Bridge Report:(7242)KYB the Fiscal Year March 2020
 Representative Director, President Executive Officer Masao Ono | KYB Corporation (7242) |
 |
Company Information
Market | TSE 1st Section |
Industry | Equipment for transportation |
Representative Director, President Executive Officer | Masao Ono |
HQ Address | World Trade Center Bldg., 4-1, Hamamatsu-cho 2-chome, Minato-ku, Tokyo |
Year-end | End of March |
HOMEPAGE |
Stock Information
Share Price | Number of shares issued | Total market cap | ROE Act. | Trading Unit | |
¥2,111 | 25,748,431 shares | ¥54,354million | -55.4% | 100 shares | |
DPS Est. | Dividend yield Est. | EPS Est. | PER Est. | BPS Act. | PBR Act. |
undecided | - | undecided | - | ¥2,900.73 | 0.7x |
* Share price as of closing on June 22. Each number was based on the results of the term ended March 2020. It’s currently difficult to reasonably calculate the effects of COVID-19, thus this term’s forecast is undetermined.
Earnings Trends
Fiscal Year | Net Sales | Operating Income | Pretax Income | Net Income | EPS | DPS |
March 2017 (results) | 355,316 | 19,247 | 18,852 | 14,544 | 56.93 | 12.00 |
March 2018 (results) | 393,743 | 20,885 | 20,881 | 15,202 | 595.09 | 150.00 |
March 2019 (results) | 412,214 | -28,496 | -29,510 | -24,757 | -969.18 | 0.00 |
March 2020 (results) | 381,584 | -40,298 | -41,419 | -61,819 | -2,422.53 | 0.00 |
March 2021 (estimate) | - | - | - | - | - | - |
* Unit: Million yen or yen. IFRS adjustment. Net income is profit attributable to owners of the parent. The company conducted 1-for-10 reverse share split on October 1, 2017. DPS for the term ending March. 2018 represent the amounts taking the 1-for-10 reverse split into account. EPS and DPS are not adjusted. It’s currently difficult to reasonably calculate the effects of COVID-19, thus this term’s forecast is undetermined.
This Bridge Report presents details and analysis of KYB earnings results for the fiscal year ended March 2020.
Table of Contents
Key Points
1.Company Overview
2. Fiscal Year ended March 2020 Earnings Results
3. Fiscal Year ending March 2021 Earnings Estimates
4. Current management issues
5. Conclusions
<Reference: Regarding Corporate Governance>
Key Points
- The sales for the term ended Mar. 2020 were 381.6 billion yen, down 7.4% year on year. The full-year results were affected by the decline in the Chinese market due to the trade friction between the U.S. and China and the appreciation of the Japanese yen, while the performance in the fourth quarter (January to March) was affected by the novel coronavirus. Sales decreased for the AC Business and the HC Business. The segment profit was 17.6 billion yen, down 20.2% year on year. The profit of the AC business increased as it improved its profitability. The profit of the HC Business declined due to the drop in the number of orders. The company posted expenses due to nonconforming acts related to the seismic isolation/mitigation oil dampers, resulting in an operating loss of 40.3 billion yen and the loss before taxes of 41.4 billion yen. Net loss was 61.9 billion yen. Given the recent business results, the company considered collectability and partially reversed deferred tax assets. Compared to the revised forecast announced in February 2020, sales and segment profit were almost as estimated, while net income did not reach the estimate.
- Due to the uncertainties owing to the spread of COVID-19, the forecast for the term ending Mar. 2021 as well as the dividend forecast are still to be determined. The company will promptly disclose the forecast when it becomes possible to estimate business results.
- According to the “2017 Mid-term Management Plan,” which was announced in May 2017, the company aimed for sales of 398 billion yen, a segment profit of 26 billion yen, and ROE of 10.0% for the term ended Mar. 2020. However, unfortunately, all of them were unachieved. The main reason for failing to achieve the targets is the nonconforming acts in the non-core business and the delay in reforming the structure of unprofitable businesses, both of which are issues that need to be reflected on. However, the company has confirmed other achievements such as releasing value-added products for automobiles, estimating the timing for transferring and integrating product lines for construction machinery, and making some progress in the reconstruction of unprofitable bases. As for the next mid-term management plan, it is currently difficult to set a plan due to the uncertainty over the COVID-19 effects; the company will pay attention to the situation and will design and announce a plan accordingly.
- As for the post-pandemic world, the company thinks that the AC business and the HC Business, which are the 2 core businesses, will take full advantage of KYB’s strengths and as COVID-19 changes values, the company plans to evolve into a company that will be chosen by society. To achieve this, the company set the 3 keywords: selection & concentration, unmanned operations & labor-saving, and improvement of core technologies. Particularly, for promoting innovative manufacturing, it plans to adopt automation and unmanned operations domestically and abroad for production lines so that by the final term it will reduce the processing costs by 30%.
- The current term’s forecasts are undetermined due to the effects of COVID-19 and investors will have to wait until a quarterly announcement; we expect to have some qualitative information about the current situation if possible.
- The main measures against the post-pandemic world have been taken before COVID-19 had spread, while recognizing it as a serious issue. The business environment is harsh and we will pay attention to whether the company will overcome issues with the AC Business and the HC Business, which should be addressed swiftly.
