Bridge Report: (6722) A&T
 President Shigetaka Misaka | A&T Corporation (6722) |
 |
Company Information
Market | JASDAQ |
Industry | Electrical equipment (manufacturing industry) |
President | Shigetaka Misaka |
HQ Address | Yokohama Plaza Bldg. 2-6 Kinko-cho, Kanagawa-ku, Yokohama-shi |
Year-end | December |
Homepage |
Stock Information
Share Price | Number of shares issued | Total market cap | ROE(Actual) | Trading Unit | |
¥926 | 6,257,900 shares | ¥5,794 million | 7.4% | 100 shares | |
DPS (Est.) | Dividend yield (Est.) | EPS (Est.) | PER (Est.) | BPS (Actual) | PBR (Actual) |
¥24.00 | 2.6% | ¥115.07 | 8.0 x | ¥1,147.47 | 0.8 x |
*The share price is the closing price on February 22, 2019.
The number of shares issued and BPS are as of the end of second quarter. ROE is from previous term.
Earnings Trends
Fiscal Year | Net Sales | Operating Income | Ordinary Income | Net Income | EPS | DPS(¥) |
Dec. 2011 (Actual) | 8,485 | 823 | 803 | 477 | 76.34 | 12.00 |
Dec. 2012 (Actual) | 8,663 | 757 | 738 | 484 | 77.51 | 12.00 |
Dec. 2013 (Actual) | 9,221 | 742 | 716 | 471 | 75.29 | 16.00 |
Dec. 2014 (Actual) | 9,569 | 856 | 832 | 455 | 72.80 | 16.00 |
Dec. 2015 (Actual) | 10,138 | 1,202 | 1,183 | 839 | 134.18 | 20.00 |
Dec. 2016 (Actual) | 10,234 | 1,015 | 1,004 | 651 | 104.14 | 20.00 |
Dec. 2017 (Actual) | 10,371 | 773 | 757 | 678 | 108.41 | 20.00 |
Dec. 2018 (Actual) | 10,430 | 774 | 768 | 518 | 82.80 | 24.00 |
Dec. 2019 (Forecast) | 11,200 | 1,010 | 1,000 | 720 | 115.07 | 24.00 |
*Forecasts are those of the Company. Unit: ¥mn
This report outlines A&T Corporation, briefly reports the results for the Fiscal Year ended December 2018, the medium-term management plan, and so on.
Table of Contents
Key Points
1. Company Overview
2. Fiscal Year December 2018 Earnings Results
3. Fiscal Year December 2019 Earnings Forecasts
4. Medium-Term Management Plan (FY Dec. 2018-FY Dec. 2020) and Progress
5. Interview with President Misaka
6. Conclusions
<Reference1: Outline of Medium-Term Management Plan>
<Reference2: Regarding corporate governance>
Key Points
- Sales for the term ended Dec. 2018 were 10,430 million yen, up 0.6% year on year. Although sales of expendable sensors and purchased products decreased, sales of clinical testing equipment and systems were healthy, which led to increased profits. Sales to China doubled. Operating income increased 0.1% year on year to 774 million yen. While gross profit decreased due to an increase in the launching cost caused by the release of the new products for laboratory information system, SG&A expenses decreased 1.5% year on year mainly in association with expenses for subcontracting development work for the new products. Although profit did not achieve the target, sales were almost as forecasted. Overseas sales ratio that the company emphasizes for growth increased in direct and real terms to 12.2% (+ 2.9 points) and 28.2% (+ 0.7 points), respectively.
- The sales for the term ending Dec. 2019 are expected to increase 7.4% year on year to 11.2 billion yen. The number of large-scale projects for clinical testing equipment and systems will increase. Sales of original products will also grow. Gross profit will also increase 7.3% year on year due to reduction of man-hours on new products for the laboratory information system and reduction of purchased products. Operating income is estimated to increase 30.4% year on year to 1,010 million yen. SG&A expenses will also increase 2.4% year on year due to an increase in employees for sustainable growth and new product development expenses for the laboratory automation system, but it will be offset by an increase in gross profit. The dividend is estimated to be 24 yen per share, unchanged from the previous year. The estimated payout ratio is 20.9%.
- Year-on-year growth rate was small for the term ended Dec. 2018, but the company seems to have good results including expansion of sales of original products and growth of businesses in China. Sales in China, which doubled from 351 million yen to 780 million yen, will be disclosed semi-annually in the coming years, allowing investors to watch important indicators to judge the company. Looking at the final year of the medium-term management plan, which is the term ending Dec. 2020, positive signs for achieving sales targets, such as business growth in China and alliance with ARKRAY, have been seen. We will pay attention to efforts and progress, including changes in sales of original products, to achieve an ordinary income rate of over 10%.
1. Company Overview
The core businesses of A&T Corporation are the “blood testing business,” in which the company develops, manufactures, and sells IVD devices, reagents, etc. mainly for electrolyte and glucose tests, and the “IT and automation support business,” which facilitates the streamlining of clinical tests.
The company excels at proposing an optimal one-stop solution for preparing necessary products in a laboratory, installing and operating equipment while proposing a layout, and possesses advanced technologies that are highly evaluated by leading overseas OEM clients.
1-1 Corporate History
In the 1980s, the general chemical manufacturer Tokuyama Corporation (4043, 1st section of Tokyo Stock Exchange) was expanding its business scope from materials to fine chemicals. While taking inventory of various technologies and items, Tokuyama Corporation decided to develop latex (rubber material; one of the chemical products) reagents for testing antigen-antibody reactions.
In the development process, Tokuyama Corporation formed a business tie-up with Analytical Instruments Inc., which develops, manufactures, and sells clinical test equipment and had been leading the industry by releasing such products as fully automatic blood sugar analyzer in 1978, and in Apr. 1988, they founded a joint venture for distributing their products, A&T Corporation. (“A” of Analytical Instruments and “T” of Tokuyama were combined.)
In November 1990, the company established Esashi Factory, which is now the primary production site, in Iwate Prefecture.
In 1994, A&T Corporation underwent an absorption-type merger, integrating the diagnosis system division of Tokuyama Corporation. The period from the 1980s to the 1990s was the growth period of the clinical testing industry, in which many core technologies were developed, and the company expanded its business steadily while taking advantage of that trend.
In Jul. 2003, the company issued over-the-counter shares. It is now listed in the JASDAQ market of Tokyo Stock Exchange.
1-2 Corporate Philosophy, etc.
A&T Corporation upholds its corporate ethos: “Support medical care and contribute to people’s health around the world,” and aims to improve the quality of medical care and reduce cost, under following three management policies.
1. C.A.C.L. | Commit to research and development of unique products and technologies in all areas’ of “C.A.C.L.” in clinical laboratory testing. |
2.Consistent Framework | Increase market value and reduce the cost of products through an integrated system of development, manufacture, distribution and customer support. |
3.Alliance | Promote market expansion and quality improvement of products with business partners domestic and overseas. |
* C.A.C.L.: Acronym of “Chemicals (diagnostic reagents),” “Analyzers (Analyzers),” “Computers (laboratory information system),” and “Lab-Logistics (laboratory automation system)” in the field of products required for operating a clinical test room
1-3 Market environment
1-3-1 Market scale
(Domestic and global markets)
Based on the information in the website of the Japan Association of Clinical Reagents Industries, A&T Corporation estimated that the scale of the Japanese market of related devices and reagents is about 590 billion yen. The market scales of biochemical tests and hematology tests are 195.8 billion yen and 30.6 billion yen, respectively.
