market of engine products, and aim to expand its market share, which has been increasing steadily.
As priority measures, the company will augment the lineup of “X Series,” which is a highly functional product lineup for professionals and continue to enhance digital marketing activities. The company will strive to enhance its brand recognition, by diffusing professionals’ comments on the latest products via social media, optimizing marketing activities for each generation, and posting ads in baseball (MiLB) and football (MSL), which attract users.
At The Home Depot, which is the primary sales route, the company will concentrate on the sale of flagship products, expand sales area, and continue effective sales promotion for a limited period of time.
In addition, the company will put energy into the cultivation of the U.S. market for robot products.
(Europe)
The company will promote the sales of products –conforming to the needs of the market and enhance its brand recognition level.
As priority measures, the company will promote the sales of “X Series,” which is the lineup for professionals, and augment enrich the lineups of battery products and engine products that comply with regulations on emissions, promote the sales of robot products, cultivate the relative market, and enhance the market recognition through digital marketing activities, etc.
In order to improve the performance of robot products further, the company will reorganize Quimesis S.R.L. into an equity-method affiliate (capital contribution rati 24.9%) and proceed with software development.
(Japan)
As priority measures, the company will launch top handle chain saws as a new DC product, continue effective campaigns, promote the launch of labor-saving, efficient products (robotic mowers), and enhance the sales via home centers.
◎Agricultural machinery business
Market | Target sales | Policy |
Japan | 16.2 billion yen (+4.0%) | To actualize monetization and adapt to smart agriculture |
*The parenthesis represents the growth rate from the term ended December 2019.
In detail, the company will reduce production costs and improve profitability through close collaboration between the development, manufacturing, and sales department, and expand sales routes, continue effective sales campaigns, and adapt to smart agriculture, etc.
◎Industrial machinery business
Market | Target sales | Measures |
Japan | 13.7 billion yen (-9.9%) | To expand shares in Japanese and North American markets and improve profitability, in a compatible way. To launch new products and improve production efficiency |
Overseas | 5.4 billion yen (+59.7%) |
*The parenthesis represents the growth rate from the term ended December 2019.