1.Company Overview
The largest manufacturer of independent hydraulic equipment in Japan. Based on hydraulic technology, the company offers products and technologies in a wide range of fields such as "automobiles", "motorcycles", "construction machinery", "industrial vehicles", "aircraft", "railroads" and “special purpose vehicles”.
KYB has a high market share with many products. For instance, shock absorbers for automobiles account for 42% of the domestic market and 16% of the global market.
【1-1 Corporate history】
The roots come from “Kayaba Research Center”, which was established by Shiro Kayaba, who is an inventor and a founder, in November 1919.
In January 1927, a self-employed enterprise, Kayaba Seisakusho, was established for manufacturing hydraulic dampers, catapults, etc. for aircraft.
In March 1935, Kayaba Manufacturing Co., Ltd. was established.After the end of World War II, in June 1956, Kayaba Auto Service Co., Ltd. was established for offering products and services.In October 1959, company’s stocks were listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange.
In July 1974, KYB Corporation of America was established in the United States in order to enter the North American commercial market. Then, the company actively entered foreign markets such as Asia and Europe.
In October 1985, the company name “Kayaba” was changed from kanji (Chinese characters) to katakana (Japanese Characters).In October 2015, the trade name was changed from Kayaba Manufacturing Co., Ltd. to KYB Corporation in order to further strengthen the brand image.
【1-2 Corporate Philosophy/Management Philosophy】
◎KYB Corporate Symbol
As they changed the corporate name from "Kayaba Manufacturing Co., Ltd." to "KYB Corporation" in 2015, they aim to popularize the KYB brand on a global basis.Therefore, as shown below, the logo “KYB” has the meaning and spirit

(Taken from KYB’s website)
Slanted slits in each letter represent comfortable sunlight cast through the trees and sunbeams illuminating the road ahead. The logo represents an image of unconstrained growth and flexible response to the trends of the era. The right side of the letter “B” represents liquid pressure indicating the origin of KYB. Using italic letters expresses a sense of speedy movement, progressiveness, growth potential, innovativeness.
(What the corporate color means)
The corporate color, red stands for love, enthusiasm and passion, etc. and it gives the image of a sun’s warmth, heat and power to grow life that realize an epoch-making society. Red is also a positive color, and represents manufacturing that goes the extra mile.
(Taken from KYB’s website)
◎Corporate Statements

The characteristics of products such as precise quality and reliable technology are expressed with the statement.It means that not only providing reliable quality to general consumers and business partners leads to stakeholders’ “advantage (superiority)”, but also the joy of manufacturing, which enables each employee to realize that they can change the world with sure quality, becomes “advantage (merit).”
◎Corporate Spirit
As the KYB Group, which aims to contribute to society by providing technologies and products for making the living of people safe and comfortable, it reflected on the improper act revealed in Oct. 2018, and revised its Corporate Spirit and Corporate Guiding Principles.
(Corporate Spirit)
We shall follow all rules and face all issues with honesty. |
We shall build a corporate culture full of vitality, and hold high goals. |
We shall value sincerity, cherish nature, care for the environment. |
We shall constantly pursue creativity, contribute to the prosperity of customers, shareholders, suppliers and society. |
(Management Vision)
Human Resources Development | To cultivate the talent to achieve the objectives with a thorough understanding of the principles and the strategy. |
Technology and product development | To provide products that are impressive, comfortable and reliable to customers throughout the world. |
Monozukuri (Manufacturing expertise) | To make our plants enjoyable, dynamic places to work, and at the same time full of discipline based on the field priority doctrine, in order to produce products satisfactory to the customer. |
Management | Always keep social responsibilities of the corporation in mind and provide efficient group management. |
(Corporate Guiding Principles)
See the following URL:
https://www.kyb.co.jp/english/company/guidelines.html
【1-3 Environment Surrounding the Company】
(1) Market Environment
The automobile market and the construction machinery market have a great effect on KYB's performance.
KYB recognizes the current and future situations of the two markets as follows.
①Automobile Market
The global demand for automobiles is expected to increase for Hybrid and EV cars in the middle to long-term, but as the COVID-19 effects are added to other issues such as the heating up of the trade war started by the U.S. and the negotiations for Brexit, the uncertainties for the short term are significant.
KYB supplies shock absorbers (SA) for new vehicles directly to automobile manufacturers as Tier 1, and also supplies them to auto parts stores, repair shops, etc. through agencies for aftermarket as well. The company calls the former "OEM" and the latter "marketed".
Japanese cars are popular in Asia, the Middle East and others, and the commercial market is important for KYB.