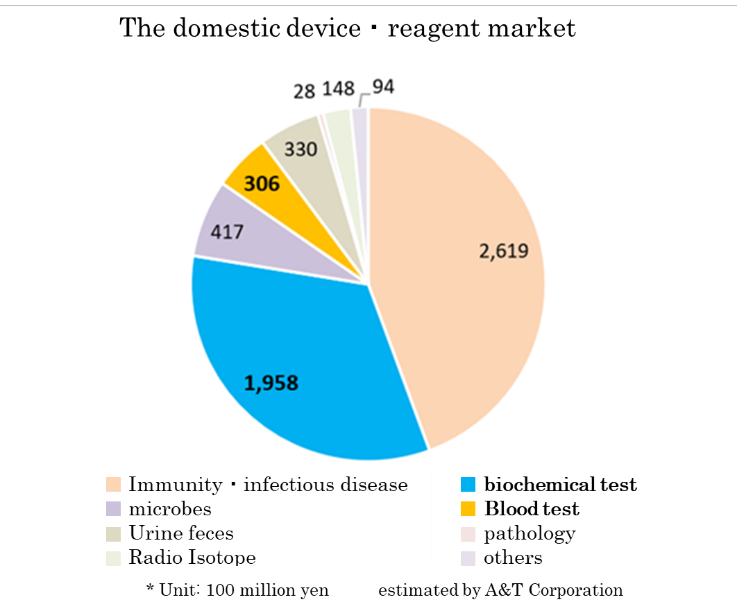
(Trend of IVD devices)
According to “Statistical Survey on Trends in Pharmaceutical Production” by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, the scale of the Japanese medical products market (domestic production amount) in 2015 was about 1.9 trillion yen. Products for medical treatment is dominant, and medical Analyzers, which is handled by A&T Corporation, has a market scale of about 180 billion yen.
While there is a significant excess of imports of the overall medical product, there is an excess of exports of IVD devices. This indicates how competitive Japanese companies are. Hitachi and Canon Medical Systems (former Toshiba) supply testing equipment to Roche in Switzerland and Abbott in the U.S., respectively. Likewise, A&T Corporation supplies OEM products to Siemens. Namely, testing equipment made in Japan is now indispensable in the global clinical testing field.
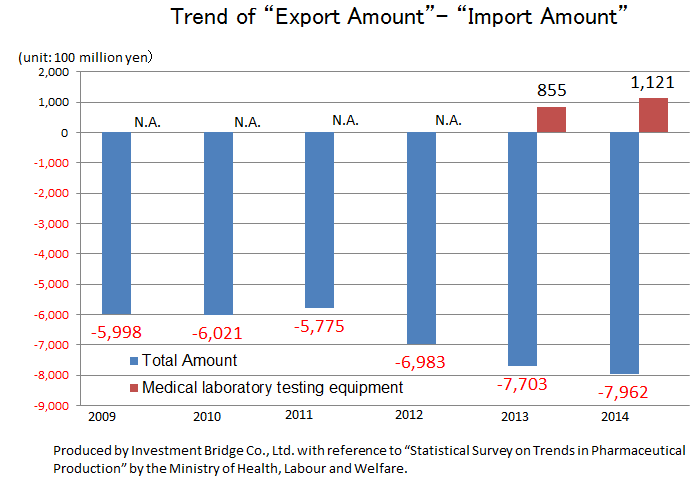
| 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 |
Total amount |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Production | 15,760 | 17,130 | 18,080 | 18,950 | 19,050 | 19,890 | 19,450 |
Import | 10,740 | 10,550 | 10,580 | 11,880 | 13,000 | 13,680 | 14,240 |
Export | 4,750 | 4,530 | 4,800 | 4,900 | 5,300 | 5,720 | 6,220 |
Export - Import | -5,998 | -6,021 | -5,775 | -6,983 | -7,703 | -7,962 | -8,023 |
IVD devices |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Production | 1,100 | 1,030 | 1,450 | 1,580 | 1,470 | 1,690 | 1,800 |
Import | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | 210 | 200 | N.A. |
Export | 750 | 620 | 980 | 1,100 | 1,060 | 1,320 | 1,420 |
Export - Import | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | +855 | +1,121 | N.A. |
*Unit: 100 million yen. The import amounts of medical Analyzers from 2009 to 2012 and 2015 are N.A., because they were not in the top 10.
1-3-2 Companies in the same field
Code | Corporate name | Sales | Sales growth rate | Operating income | Profit growth rate | Operating income margin | ROE | Market cap | PER | PBR |
4549 | Eiken Chemical | 36,760 | +5.1 | 4,200 | +20.7 | 11.4% | 8.3 | 111,640 | 31.1 | 2.7 |
6678 | Techno Medica | 9,300 | +7.5 | 1,400 | -6.1 | 15.1% | 10.4 | 18,071 | 19.7 | 1.4 |
6722 | A&T | 11,200 | +7.4 | 1,010 | +6.0 | 9.0% | 7.4 | 5,794 | 8.0 | 0.8 |
6869 | Sysmex | 300,000 | +6.4 | 59,000 | -0.1 | 19.7% | 17.4 | 1,422,798 | 35.9 | 5.9 |
6951 | JEOL | 110,000 | +5.2 | 5,200 | +32.4 | 4.7% | 13.0 | 90,386 | 22.3 | 2.4 |
8036 | Hitachi High-Technologies | 750,000 | +9.1 | 63,000 | +13.5 | 8.4% | 10.9 | 591,587 | 13.1 | 1.5 |
*The results for this term were forecasted by the company. The units are million yen, %, and times. Share price-related indices are based on the closing prices on February 22,2019.
* Sysmex, Hitachi High-Technologies adopted IFRS. Hitachi High-Technologies' operating income is "adjusted operating income" which is calculated by subtracting the cost of sales and selling, general and administrative expenses from sales revenue.
We compared major listed clinical testing device manufacturers. A&T Corporation has the smallest business scale among them and the share price evaluation is the lowest as its price-to-book ratio is under one. It would be necessary to manifest its strategies to enhance popularity and expand business as well as promoting understanding.
1-4 Business Description
In addition to the development, manufacturing, and sale of products, including testing devices and reagents used in the clinical testing rooms of hospitals, A&T Corporation offers customer support. The company also offers comprehensive consulting services, including the proposal for the layout of a laboratory, installation and operation.