(Japan)
As there is the initiative of investment in infrastructure for preventing and mitigating natural disasters and promoting national resilience, the company will continue effective sales campaigns and enhance the sale to rental companies, so as to meet the increased demand adequately.
(Overseas)
The company will develop a market on a full scale targeting at wide-area rental companies in North America, promote sales of welders targeted at resource markets in Russia, and build new sales networks in Asia and Africa.
③ Intensive measures
◎Total cost reduction and product quality improvement
The company will keep improving production efficiency for further cost reduction.
The company will aim to establish a new production system for shortening manufacturing lead time and reducing inventory of products and also improve quality control continuously for actualizing “absolute quality.”
◎Strengthening of service capabilities
The company will strive to enhance its service capabilities, which would lead to the improvement in profitability.
The company will concentrate on the augmentation and expansion of sales of highly profitable service parts and accessories, the enrichment of service materials for each product, the strengthening of training systems, the reduction of total logistics costs, the decrease of inventory, etc.
④ Capital investment, R&D costs, and depreciation
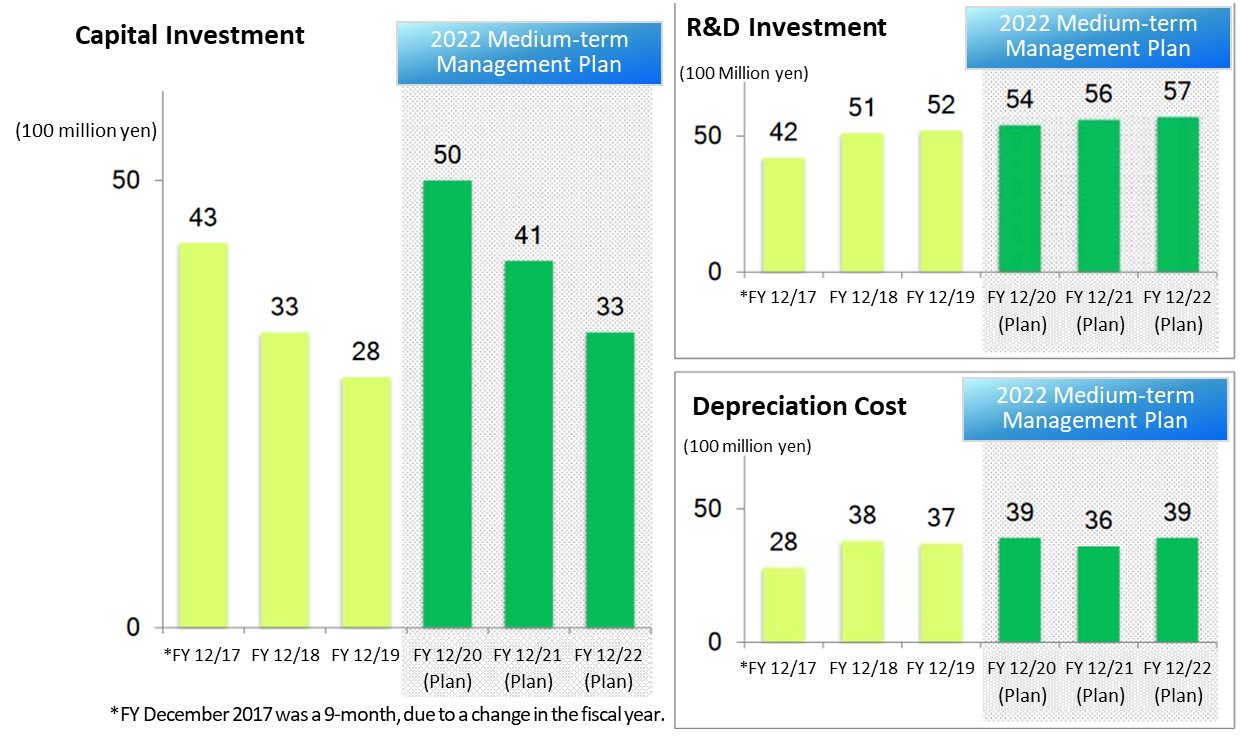
Capital investment is estimated to be 12.4 billion yen, exceeding the total amount in the previous Mid-term Management Plan: 10.4 billion yen.
⑤ Numerical goals
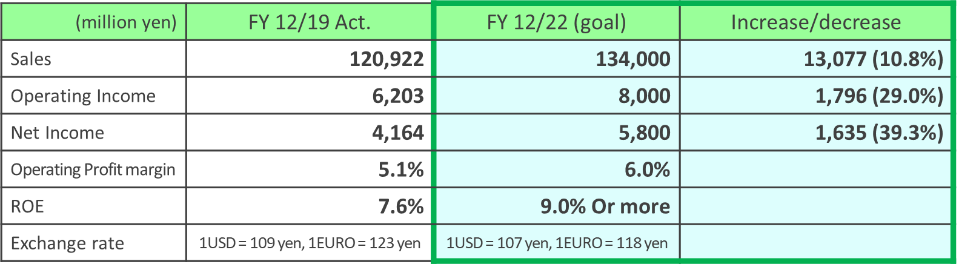
The company aims to achieve “sales of 134 billion yen and an operating income of 8 billion yen” in the term ending December 2022.
(Source: the company)
(Source: the company)
5. Conclusions
The company announced a new Mid-term Management Plan. Based on the premise of the yen appreciation, they plan to increase sales by 10.8% and CAGR by 3.5% from the term ended December 2019.
The largest driver is outdoor power equipment. Its performance in the U.S. market, where domestic demand is strong, is especially the key. By releasing highly functional products, etc., the company aims to expand its business and share in the professional market. In Japan, the sales of industrial machinery increased significantly in the previous term, but are estimated to decline, so it is forecasted that total sales will be on a plateau, but outdoor power equipment will perform well.
The external environment has uncertainties due to Covid-19, etc., but we would like to pay attention to the progress of measures for achieving the plan in each segment inside and outside Japan.