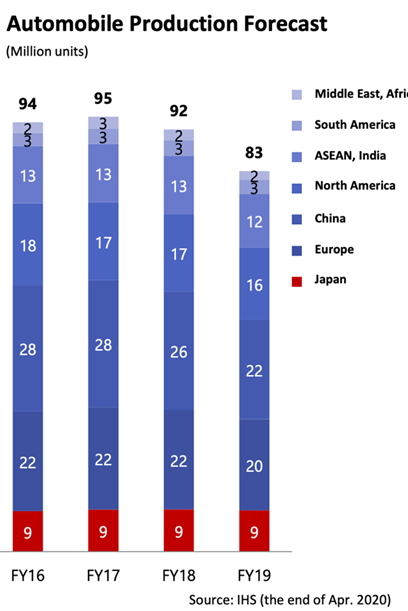
(Taken from the reference material of KYB)
②Construction Machinery Market
The slowdown in the Chinese and Indian markets is forecasted and due to the addition of COVID-19 effects, the uncertainties for the short term are strong.
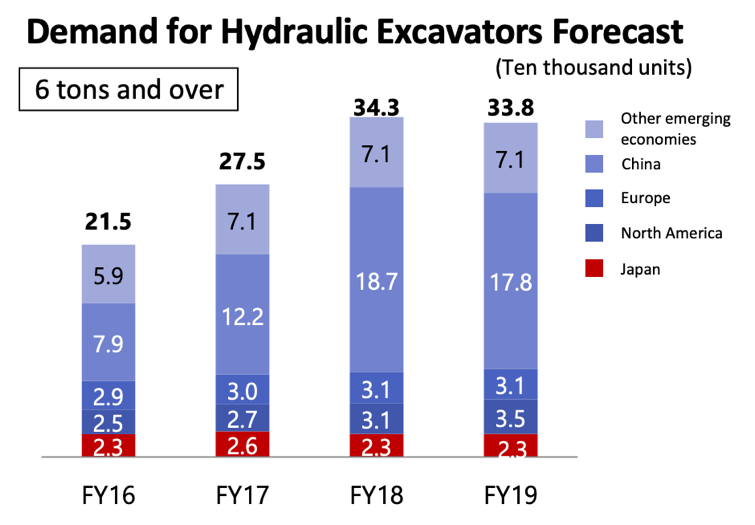 |
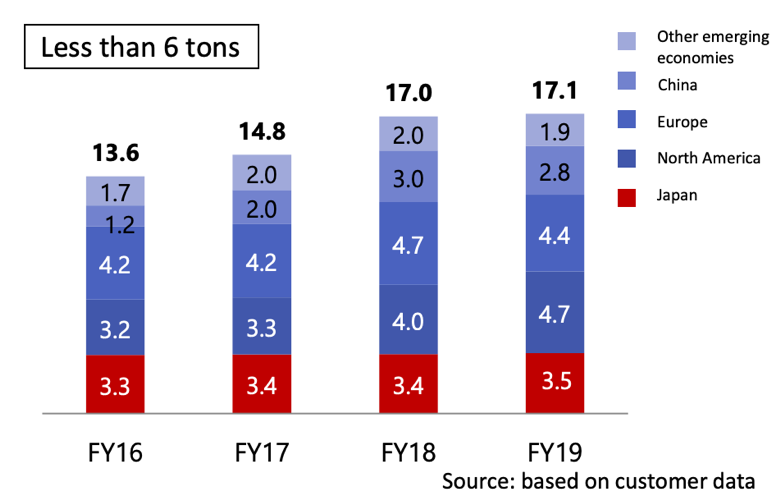 |
(Taken from the reference material of KYB)
(2) Competitors
①AC Business
KYB’s domestic competitors include Showa Corporation (7274, TSE 1st section), and Hitachi Automotive Systems, Ltd. (unlisted), a group company of Hitachi. Furthermore, Showa Corporation will be acquired by Hitachi Automotive Systems, Ltd. through absorption-type merger.
Its global competitors consist of ZF in Germany, Tenneco in the U.S., and so on. ZF has a long history and intimate relationships with European automobile manufacturers.
The company’s share in the commercial product market is slightly less than 20%. Tokico (which was acquired through M&A by Hitachi and is unlisted; today it is one of the brands of Hitachi Automotive Systems) and Monroe (a commercial brand of Tenneco) have earned a large market share in Japan and globally, respectively.
KYB competes with Showa in the market of shock absorbers for motorcycles, and with JTEKT Corporation (6473, TSE 1st section) and NSK Ltd. (6471, TSE 1st section) in the steering market.
②HC Business
In the market of cylinders, which are the parts with the highest sales ratio in KYB, Chinese manufacturers and the like are extending their influences.
KYB’s competitors include Nabtesco (6268, TSE 1st section) in the market of control valves for which KYB has the advanced technology, and Nabtesco and Nachi-Fujikoshi (6474, TSE 1st section) in the market of travel motors.
In addition, the largest construction machinery manufacturer in Japan manufactures a number of parts internally.
Code | Corporate name | Sales | Growth rate | Operating income | Growth rate | Operating income rate | ROE | Market cap | PER | PBR |
5994 | Fine Sinter | - | - | - | - | - | 3.4% | 7,005 | - | 0.4 |
6268 | Nabtesco | 303,000 | +4.6% | 32,000 | +26.4% | 10.6% | 9.8% | 425,454 | 18.3 | 2.3 |
6471 | NSK | - | - | - | - | - | 3.3% | 460,308 | - | 0.8 |
6473 | JTEKT | - | - | - | - | - | -1.3% | 303,808 | - | 0.6 |
6474 | Nachi-Fujikoshi | 230,000 | -7.7% | 12,500 | -6.4% | 5.4% | 7.1% | 85,099 | 10.4 | 0.7 |
7212 | F-Tech | - | - | - | - | - | 0.8% | 9,842 | - | 0.2 |
7242 | KYB | - | - | - | - | - | -55.4% | 57,110 | - | 0.8 |
*The sales and growth rates are forecasts for this term estimated by the company with the unit being million yen. ROE is the results from the previous term.