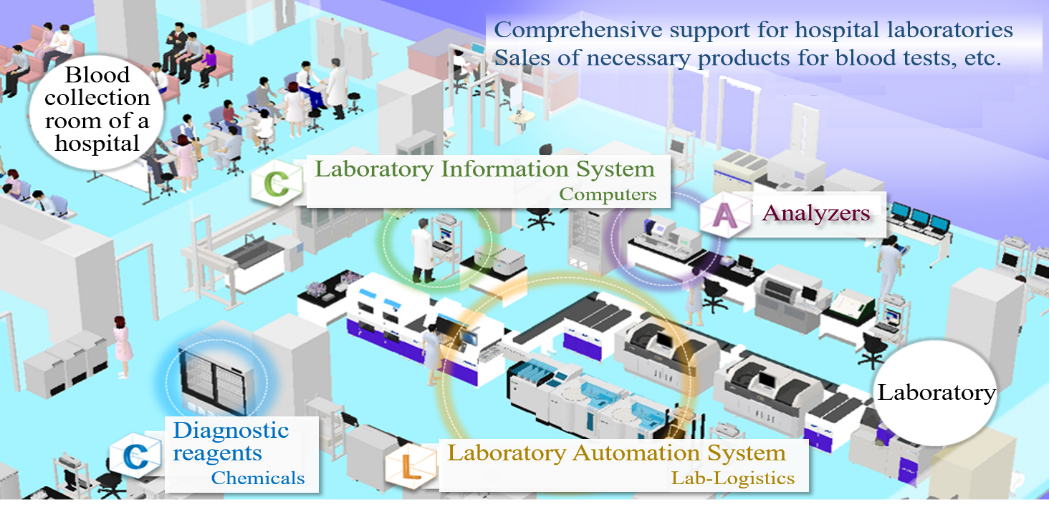
(Source: The company)
What is clinical testing?
Clinical tests can be classified into “biopsies” for directly examining the body with medical equipment, such as X-ray equipment, CT, MRI, electrocardiographic and ultrasonic equipment, and “laboratory tests” for examining biological samples (specimens), such as blood, urine, stool, and cells, collected from patients.
A&T Corporation handles products used for laboratory testing, especially blood tests.
There are a variety of blood tests conducted at hospitals and in comprehensive medical checkups, including the tests of the hepatic system, the renal system, uric acid, the lipid system, glucose metabolism, blood cells, and infectious diseases. A&T Corporation mainly conducts business related to “electrolyte tests” and “glucose tests.”
“Electrolyte tests”
The water content constitutes about 60% of the human body, as body fluids, including intracellular fluid and blood plasma. Body fluids are classified into electrolytes, which are mineral ions that dissolve in water and conduct electricity (such as sodium, potassium, calcium, and chlorine), and non-electrolytes, which dissolve in water, but do not conduct electricity (such as glucose and urea).
Each electrolyte takes important roles for keeping human beings alive while maintaining a healthy balance - “sodium” adjusts the water content of the body, “potassium” controls muscles and nerves, “calcium” forms bones and teeth, conveys nervous stimuli, and coagulates blood, and “chlorine” supplies oxygen to the inside of the body. If the concentration of electrolytes in blood is abnormal, there is a possibility that the kidneys or hormones are malfunctioning.
The purpose of electrolyte tests is to measure the concentration of each electrolyte ion in body fluid, detect the disruption of a balance, and then diagnose a disorder in the body. Sampled blood and urine are examined with testing device.
*Major diseases
Sodium | Diabetic coma, dehydration, acute nephritis, chronic renal failure, nephrotic syndrome, heart failure, hypothyroidism, Addison disease, diabetic acidosis, etc. |
Potassium | Acute renal failure, chronic renal failure, respiratory insufficiency syndrome, etc. |
Calcium | Malignant tumor, multiple myeloma, hyperparathyroidism, renal failure, hypoparathyroidism, vitamin D deficiency, etc. |
Chlorine | Dehydration, renal failure, chronic nephritis, emphysema, etc. |
“Glucose tests”
The sugar in blood plasma (blood sugar) is composed mostly of glucose, which is the only energy source for the central nervous system, including the cerebrum. When the stomach is empty (over 5 hours after eating), the liver emits about 8 grams of glucose per hour, and the brain consumes about half of them, and muscles and red blood cells consume one fourth of them, respectively.
Blood sugar level in its normal condition is strictly controlled while keeping a balance between the increase through the absorption from the intestine and the generation in the liver and the decrease through the consumption in the muscles. If this control does not work properly, hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia will occur.
A glucose test is conducted for measuring the concentration of glucose in blood or urine.
*Major diseases
Hyperglycemia | Diabetes (insulin, which is a hormone secreted from the pancreas, does not work, and so cells cannot use glucose in blood), pancreatitis, thyroid disease, postgastrectomy dumping syndrome, etc. |
Hypoglycemia | Liver damage, hypopituitarism, adrenal hypofunction, etc. |
1-4-1 Business Field
The business of A&T Corporation is composed of the “blood testing business,” in which the company develops, manufactures, and sells clinical testing devices, reagents, supplies, etc. for blood tests, and the “IT and automation support business,” which facilitates the streamlining of manual work in hospital laboratories with IT and automated systems. The company comprehensively supports hospital laboratories.
(Since this company conducts this business only, neither its brief financial reports nor securities reports contain segment information. It should be noted that the company discloses the sales of each product series in reference materials for briefing results, etc., but not the sales of each type of business.)