| FY 12/19 | FY 12/20 | FY 12/22 | Increase/decrease |
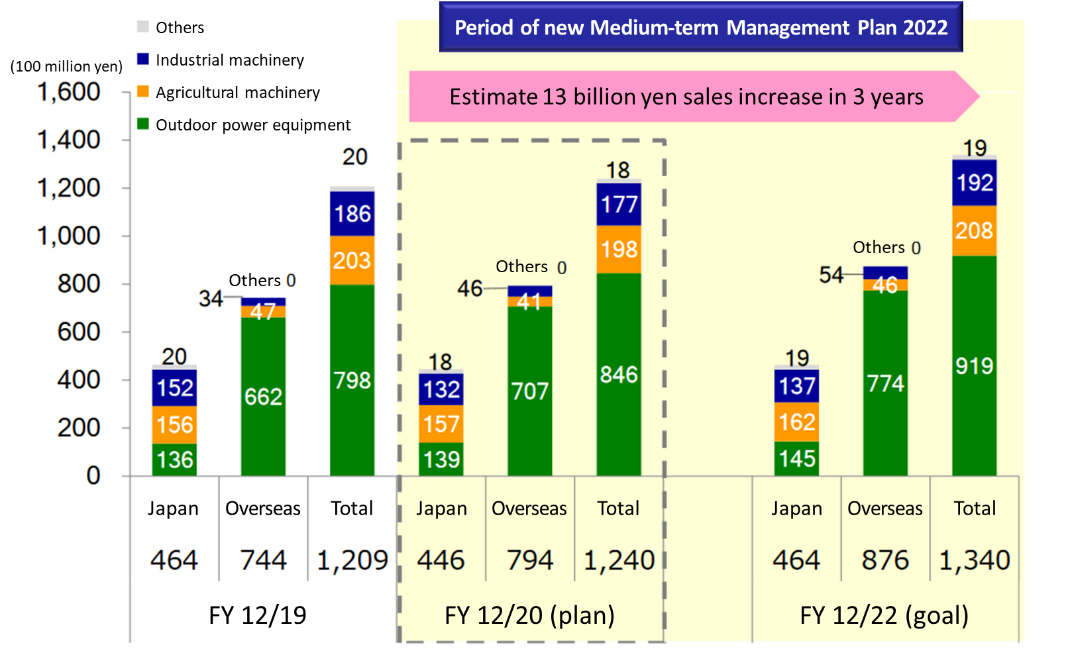
Sales | 1,209 | 1,240 | 1,340 | +10.8% |
Outdoor power equipment | 798 | 846 | 919 | +15.2% |
Agricultural machinery | 203 | 198 | 208 | +2.5% |
Industrial machinery | 186 | 177 | 192 | +3.2% |
Others | 20 | 18 | 19 | -5.0% |
Japan | 464 | 446 | 464 | 0.0% |
Outdoor power equipment | 136 | 139 | 145 | +6.6% |
Agricultural machinery | 156 | 157 | 162 | +3.8% |
Industrial machinery | 152 | 132 | 137 | -9.9% |
Others | 20 | 18 | 19 | -5.0% |
Overseas | 744 | 794 | 876 | +17.7% |
Outdoor power equipment | 662 | 707 | 774 | +16.9% |
Agricultural machinery | 47 | 41 | 46 | -2.1% |
Industrial machinery | 34 | 46 | 54 | +58.8% |
Others | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
*Unit: million yen. For FY 12/20, the forecast for this term is shown. For FY 12/22, target values are shown. Increase/decrease rate refers to the increase/decrease rate from FY 12/19.
<Reference:Concerning corporate governance>
*Composition of the organizational structure, directors and auditors
Organizational structure | Company with Audit and Supervisory Board |
Directors | 7 (including 2 outside director) |
Auditors | 4 (including 2 outside auditors) |
◎Corporate Governance Report
Last update date: March 30,2020
<Basic policy>
YAMABIKO CORPORATION (“the company”) actively promotes various measures to enhance the corporate value of the entire Group, including an optimization strategy and supervision function at the Group level, as well as the allocation of resources in order to achieve the Group’s global management strategy and growth.
To realize these objectives, the company implements sound and highly transparent Group management in order to deliver value to all of its stakeholders, including regional companies, shareholders, customers and employees. We do this by building a robust corporate culture based on our Corporate Philosophy and Code of Conduct, while enhancing and strengthening a system of corporate governance focused on Group compliance and risk management.
Our board of directors is composed of 7 directors, including 2 outside ones, and makes important decisions regarding our group’s management policy and strategy, and the guidance and supervision for business administration of group companies. In the board of directors, directors monitor and oversee the work of other directors and report their own performance regularly at their meetings. In order to put resolutions of the board of directors into action accurately and swiftly, the management strategy council deliberates them to a sufficient degree.
Our company adopted the auditor system, organizing the board of auditors with a total of 4 auditors, composed of 2 corporate auditors and 2 outside ones.
Auditors participate in the meetings of the board of directors, the management strategy council, and operating officers, and other important in-house meetings, to audit the business execution of directors, and secure the effectiveness of audit in cooperation with accounting auditor and the internal audit section, in accordance with the regulations for the board of auditors and the standards for auditors’ audit.