The aggregate market capitals are the closing price on June 17. The unit is million yen. PER (estimates) and PBR (results) are based on the closing price on June 17 with the unit being times.
Due to the effects of COVID-19, this term’s forecast is undetermined for all companies except for Nabtesco and Nachi-Fujikoshi.
Nabtesco, whose accounting year ends in December, and Nachi-Fujikoshi, whose accounting year ends in November, haven’t changed their forecasts for this term, which were released at the time of announcement of financial statements for the previous term.
【1-4 Business contents】
(1) Segments
KYB’s business segments are composed of the following four segments: the “AC Business” consisting of hydraulic shock absorbers for automobiles and motorcycles, power steering, etc., the “HC Business” including hydraulic equipment for industrial use mainly for construction machinery, “System products,” which produces theater equipment, equipment for military vessels, seismic isolation and vibration suppression devices, etc., and the “Aircraft components business,” which produces devices for take-offs and landings of aircrafts, steering components, control devices, etc. It also has the “Others” segment which handles special purpose vehicles, electronics, and the like.
Fiscal year ended March 2020 results
| Sales | Composition Ratio | Segment profit | Profit rate |
AC Business | 232,101 | 60.8% | 11,696 | 5.0% |
HC Business | 125,321 | 32.8% | 5,534 | 4.4% |
System products | 8,148 | 2.1% | 1,531 | 18.8% |
Aircraft components business | 5,481 | 1.4% | -2,185 | - |
Others | 10,534 | 2.8% | 1,000 | 9.5% |
Total | 381,584 | 100.0% | 17,575 | 4.6% |
*Unit: million yen
① AC(Automotive Component)Business
This segment consists of shock absorbers for automobiles and motorcycles, hydraulic equipment for automobiles, and other products.
Composition ratio for the Fiscal Year ended March 2020
Product | Sales | Composition ratio | Major products |
Shock absorbers for automobiles | 167,134 | 72.0% | Shock absorbers |
Shock absorbers for motorcycles | 28,234 | 12.2% | Front forks, rear cushion units |
Hydraulic equipment for automobiles | 32,065 | 13.8% | Vane pumps, CVT pumps, EPS |
Others | 4,668 | 2.0% | Shock absorbers for ATVs, Stay dumpers |
Total | 232,101 | 100.0% | - |
*unit: million yen
<Major Products>
◎Automobiles
(Shock absorbers)
A shock absorber is a device that absorbs vibration of the car body, being mounted between the body and the tires together with a spring.
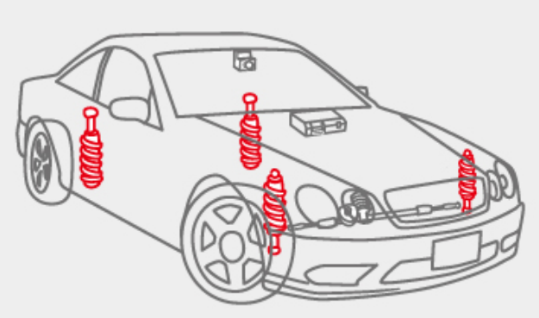 |
 |
(Taken from KYB’s website)
Each automobile is equipped with a “suspension” which is the system that improves riding comfort and operational stability.
Suspensions have two main functions; one is, as buffers, to prevent transmission of rough road profiles to the car body and another is to set the position of the wheels and axles and press the wheels down on the roads.
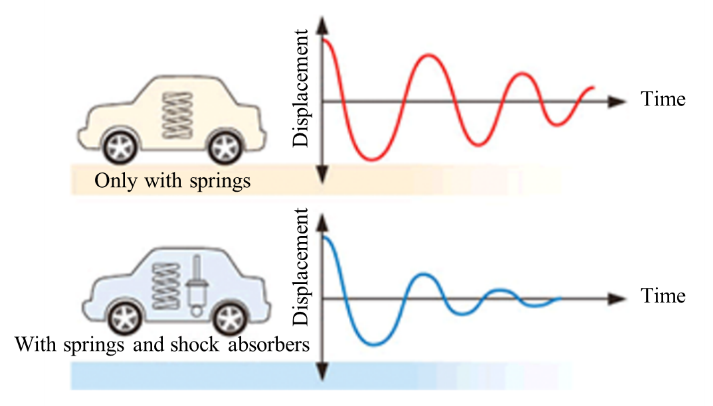
Basically, a suspension is composed of a suspension arm which fixes the wheel position, a spring which supports the car weight and absorbs vibration, and a shock absorber (damper) which dampens vibration of the spring
Automobiles absorb shock caused by uneven road profiles by contracting the springs, but due to their characteristics, the springs rebound to get back to their original position after the contraction.