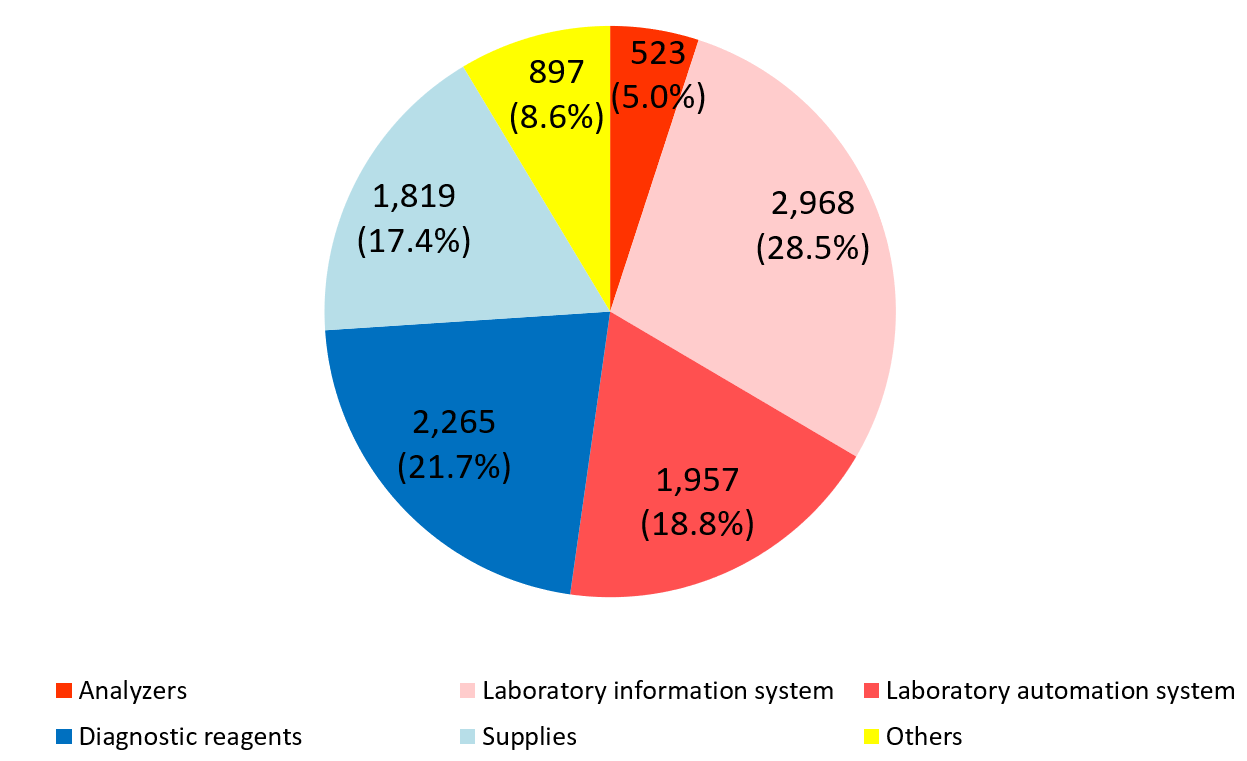
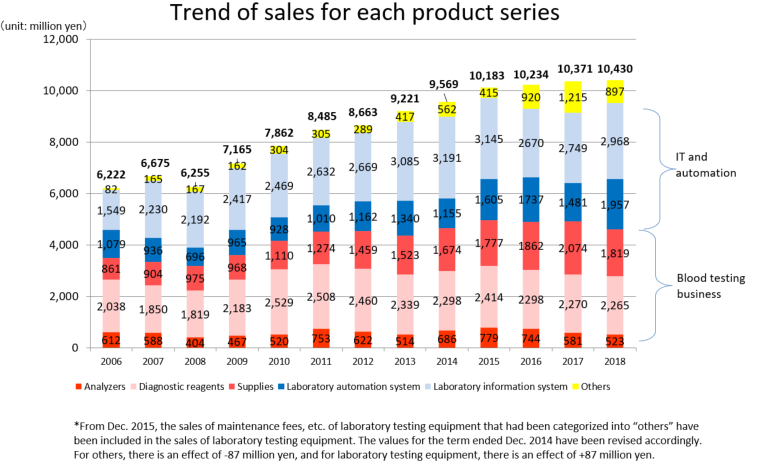
Product series | Results for FY Dec.18 | Ratio to total sales |
Clinical testing devices and systems | 5,448 | 52.2% |
Analyzers | 523 | 5.0% |
Laboratory information system | 2,968 | 28.5% |
Laboratory automation system | 1,957 | 18.8% |
Diagnostic reagents | 2,265 | 21.7% |
Supplies | 1,819 | 17.4% |
Others | 897 | 8.6% |
Total | 10,430 | 100.0% |
The red letters denote the “Blood testing business” (analyzers, diagnostic reagents, and supplies), while the blue letters denote the “IT and automation support business” (Laboratory Information System, Laboratory Automation System). The sales distribution ratio for the term ended December 2018 was 44.2% for the blood testing business, and 55.8% for the IT and automation support business.
1) Blood testing business
Outline
The company works on developing, manufacturing, and selling Analyzers for clinical tests such as “electrolyte tests” and “glucose tests,” reagents for clinical tests (for measuring the concentrations of electrolytes, blood sugar, etc.), and supplies (such as sensors installed in analyzer), and offers customer support.
(Source: A&T’s website)
Commercial distribution
*Inside Japan
The company directly sells analyzers, reagents, and supplies to small and medium-sized hospitals via 8 branches nationwide. As of now, about 4,300 units of equipment are in operation.
*Outside Japan
The company sells analyzers as an OEM. It supplies electrolyte units, which are the specialty products of the company, to other Japanese manufacturers, including JEOL (6951, 1st section of TSE). The OEM clients combine the unit with large-size clinical chemistry analyzers and sell them. As an OEM, JEOL supplies products to Siemens, which is one of global enterprises handling large-size clinical chemistry analyzers.
Business model
Once Analyzers is newly installed, clinical reagents and supplies will be continuously delivered, and the maintenance service for the equipment will be offered.
Once adopted, it is rare for client hospitals to change manufacturers considering the continuity of test data and usability, and so it is difficult for new manufacturers to enter the market. 7 to 10 years later, upgraded models will replace them. This characterizes this business field.
Major enterprises in this field
Sysmex (6869, 1st section of TSE), Hitachi High-Technologies (8036, 1st section of TSE), JEOL (6951, 1st section of TSE), Fuji Film Wako Pure Chemical (unlisted), ARKRAY (unlisted)
2) IT and automation support business
Outline
In the case of blood tests, it is necessary to convey patient’s blood (specimen) sampled in a blood collection room to a clinical laboratory and manually set the specimen at testing equipment.
As several kinds of tests need to be conducted for many specimens at the same time, this work is extremely labor-intensive and inefficient, and the human error of taking a wrong specimen is difficult to avoid.
In these circumstances, A&T Corporation supports the streamlining of the testing process with the following 2 systems.

(Source: A&T’s website)
Laboratory Information System (LIS) | Software for a clinical laboratory, which receives requests for tests from medical doctors, sends a command for testing to Analyzers, and inputs test results in electronic medical charts, etc. accurately and swiftly. This also manages cost, etc. and serves as a core system of a laboratory. |
Laboratory Automation System (LAS) | The specimens delivered to a laboratory are automatically conveyed to Analyzers via a computer-controlled conveyor line, and then undergo measurement. Blood tests, which had been manually conducted, are fully automated, to streamline and speed up the testing process. |
It is expected that the installation of LAS will decrease the necessary number of workers from 7-8 to about 2, and the necessary time of testing from 90 min. to 30-40 min.
Through the introduction of LIS, it became possible to put together the data of test results, which had been printed out for each test item, and give feedback to medical doctors swiftly and accurately. In addition, the data mining function is helpful for reducing the number of times of abnormal value retesting and the duration of testing.
Commercial distribution
*Inside Japan
Targeting the laboratories of medium and large-sized hospitals, the sales division of A&T Corporation sells LIS in cooperation with hospital information system manufacturers, including Hitachi, IBM, and Fujitsu, and LAS in cooperation with large-size clinical chemistry and immunoassay analyzer manufacturers, including Hitachi, Toshiba, and JEOL, as comprehensive solutions *.
*For the details of comprehensive solutions, see the section “1-5 Characteristics and Strengths.”
*Outside Japan
Previously, the company has been selling LAS directly in Korea, China, etc., but in China it has started OEM supply. In the United States, OEM sales of blood aliquoting modules, which are the main components in LAS, are made to partner companies.
Business model
In addition to the maintenance service of LIS and LAS after their installation, the company can connect additional systems, customize the system, and so on for LIS, and can offer maintenance services, sell supplies, and so on for LAS. For both of the systems, stable sales can be expected.
Like Analyzers, clients are rarely motivated to shift to other manufacturer’s equipment, considering usability, data continuity, etc. The price range per transaction is 10 to 50 million yen for LIS, and 10 to 100 million yen for LAS.
Major enterprises in this field
LIS: Sysmex CNA (subsidiary of Sysmex), local vendors, etc.