<Reasons for Non-Compliance with the Principles of the Corporate Governance Code (Excerpts)>
Principle | Reasons for not following the principle |
【Supplementary Principle 1-2. (4) Electronic exercise of voting rights, English translation of convocation notices, etc.】 | As of the end of December 2019, the ratio of overseas investors for our company is as low as about 16%. Accordingly, we have not yet adopted the electronic exercise of voting rights. As we recognize that it is necessary to offer an environment in which institutional investors and overseas investors can exercise their voting rights easily, we will think of adopting the platform for the electronic exercise of voting rights when the ratio of overseas investors exceeds a certain value (e.g. 30%). As for the English translation of convocation notices, we started producing the English version, excluding business reports and notes, and uploading it to our website. |
【Supplementary principle 4-11-1. Balance, diversity, and size of the board of directors as a whole】 | Our company’s Article of Incorporation stipulates that the Board of Directors shall be composed of 10 members of fewer, and our Board of Directors currently consists of 7 directors, which we believe is a proper size that enables swift decision-making. The members of the Board of Directors are 5 internal directors, including 3 people who are familiar with each of the businesses that our company conducts and have extensive experience in working abroad, and 2 outside directors, including 1 person with experience in working as a top management and 1 person who have abundant knowledge and practical experiences as a lawyer. We believe that managerial issues and challenges are proactively discussed from multilateral perspectives and proper judgments are made at meetings of the Board of Directors. We consider designation and securing of diverse human resources as directors, including women, to be our company’s future challenges. Please refer to the description for Principle 3-1. (4) regarding the policies and procedures for nominating directors. |
<Disclosure Based on the Principles of the Corporate Governance Code (Excerpts)>
Principles | Disclosure contents |
[Principle 1-4 the strategically held shares] | (1) Policy Regarding Strategic Shareholding Our company conducts business in landscaping, agriculture, construction and civil engineering, and a variety of other fields inside and outside Japan. Therefore, it is required for our company to cooperate with a number of firms involved in each of our businesses. We will strategically hold shares when we have judged that doing so will contribute to improving our corporate value in the medium- and long-term. Meanwhile, when we have determined that the significance of strategically holding shares is not sufficient, we will have dialogue with a relevant company, and then sell or reduce all or part of the strategically held shares by comprehensively taking into account various factors, such as the impact on the market. Each year, regarding the strategically held shares of each listed company, our Board of Directors carefully verifies a multitude of matters, including the purposes of strategically holding the shares, such as maintenance and strengthening of partnerships, and economic rationality, and then determines whether or not our company will continue holding the shares and reviews the number of shares to hold strategically. After the adoption of the Corporate Governance Code in 2015, our company reduced the number of corporations whose shares we have held from 25 to 18. (2) Criteria for Exercising a Voting Right in Regard to Strategic Shareholding Our company properly exercises our voting rights on the strategically held shares after making comprehensive judgment by taking into consideration not only business performance, but also whether or not strategically holding shares will contribute to properly strengthening the corporate governance framework and improving shareholder value, and the impact on our company. Furthermore, we hold dialogue with a relevant company as necessary regarding the contents of a proposal. |
[Principle 5-1 Policies Regarding Constructive Dialogue with Shareholders] | Our company has implemented the following measures as policies for maintaining a framework and making efforts to promote constructive dialogue with shareholders. (1) Our company has established the investor relations section within the administration division, as a section in charge of communicating with shareholders. In principle, the division officer will conduct overall management of all matters concerning the shareholders. (2) Relevant internal departments that assist in dialogue with the corporate planning department and the finance & accounting department conduct their duties while actively collaborating with them to create constructive dialogue, for example, by producing and reviewing materials to be disclosed and sharing necessary information. (3) As a means of dialogue other than individual meeting with shareholders and investors, we regularly hold briefings for financial highlights and plant tours for institutional investors, and distribute booklets summarizing our company’s topics and business performance to shareholders. Furthermore, we use feedback and requests from shareholders and investors to improve the content of our website. We plan to improve our news releases page in the future. (4) For information sharing, we give the thoughts of shareholders understood in dialogue to directors and relevant departments as feedback via the distribution of reviews and reports in a meeting body. (5) Our company has set up the Insider Trading Management Regulation to prevent insider trading and thoroughly manage information on insider trading such as promoting the understanding and awareness within our company by posting articles on insider trading at new employee training program and in our company’s internal bulletin. |
This report is intended solely for information purposes, and is not intended as a solicitation to invest in the shares of this company. The information and opinions contained within this report are based on data made publicly available by the company, and comes from sources that we judge to be reliable. However, we cannot guarantee the accuracy or completeness of the data. This report is not a guarantee of the accuracy, completeness or validity of said information and or opinions, nor do we bear any responsibility for the same. All rights pertaining to this report belong to Investment Bridge Co., Ltd., which may change the contents thereof at any time without prior notice. All investment decisions are the responsibility of the individual and should be made only after proper consideration. Copyright(C) 2020 Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. |
The back issues of the Bridge Report (YAMABICO: 6250) and the contents of the Bridge Salon (IR Seminar) can be found at : www.bridge-salon.jp/