The top of a spring is connected to the car body and the bottom is coupled with a suspension that includes the heavy tires and brake, which results in, due to inertia, repetition of expansion and contraction of a spring in a range wider than one necessary for returning to its original position.
The role of shock absorbers is to reduce the above-mentioned excess vibration as soon as possible in order to stabilize the car body.
(Taken from KYB’s website)
The vehicle in which the shock absorber is functioning properly achieves the following:
☆ | Reduction in unnecessary movement of springs to secure riding comfort |
☆ | Improvement of the brake performance |
☆ | Smoothness in taking corners |
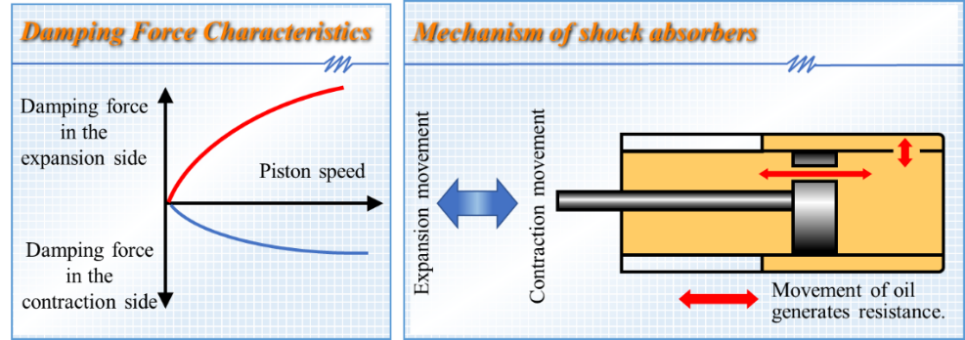
The force that controls expansion and contraction of springs and reduce vibration is called “damping force.” The “hydraulic technology,” which KYB has cultivated and improved since its inauguration, plays a significant role in generating “damping force.”
A piston has holes through which oil passes when the piston moves following vibration, and the resistance of the oil generates “damping force.” In addition, the moving speed of pistons varies with the degree and velocity of vibration from the car body, and the faster a piston moves, the larger “damping force” becomes. This is called “damping force characteristics.”
(Taken from KYB’s website)
KYB’s shock absorbers developed based on its sophisticated technology has earned reputation from a number of automobile manufacturers worldwide, leading to the large market share as mentioned below.
Furthermore, it is said that shock absorbers usually need to be replaced after 5 years from the date of first registration or when the travel distance reached 100,000 km as they deteriorate due to various factors including travel distance and lapse of time and the function decreases.
This replacement demand, which in other words is the commercial product market, is one of the greatest business opportunities for the company.
(Steering)
It is the steering system that provides “the function of taking curves,” one of the three basic functions of automobiles including “driving,” “taking curves,” and “stopping.”
(Taken from KYB’s website)
KYB’s steering components include the “hydraulic power steering (PS)” that uses the hydraulic power assist unit to support turning of the steering wheel done by drivers and steer the tires, and the “electric power steering (EPS)” that uses the electric power assist unit composed of a motor, a controller, a torque sensor, etc. to support turning of the steering wheel and steer the tires.
The “PS” enables steering operation by a mere movement thanks to hydraulic force and is an indispensable component for safe driving because of its ability to expeditiously avert risks, whereas the “EPS” whose power source is a battery improves fuel efficiency compared to the “PS” whose power source is the engine of a car.

◎ Motorcycles
(Suspensions)
Suspensions minimize shock to the car body regardless of road surface conditions, pursuing comfort.
*Rear cushion unit (RCU)
The company’s RCUs boost riding comfort by maintaining the posture of vehicles and absorbing vibration and shock from the road surfaces.

② HC (Hydraulic Components) Business
The HC Business consists of hydraulic equipment for industrial use and other products.
Composition ratio for the Fiscal Year ended March 2020
Products | Sales | Composition ratio | Major products |
Hydraulic equipment for industrial use | 117,014 | 93.4% | Cylinders, valves, pumps, motors |
Others | 8,306 | 6.6% | Railroad dampers, railroad brakes |
Total | 125,321 | 100.0% | - |
* unit: million yen
<Major Products>
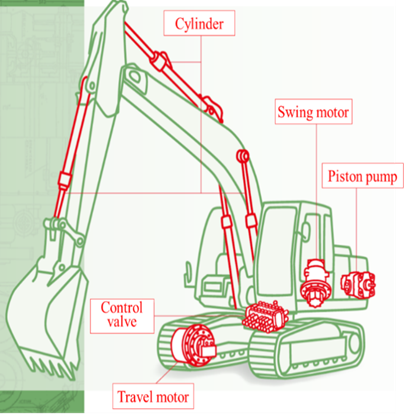
The mechanism of the drive system of construction machinery such as shovels consists of various parts as shown below, including control valves, piston pumps, travel motors, swing motors, and cylinders; it is the control valve, which is the “brain” of construction machinery, that controls a variety of actuators (a drive unit which converts energy to translational or rotary motion through hydraulic pressure and electric motors) to enable smooth movement of driving, turning, and bending and stretching of the arms.
KYB’s control valves have realized more advanced control by combining electric control with its special hydraulic technology.