LAS: IDS (unlisted), Hitachi-Aloka (unlisted), Siemens, etc.
1-4-2 Development systems
The company established development groups by product types in order to apply elementary technologies cultivated over many years to a wide range of product development. In addition, it places a chief technology officer for each field including electricity, machinery, and chemistry and promotes product development through management of a matrix organization structure.
About 70 staff members are employed at the headquarters and Shonan Office.
The research and development cost for the term ended December 2018 was 958 million yen. It will continue to actively promoto reseach and development with a target sales of around 10%.
1-4-3 Production systems
There are two production sites: Shonan Factory, in Kanagawa Prefecture, for manufacturing some clinical reagents and supplies and Esashi Factory, in Iwate Prefecture, for producing equipment, Laboratory Automation System (LAS) and some clinical reagents.
The company manufactures high-quality, safe products with advanced equipment under rigorous management. In cooperation with the development section, the company is striving to improve quality and streamline operation.
In order to develop the foundation for expanding sales further, the company constructed a new building with a total floor area of 7,300 m2 at Esashi Factory by investing 1.7 billion yen in August 2017.The Company strengthens capabilities considerably through this construction.
1-4-4 Sales routes and methods
As mentioned above, A&T Corporation sells its products to client hospitals via 8 branches in Japan, by utilizing its capability of proposing comprehensive solutions.
Outside Japan, the company supplies products to overseas clients and dealers including Siemens through domestic OEM partners such as JEOL.
To expand its business scale by supplying products as an OEM like this is the basic strategy, and the company concentrates on the diversification of OEM clients.
The direct overseas sales to overseas clients and dealers and its ratio for the term ended December 2018 were about 1.3 billion yen and 12.2%, respectively.
But, as the ratio of virtual overseas sales, including the (estimated) overseas sales via domestic OEM clients, for the term ended Dec. 2015 for the term ended Dec. 2016, and for the term ended Dec. 2017 was 23.4%, 24.7%, 27.5% respectively, the ratio of overseas sales is in upward momentum.
Especially in the term ended Dec. 2018, sales to China soared to 780 million yen, more than doubled from 351 million yen in the previous fiscal year. With the future development of the Chinese market, the company aims for an the ratio of virtual overseas sales over 50% in the medium term.
(The ratio of overseas sales, unit: %)
| FY Dec.12 | FY Dec.13 | FY Dec.14 | FY Dec.15 | FY Dec.16 | FY Dec.17 | FY Dec.18 |
Direct | 3.3 | 5.7 | 6.9 | 5.9 | 7.4 | 9.3 | 12.2 |
Virtual | 21.8 | 23.4 | 24.0 | 23.4 | 24.7 | 27.5 | 28.2 |
1-5 Characteristics and strengths
1-5-1 Capability of proposing comprehensive solutions
A&T Corporation handles products mainly for electrolyte and glucose tests, and does not handle large products for analyzing other tests. However, client hospitals need to install a variety of testing instruments in their clinical laboratories.
To meet their needs, the Laboratory Automation System (LAS) has an automatic conveyor line that is compatible with not only its own products, but also other manufacturers’ instruments.
There are few manufacturers that possess technologies for producing systems for connecting their own products and other manufacturers’ products freely and conveying them. Accordingly, the company occupies about 30% of the Japanese market.
The sales staff of the company not only delivers equipment, but also proposes a layout for the most efficient testing with 3D CAD or the like, while considering the area and shape of a laboratory.
All above, the company can offer optimal one-stop solutions for preparing necessary products in a laboratory, installing and operating equipment while proposing a layout. This is highly evaluated by client hospitals.
1-5-2 Advanced technologies in specific fields
A&T Corporation handles products mainly for “electrolyte tests” and “glucose tests.” Especially, its advanced technology for electrolyte analyzers can be verified by the fact that its products are supplied to JEOL, which is a leading manufacturer of measurement devices, including medical instruments, and Siemens, which is a large global company.
As mentioned in the section of the market environment, Japanese medical Analyzers is highly competent in the world, and A&T Corporation contributes to the competitiveness of Japanese products.
1-6 ROE analysis
| FY Dec.12 | FY Dec.13 | FY Dec.14 | FY Dec.15 | FY Dec.16 | FY Dec.17 | FY Dec.18 |
ROE (%) | 12.2 | 10.7 | 9.5 | 15.7 | 10.9 | 10.4 | 7.4 |
Ratio of net income to sales [%] | 5.60 | 5.11 | 4.76 | 8.28 | 6.37 | 6.54 | 4.97 |
Total asset turnover ratio [times] | 1.02 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 1.04 | 1.03 | 0.92 | 0.84 |
Leverage [times] | 2.14 | 2.13 | 1.99 | 1.83 | 1.67 | 1.73 | 1.79 |
ROE for the term ended December 2018 was below 8%, mainly due to the recording of relocation costs of manufacturing facilities and losses on cancellation of service contracts as extraordinary losses. The estimated ratio of net income to sales for the term ended December 2019 is 6.4%.
2.Fiscal Year December 2018 Earnings Results
2-1 Consolidated Business Results
| FY Dec. 17 | Ratio to sales | FY Dec. 18 | Ratio to sales | YOY | Compared with Initial Forecast |
Sales | 10,371 | 100.0% | 10,430 | 100.0% | +0.6% | -0.7% |
Gross margin | 4,499 | 43.4% | 4,446 | 42.6% | -1.2% | +0.6% |
SG&A expenses | 3,726 | 35.9% | 3,671 | 35.2% | -1.5% | +2.0% |
Operating income | 773 | 7.5% | 774 | 7.4% | +0.1% | -5.5% |
Ordinary income | 757 | 7.3% | 768 | 7.4% | +1.4% | -3.9% |
Net income | 678 | 6.5% | 518 | 5.0% | -23.6% | -12.2% |
* Unit: ¥mn
Even though it was a modest pace, growth of sales and profits was secured.
Sales for the term ended December 2018 were 10,430 million yen, up 0.6% year on year. Although sales of expendable sensors and purchased products decreased, sales of clinical testing equipment and systems were healthy, which led to increased profits. Sales to China doubled. Operating income increased 0.1% year on year to 774 million yen. While gross profit decreased due to an increase in the launching cost caused by the release of the new products for laboratory information system, SG&A expenses decreased 1.5% year on year mainly in association with expenses for subcontracting development work for the new products.
Net income decreased 23.6% year on year to 518 million yen. The cost for transferring equipment from Shonan Factory to the new building at Esashi Factory as well as the loss on cancellation of a service contract due to discontinuation of outsourcing production of equipment for automatic manufacturing process for sensors were recorded as extraordinary losses.
Although profit did not achieve the target, sales were almost as forecasted. Overseas sales ratio that the company emphasizes for growth increased in direct and virtual terms to 12.2% and 28.2%, respectively.