In addition, KYB is one of the few manufacturers that manufacture all of the above-mentioned parts.
KYB’s competitive edge is that it can make suggestion to construction machinery manufacturers because its manufacturers all kinds of parts as just mentioned.

(Taken from KYB’s website)
③ Segments other than the AC Business and the HC Business
Segments | Sales | Major products |
System products | 8,148 | Theater equipment, equipment for military vessels, seismic isolation and vibration suppression devices, simulators, hydraulic systems, tunnel boring machines, and environmental devices |
Aircraft components business | 5,481 | Devices for take-off and landing of aircrafts and its steering components, control devices, and emergency equipment |
Others (special purpose vehicles, electronics, and the like) | 10,534 | Concrete mixer trucks, granule carriers, special purpose vehicles, and electronic devices |
* unit: million yen
KYB’s concrete mixer trucks have high mixing and emission performance, accounting for about 80% of the domestic market share.
It offers highly-reliable products for aircraft, including various actuators, weight-saving accumulators, and wheel brakes.
 |
 |
(2) Clients and sales channels
◎Clients
The following is a list of KYB’s major clients.
Its shock absorbers are mounted on about 60% of automobiles manufactured by Toyota globally. They are also adopted to about 30% and about 10% of automobiles manufactured by Nissan and Honda, respectively, contributing to KYB’s large market share.
| Japanese company | Non-Japanese company |
AC Business | Toyota Motor Nissan Motor Yamaha Motor JATCO Suzuki Motor SUBARU Mitsubishi Motors Honda Motor Isuzu Motors Daihatsu Motor Hino Motors | PSA Renault Volkswagen Daimler Chrysler |
HC Business | Hitachi Construction Machinery Sumitomo Construction Machinery Kubota Kobelco Construction Machinery Takeuchi Mfg Yanmar Komatsu Forklift | Caterpillar Trasmital Bonfiglioli Doosan Sany |
◎Sales channels
As previously mentioned, KYB supplies its shock absorbers through 2 sales channels including the OEM production system for new vehicles and sale on the market for used vehicles.
Although sales of OEM products are higher, its commercially-available products sold as its private brand show great profitability and thus the company will expand the business to the global markets.
KYB’s commercially-available shock absorbers can be mounted on about 90% of Japanese, American, and European automobiles used worldwide today. What is behind such a high coverage rate is the strong relationships KYB has with major automobile manufacturers including Toyota.
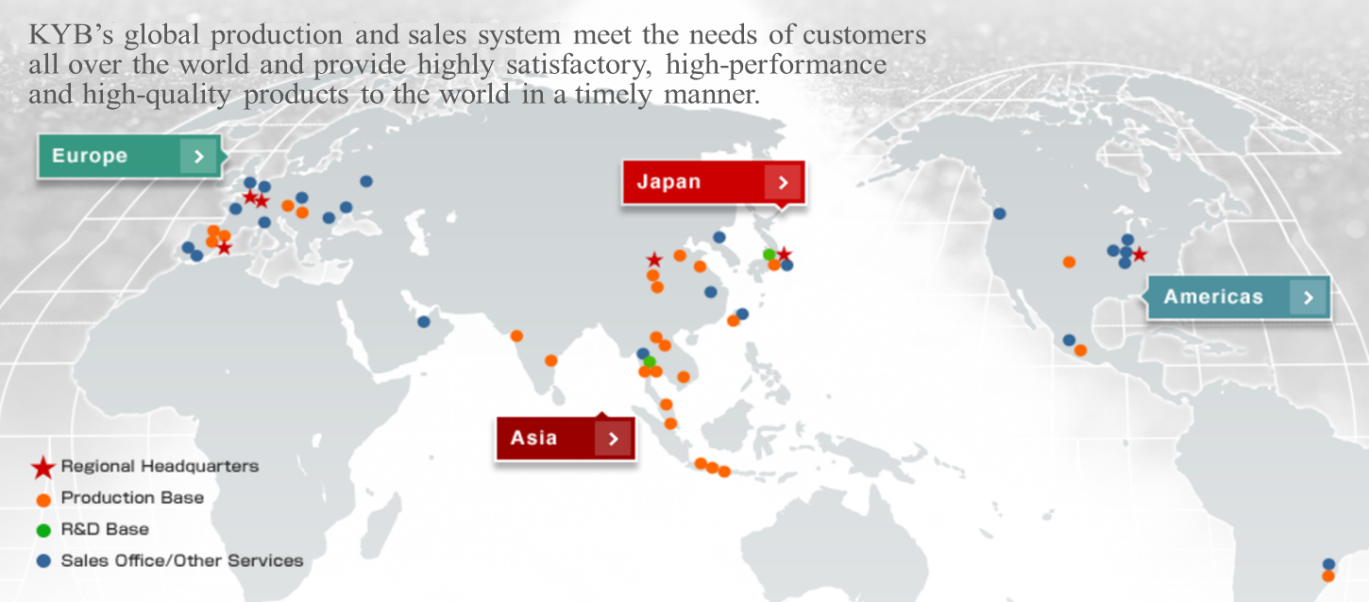
(3) Global network
In 23 countries worldwide including Japan, KYB has 46 group companies, establishing strong global networks.
| No. of Countries | No. of group companies |
Japan | 1 | 14 |
Asia | 7 | 17 |
Europe | 12 | 8 |
America | 3 | 7 |
Total | 23 | 46 |
(As of the end of June.2020)
(4) Research and Development
(Structure)
KYB has established a global and optimum research and development (R&D) structure by setting R&D bases in 5 regions including Japan, North America, Europe, China, and Thailand.