2-2 Sales of each product series
Product series | FY Dec. 17 | Composition Ratio | FY Dec. 18 | Composition Ratio | Year on Year | Compared with Initial Forecast |
Clinical Testing devices and Systems | 4,812 | 46.4% | 5,448 | 52.2% | +13.2% | -5.4% |
Analyzers | 581 | 5.6% | 523 | 5.0% | -10.0% | -3.1% |
Laboratory Information System (LIS) | 2,749 | 26.5% | 2,968 | 28.4% | +8.0% | +2.3% |
Laboratory Automation System (LAS) | 1,481 | 14.3% | 1,957 | 18.8% | +32.1% | -15.6% |
Diagnostic reagents | 2,270 | 21.9% | 2,265 | 21.7% | -0.2% | -0.6% |
Supplies | 2,074 | 20.0% | 1,819 | 17.5% | -12.3% | -2.2% |
Others | 1,215 | 11.7% | 897 | 8.6% | -26.2% | +49.5% |
Total | 10,371 | 100.0% | 10,430 | 100.0% | +0.6% | -0.7% |
*The Year-on-Year value is against the modified forecast as of August 2018. Unit: ¥mn
Clinical Testing devices and Systems
Sales grew 13.2% year on year.
Sales of analyzers to OEM clients for electrolytes were strong, while direct sales decreased due to sluggish growth of the number of customers.
As for the laboratory information system, although sales of additional system connections and customization dropped, sales grew due to the steady acquisition of renewal projects and the increased number of new projects.
As for the laboratory automation system, sales grew due to the increased number of new projects in Japan and steady OEM sales to Runda Medical in China.
Diagnostic reagents
Sales declined 0.2% year on year.
Domestic and overseas OEM sales slightly increased. As for direct sales, sales declined due to a decrease in the number of operating equipment.
Supplies
Sales dropped 12.3% year on year.
Sales declined due to a reaction to demand rise in the previous term in anticipation of a switch to new products to respond to overseas regulations on sensors at existing OEM clients as well as holding-off buying due to price revisions from the middle of the fiscal year.
Others
Sales dropped 26.2% year on year.
As the company concentrated on the sale of its original products, the purchased products sales accompanying the transactions for LIS and LAS decreased.
2-3 Financial condition and Cash Flow
◎ Main BS
| End of Dec. 2017 | End of Dec. 2018 |
| End of Dec. 2017 | End of Dec. 2018 |
Current assets | 7,752 | 8,272 | Current liabilities | 4,143 | 4,656 |
Cash and deposits | 1,157 | 1,051 | Trade payables | 1,623 | 1,536 |
Trade receivable | 4,952 | 5,354 | ST Interest-Bearing Liabilities | 1,520 | 2,100 |
Inventories | 1,362 | 1,795 | Noncurrent liabilities | 1,400 | 776 |
Noncurrent assets | 4,578 | 4,339 | LT Interest-Bearing Liabilities | 1,350 | 750 |
Property, plant and equipment | 3,986 | 3,794 | Total liabilities | 5,544 | 6,432 |
Intangible assets | 49 | 38 | Net assets | 6,785 | 7,179 |
Investments and other assets | 542 | 505 | Total liabilities and net assets | 12,330 | 12,611 |
Total assets | 12,330 | 12,611 | Total Interest-Bearing Liabilities | 2,870 | 2,850 |
*Unit: ¥mn
Current assets increased 520 million yen from the end of the previous term, due to an increase in trade receivables, etc. Noncurrent assets decreased 239 million yen from the end of the previous term to 4,339 million yen as depreciation progressed. Total assets increased 281 million yen from the end of the previous term to 12,611 million yen.
Total liabilities increased 887 million yen from the end of the previous term to 6,432 million yen, due to an increase in reserve for product warranties, etc.
Net assets increased 394 million yen from the end of the previous term due to an increase in retained earnings.
As a result, equity ratio rose 1.9% from 55.0% at the end of the previous term to 56.9%.
Cash Flow
| FY Dec. 17 | FY Dec. 18 | Increase/Decrease |
Operating CF | 277 | 217 | -60 |
Investing CF | -1,348 | -177 | +1,171 |
Free CF | -1,071 | 39 | +1,110 |
Financing CF | 1,064 | -145 | -1,209 |
Cash and equivalents | 1,157 | 1,051 | -105 |
* Unit: ¥mn
Operating CF was nearly unchanged. As expanding facilities in Esashi Factory was completed, the deficit of investing CF decreased due to a decrease in purchase of property, plant and equipment. Free CF turned positive. Financing CF became negative, as there were no more proceeds from long-term loans payable. The cash position declined.
2-4 Topics
The company established a business alliance with ARKRAY, Inc., a pioneer in diabetes testing.
In September 2018, the company concluded a business alliance agreement with ARKRAY, Inc. (Kyoto City), a pioneer in diabetes testing, in the field of clinical testing business.
Outline of ARKRAY, Inc.
The company was established in 1963. It researches, develops, manufactures and distributes clinical testing equipment, reagents and data management systems. It also researches, develops and distributes functional food materials.
As a pioneer in diabetes testing, ARKRAY developed the world’s first HPLC-based HbA1c analyzer, which is still used at many medical institutions, in 1981. In addition, it offers various products including glucose testing systems and device for self-monitoring of blood glucose and is leading the diabetes testing industry both in Japan and the world. Furthermore, it has one of the largest sales networks in Japan in the field of testing for clinical facilities in Japan.
Background of Concluding the Business Alliance Agreement
An agreement was concluded with the aim of using each other’s strengths, complementing each other, and responding to diversification and sophistication of customers’ requests in the field of clinical testing business.
Contents of Business Alliance
A consultation body was set up by the executives of both companies, and discussions as to a wide range of fields are taking place.
In 2019, the company will promote collaboration in the field of glucose testing. The major testing items for diabetes include glucose (blood glucose level) and HbA1c (glycohemoglobin). As A&T has its strength in glucose and ARKRAY, Inc. has its strength in HbA1c, A&T supplies glucose analyzers “GA09II” to ARKRAY, Inc. and the sales started in February.
They are also examining the possibility to develop a small transporter to connect “GA09II” and “HbA1c Analyzer” and sell the product at both companies.
In addition, they will examine specific themes on the linkage of laboratory information system and will explore product supply and overseas sales in a wide range of fields.
3. Fiscal Year December 2019 Earnings Forecasts
3-1 Consolidated earnings forecasts
| FY Dec. 18 | Ratio to sales | FY Dec. 19 Est. | Ratio to sales | Year on Year |
Sales | 10,430 | 100.0% | 11,200 | 100.0% | +7.4% |
Gross margin | 4,446 | 42.6% | 4,770 | 42.6% | +7.3% |
SG&A expenses | 3,671 | 35.2% | 3,760 | 33.6% | +2.4% |
Operating income | 774 | 7.4% | 1,010 | 9.0% | +30.4% |
Ordinary income | 768 | 7.4% | 1,000 | 8.9% | +30.1% |
Net income | 518 | 5.0% | 720 | 6.4% | +39.0% |
*The forecasted values were provided by the company. Unit: ¥mn
Both sales and profit will grow.