While the R&D bases in regions other than Japan basically engage in development of model products and development for enhancing product appeal such as performance improvement and cost reduction, R&D from the long-term perspectives are carried out mainly in Basic Technology R&D Center (Sagamihara-shi, Kanagawa) and Production Technology R&D Center (Kani-shi, Gifu) in Japan and R&D of highly unique prior art, etc are performed.
In addition, the know-how about production equipment designing which has been cultivated in Production Technology R&D Center and each plant is gathered in Machine Tools Center (Kani-shi, Gifu) in order to strengthen and propel internal manufacturing of equipment, jigs, and tools for which KYB has strived to boost innovative spirit and reliability.
Regarding high-functionality and systematization of its products, KYB, in addition to independent development, propels joint research and development with its clients or related equipment manufacturers. The company is also endeavoring proactively to developing advanced technology through industry-academia collaboration.
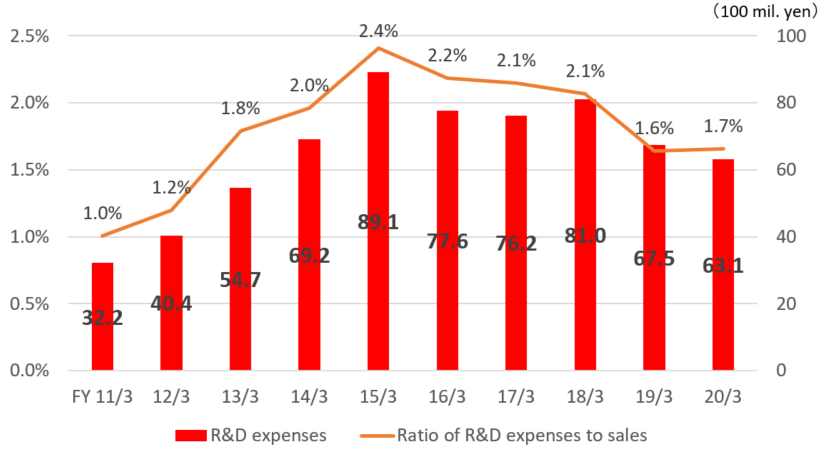
(Variation in R&D expenses)
Since the term ended Mar. 2013, the company has raised its awareness about the ratio of R&D expenses to sales, maintaining the ratio at about 2%.
(Area of focus)
KYB is propelling the development of products by dealing with performance improvement, high functionality, and systematization and considering eco-friendliness with respect to energy and environmental issues through weight saving, energy saving, reduction in environmentally hazardous substances. At the same time, it is striving to strengthen its production technology capabilities.
In addition, following the accelerated globalization, it aims to set up a strategic and global production, sales, and technological structure, including development of human resources with global outlooks and establishment of a standardized management system.
Lately, the company has focused on product development related to autonomous driving systems.
One example is the technology that integrates EPS (electronic steering) and shock absorbers.
KYB considers that the technology, which enables more comfortable and smoother driving in any road surface conditions independently of the drivers’ skills and judgment, is definitely indispensable for automobiles with the autonomous driving system.
Furthermore, KYB deems the “steering by wire” system is another technology whose importance will grow in the future.
In the conventional steering operation, movement is transmitted to the steering gear box and tires through the steering shaft, whereas the “steering by wire” system conveys steering movement via electronic signals.
Some of the system’s advantages include the capability of relieving drivers’ fatigue due to less vibration from the tires, and the capability of automatically adjusting sideslips of the car body due to strong winds which conventionally needed to be adjusted through an intentional steering operation by drivers. In addition, thanks to the “steering by wire” system, the steering wheel may not necessarily be mounted on the right front of a car, and therefore, the system’s potential for considerably changing the way automobiles are, including the design and functions, has attracted much attention.
Although several issues still exist, KYB is further brushing up the system as its unique EPS technology.
【1-5 Characteristics and strengths】
◎ Large shares in various product markets
KYB has earned a large market share of multifarious products, with the domestic share of OEM shock absorbers for automobiles being 42% and its global share being 16%, the global share of hydraulic cylinders for construction machinery being 28%, the domestic share of concrete mixer trucks being 86%
◎ Superior core technology
Such large market shares are attributed to the great trust in its products from clients as indicated by the fact that KYB has about 60% share on a global basis in Toyota Motor which vies with Volkswagen and GM for the position of the world’s largest automobile manufacturer. The basis of the clients’ trust is nothing else but the superior “hydraulic” technology that KYB has cultivated and enhanced for the past 100 years since its foundation.
KYB’s two core technologies, the “vibration control technology” represented by its shock absorbers and oil dampers for seismic isolation and vibration suppression and the “power control technology” typified by its control valves for shovels and electric power steering, have gained high reputation from clients and thus are used in diverse circumstances.