The sales for the term ending December 2019 are expected to increase 7.4% year on year to 11.2 billion yen. The number of large-scale projects for clinical testing devices and systems will increase. Sales of original products will also grow. Gross profit will also increase 7.3% year on year due to reduction of man-hours on new products for the laboratory information system and reduction of purchased products. Operating income is estimated to increase 30.4% year on year to 1,010 million yen. SG&A expenses will also increase 2.4% year on year due to an increase in employees for sustainable growth and new product development expenses for the laboratory automation system, but it will be offset by an increase in gross profit. The dividend is estimated to be 24 yen per share, unchanged from the previous year. The estimated payout ratio is 20.9%.
3-2 Sales for each product series
Product series | FY Dec. 18 | Composition rate | FY Dec. 19 Est. | Composition rate | Year on Year |
Clinical Testing devices and Systems | 5,448 | 52.2% | 6,270 | 56.0% | +15.1% |
Analyzers | 523 | 5.0% | 740 | 6.6% | +41.4% |
Laboratory Information System (LIS) | 2,968 | 28.5% | 3,110 | 27.8% | +4.8% |
Laboratory Automation System (LAS) | 1,957 | 18.8% | 2,420 | 21.6% | +23.6% |
Diagnostic reagents | 2,265 | 21.7% | 2,300 | 20.5% | +1.5% |
Supplies | 1,819 | 17.4% | 1,930 | 17.2% | +6.1% |
Others | 897 | 8.6% | 700 | 6.3% | -22.0% |
Total | 10,430 | 100.0% | 11,200 | 100.0% | +7.4% |
* Unit: ¥mn
*Domestic and overseas OEM sales of analyzers will steadily increase. Through business alliance, new sales of glucose analyzers to ARKRAY, Inc. are expected to increase.
*For the laboratory information system, the company has a prospect of launching new products on three subsystems. Demand for new products and renewal of existing products is strong. It also plans to hire engineers.
*For the laboratory automation system, the company will continue to build relationships with Runda Medical in China and anticipates strong sales. The number of large-scale projects is also expected to increase in Japan.
*The OEM inventory adjustment trend will continue for sensors in order to comply with overseas regulations. The company will prepare for establishing a commercial distribution with new OEMs and aim for stable growth.
*It will continuously reduce sales of purchased products and focus on selling the original products.
4. Medium-Term Management Plan (FY Dec. 2018 to FY Dec. 2020) Progress
4-1 Basic Policy and Progress Status
Basic Policy | Progress | Assessment |
1.To raise the ratio of original product sales and improve profitability. | Original product sales for the term ended Dec. 2018 increased approximately 400 million yen compared with the previous year. It is making progress as planned. | ○ |
2.To strengthen development of business targeted at China and raise the ratio of overseas sales. | Sales to China in the term ended Dec. 2018 were 780 million, up 122.2% year on year, and sales ratio also increased from 3.4% to 7.5%. Mostly due to this factor, the company achieved the target of an overseas sales ratio of over 10% ahead of schedule. | ○ |
3.To strengthen the link between development and manufacturing, and create a system for developing and producing stable, high-quality products. | The company established a system to pursue quality and production efficiency utilizing the new building at Esashi Factory. | △ |
4.To thoroughly implement work-style reforms and human resource development. | In April 2018, the company introduced the region-limited full-time employee system. Also, the establishment of a system for promoting comprehensive education programs has been completed. | △ |
4-2 Numerical goals and progress status
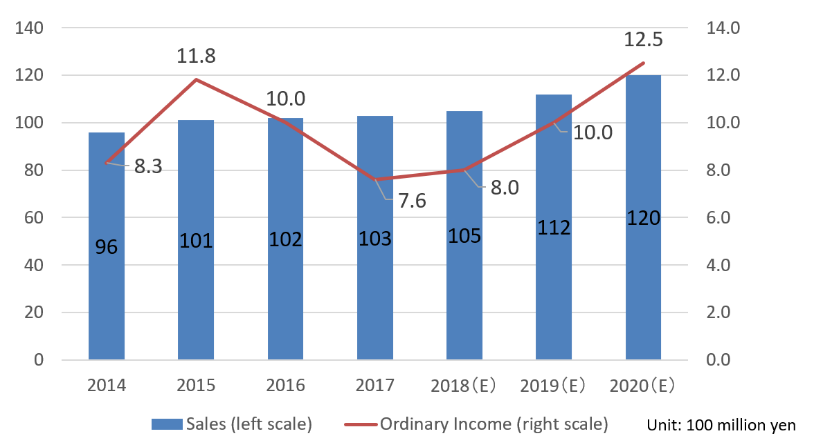
| FY Dec. 18 | FY Dec. 19 | FY Dec. 20 | |
Plan | Actual | Plan | Plan | |
Sales | 10,500 | 10,430 | 11,200 | 12,000 |
Ordinary income | 800 | 768 | 1,000 | 1,250 |
Ordinary margin to sales | 7.6% | 7.4% | 8.9% | 10.4% |
Direct sales rate in overseas | - | 12.20% | 10% over | 10% over |
* Unit: ¥mn
*FY December 2018
Although the number of clinical testing devices and systems increased, OEM sales of sensors remained sluggish due to the response to overseas regulations and holding-off buying from price revision. Ordinary income did not reach the target due to a decrease in sales of sensors and initial costs for new products exceeding the plan. However, the ratio of overseas sales exceeded 10% for the first time with strong Chinese OEMs sales for the laboratory automation system. As a result, it reached the target a year ahead of the plan.
*FY December 2019
It will increase the number of employees and further expand sales of clinical testing devices and systems. It will maintain the initial planned targets and work on the activities for sustainable growth including reduction of work-hours for new products and full operation of the new building at Esashi Factory.
*FY December 2020
Using the actions for the first and second years of the medium-term management plan as steps, it will maintain the plan to achieve the largest sales and profit. It is planning to establish the next medium-term management plan.
5. Interview with President Misaka
5-1 Self-evaluation on the progress of Medium-Term Management Plan Basic Policy
- The increase in sales of original products, which is essential for improving profitability, was approximately 400 million yen from the previous year, which was almost as planned. We were able to focus and work hard. We would like to increase our original product ratio in the current term as well.
- For the sales targeted at China, sales through Runda Medical are off to a good start. As we believed that the Laboratory Automation System business would be the key to expanding the business in the Chinese market, we were able to obtain a good partner and launch our business smoothly. Globalization is essential for pursuing our growth, but we will first focus on the business in China where we can expect significant growth.
- Our growth has been realized through the development of highly unique products and systems centered on Laboratory Automation System. Naturally, we will continue to strengthen our development capabilities. However, at the same time, it is also important for us to create a system that can stably produce high-quality products. For this reason, we are developing a system to pursue quality and production efficiency utilizing the new building constructed at Esashi Factory. The transfer of reagents from Shonan Factory to Esashi Factory progressed smoothly. Meanwhile, improvement of yield is still under way.
- As for the work-style reform and human resource development, we introduced the region-limited full-time employee system in April 2018 to create a comfortable work environment. We also established a system for a company-wide education program. We want our sales employees to be fully aware of cost conscious, and employees in charge of development to learn more about intellectual property that is becoming increasingly important. In addition, a more detailed personnel evaluation system was introduced this year. We believe it is necessary to raise the level of the entire company, including global human resource development.
5-2 Our advantage in the Chinese market
- The clinical testing systems’ sales strategies can be broadly divided into a “closed strategy” and “open strategy.”
- Major European and US companies provide equipment, transport systems and reagents to be delivered to a laboratory, all of which are their original products. This is called the “closed strategy.”
- On the other hand, our company uses the “open strategy” where we offer optimal one-stop solutions including proposing a layout and installing and operating equipment that meet the needs of hospitals and laboratories through the laboratory automation system (LAS), which enables the setting using both our original products and equipment purchased from other companies.
- However, meeting all needs may lead to a decline in profitability. Therefore, we are creating several packages of OEM products, as equipment to be installed is predetermined in accordance with the size of laboratory. It can be called as a “semi-open strategy.”
- “CLINILOG V4,” which is supplied to Runda Medical as an OEM, is exactly this type of packaged sales. This method allows us not only to reduce the time and efforts for design changes, development and modification for each hospital but also to develop stable sales and manufacturing plans. We will be able to make the “laboratory automation system (LAS)” sales business more efficient in China.
- In the fast-growing Chinese clinical testing system market, the above-mentioned two strategies are battling each other. We believe it is important to show our presence in the “Laboratory Automation System” to grow in the Chinese market. With our strength in the “Laboratory Automation System” and our advantage of receiving high praise from customers with the semi-open strategy, we will aggressively promote the expansion of our business in the Chinese market.
- In order to achieve the medium-term target of over 50% of virtual overseas sales ratio, expansion of our business in China is essential. Based on the high recognition of our performance, we are receiving business proposals from some potential partners. We will launch businesses in other fields in addition to the business for Runda Medical, which is making good start.
- In order to succeed in the medical field, cooperation with academia in addition to corporate power is essential. We will work on establishing a stable business foundation by establishing relationships with Key Opinion Leaders (KOL), which have a large impact, through organizational development of academic society activities.
6. Conclusions
The year-on-year growth rate was small for the term ended Dec. 2018, but the company seems to have good results including expansion of sales of original products and growth of businesses in China.
Sales in China, which doubled from 351 million yen to 780 million yen, will be disclosed semi-annually in the coming years, allowing investors to watch important indicators to judge the company.
Looking to accomplish the goal at the final year of the medium-term management plan, which is the term ending Dec. 2020, positive signs for achieving sales, such as business growth in China and alliance with ARKRAY, have been seen, and investors will take an interest in the profits.
We will pay attention to efforts and progress, including changes in sales of original products, to achieve an ordinary income rate of over 10%.
<Reference1: Outline of Medium-Term Management Plan>
In May 2018, as a celebration of the 40th anniversary of its founding, and in anticipation of its 50th anniversary in 2028, the company has formulated a three-year medium-term management plan starting this term.
Sales in the last three terms have been mostly unchanged, and ordinary income has declined after reaching a peak in FY Dec. 2015, but with the theme of “building a framework for sustainable growth,” the company aims to “shift toward an increasing trend in sales and profits, and quickly recover ordinary income.”
<Target Figures>
For the term ending Dec. 2020, the company mentioned “sales of 12 billion yen or greater, an ordinary income rate of over 10%, and an overseas direct sales ratio of 10% or more.”
<Analysis of the business environment, etc. at the time of formulation of the medium-term management plan and status of each business>
| Blood testing business | IT and automation support business |
Sales | *OEM sales were sluggish due to price revision, etc. *Sales of supplies and sensors increased as the number of customers increased. *Domestic clinical markets, such as the electrolyte and glucose markets, leveled off. | *LIS started full-scale introduction of new products, and grew due to focus on sales. *Large-scale LAS transactions are decreasing (lower average unit price per transaction). *Sales increased for purchased products accompanying large transactions. |
Profit (Main reason for a decreasing trend in profit) | *OEM sales were sluggish due to price revision, etc. | *In FY2017, carried out intensive investment for development of the LIS subsystem. *There was strong price competition for large transactions both domestically and overseas. *Outsourcing expenses (outsourcing of system engineers) increased. *Sales increased for purchased products accompanying large transactions. |
Business Environment | *Due to changes in the sales environment, sales to some OEM clients may decrease. *Domestic clinical markets, such as the electrolyte and glucose markets, leveled off. *The overseas market (especially China) is growing rapidly. | *There is no major change in the domestic market both in size and competitive situation, and it is in a state of equilibrium. Overseas demand is high. *While the value of each order is large, the time until the next renewal can be as long as 5 to 10 years. *Once the product is introduced, it is easy to sell subsequent renewals of the product (relatively easy to secure repeat business). On the other hand, it is relatively difficult to persuade new customers to switch to the company’s products. *In recent years, overseas demand for LAS is particularly high. |
Intensive measures | *To increase OEM clients for electrolytes, and develop stable commercial distribution to existing OEM clients. *To promote technological development for reducing costs. *To utilize the new building of Esashi Factory. | *LIS started full-scale introduction of new products, and grew due to focus on sales. *Large-scale LAS transactions are decreasing (lower average unit price per transaction). *Sales increased for purchased products accompanying large transactions. |
Progress of each business | *Start of supply of electrolyte units to a new OEM client in Japan *The commercial channels of the electrolyte unit with two new OEM clients inside and outside Japan are under development. *Development of technologies for improving the quality and yield rate of sensors *Completion of transfer of some clinical reagents from Shonan Factory to Esashi Factory | (LIS) *Introduction of new subsystems (blood transfusion, bacteria tests, infectious diseases.) to the first user *Transactions for both installation and renewal increased. (LAS) *In Japan, a large-scale module to refrigerate samples, which will be added to the product lineup, is completed and introduced to first users. *The company signed a distributorship contract with a Chinese company (Runda), and started OEM sale. |
The company believes that overseas expansion is crucial for both businesses in order to achieve the objective.
<Reference2: Regarding corporate governance>
Organization type and the composition of directors and auditors
Organization type | Company with audit and supervisory committee |
Directors | 11 directors, including 2 external ones |
Corporate Governance Report
Last Update: March 30 2018.
<Basic policy>
As a top priority, our company aims to secure the effectiveness of corporate governance and actualize fair business administration by putting importance on the transparency, fairness, and speed of decision making and business execution. In addition, we adopted the system of audit and supervisory committee in order to separate the supervision and execution of business administration, actualize highly transparent management, and streamline the decision-making process of the board of directors.
<Reasons for Non-compliance with the Principles of the Corporate Governance Code (Excerpts)>
As a JASDAQ listed company, the company fully follows the 5 items of basic principles of the corporate governance code.
This report is intended solely for information purposes, and is not intended as a solicitation for investment. The information and opinions contained within this report are made by our company based on data made publicly available, and the information within this report comes from sources that we judge to be reliable. However, we cannot wholly guarantee the accuracy or completeness of the data. This report is not a guarantee of the accuracy, completeness or validity of said information and opinions, nor do we bear any responsibility for the same. All rights pertaining to this report belong to Investment Bridge Co., Ltd., which may change the contents thereof at any time without prior notice. All investment decisions are the responsibility of the individual and should be made only after proper consideration. Copyright (C) 2019 Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. |