【1-6 ROE analysis】
| FY 3/16 | FY 3/17 | FY 3/18 | FY 3/19 | FY 3/20 |
ROE [%] | -2.0 | 9.3 | 8.8 | -15.0 | -55.4 |
Net income margin [%] | -0.89 | 4.09 | 3.87 | -6.01 | -16.22 |
Total asset turnover [times] | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.90 |
Leverage [times] | 2.35 | 2.37 | 2.30 | 2.59 | 3.81 |
2.Fiscal Year ended March 2020 Earnings Results
(1) Overview of consolidated results
| FY 3/19 | Composition ratio | FY 3/20 | Composition ratio | YoY | Comparison to initial forecast | Comparison to revised forecast |
Sales | 412,214 | 100.0% | 381,584 | 100.0% | -7.4% | -28,416 | +1,584 |
Gross profit | 82,115 | 19.9% | 71,254 | 18.7% | -13.2% |
|
|
SG&A expenses | 60,104 | 14.6% | 53,679 | 14.1% | -10.7% |
|
|
Segment profit | 22,010 | 5.3% | 17,575 | 4.6% | -20.2% | -3,025 | -425 |
Operating profit | -28,496 | - | -40,298 | - | - | -59,698 | -28,898 |
Profit before taxes | -29,510 | - | -41,419 | - | - | -59,919 | -29,219 |
Net income | -24,757 | - | -61,879 | - | - | -75,879 | -47,879 |
* unit: million yen. Segment profit corresponds to the operating income in the Japanese standard. Net income is the profit attributable to the owner of the parent company. The comparison to revised forecast is for the forecast announced in February 2020.
Sales dropped and loss increased due to non-fund profit and loss items such as the provision of reserves and impairment loss
Sales were 381.6 billion yen, down 7.4% year on year. The full-year results were affected by the decline in the Chinese market due to the trade friction between the U.S. and China and the appreciation of the Japanese yen, while the performance in the fourth quarter (January to March) was affected by the novel coronavirus. Sales decreased for the AC Business and the HC Business.
The segment profit was 17.6 billion yen, down 20.2% year on year. The profit of the AC business increased as it improved its profitability. The profit of the HC Business declined due to the drop in the number of orders. The company posted expenses due to nonconforming acts related to the seismic isolation/mitigation oil dampers, resulting in an operating loss of 40.3 billion yen and the loss before taxes of 41.4 billion yen. Net loss was 61.9 billion yen. Given the recent business results, the company considered collectability and partially reversed deferred tax assets. Compared to the revised forecast announced in February 2020, sales and segment profit were almost as estimated, while net income did not reach the estimate.
As rationalization, progressed after the improper act, the company posted the effects of provision for product warranties and its reversal for the cost for producing oil dampers for seismic isolation/mitigation, the expense for replacing oil dampers for seismic isolation, the cost for structural calculation, etc. and the expenses for personnel in the headquarters to deal with the improper act in the section of other expenses. The balance of provision for product warranties as of the end of March. 2020 is 45,799 million yen.
◎Trend in each region
Region | Sales | Composition ratio | YoY |
Japan | 1,711 | 44.8% | -7.4% |
Europe | 626 | 16.4% | -6.2% |
America | 351 | 9.2% | -4.1% |
China | 321 | 8.4% | -19.8% |
Southeast Asia | 296 | 7.8% | -6.7% |
Others | 510 | 13.4% | -2.5% |
Total | 3,816 | 100.0% | -7.4% |
* unit: 100 million yen
The sales in Europe and the U.S. declined, partially due to exchange rates. The Chinese markets of automobiles and construction machinery were sluggish. The ratio of overseas sales remains unchanged to the same period of the previous year, 55.2%.
(2) Trend in each segment
Sales | FY 3/19 | Composition ratio | FY3/20 | Composition ratio | YoY |
AC business | 245,807 | 59.6% | 232,101 | 60.8% | -5.6% |
HC business | 140,625 | 34.1% | 125,321 | 32.8% | -10.9% |
System products | 8,530 | 2.1% | 8,148 | 2.1% | -4.5% |
Aircraft components business | 5,625 | 1.4% | 5,481 | 1.4% | -2.6% |
Others | 11,627 | 2.8% | 10,534 | 2.8% | -9.4% |
Total | 412,214 | 100.0% | 381,584 | 100.0% | -7.4% |
Segment profit |
|
|
|
|
|
AC business | 9,680 | 3.9% | 11,691 | 5.0% | +20.8% |
HC business | 11,836 | 8.4% | 5,531 | 4.4% | -53.3% |
System products | 642 | 7.5% | 1,531 | 18.8% | +138.5% |
Aircraft components business | -1,227 | - | -2,185 | - | - |
Others | 869 | 7.5% | 999 | 9.5% | +15.0% |
Adjustment | 210 | - | 9 | - | - |
Total | 22,010 | 5.3% | 17,575 | 4.6% | -20.2% |
* unit: million yen. The composition ratio for profit is a profit margin.
① AC Business
Product | Sales | Composition ratio | YoY |
Shock absorbers for automobiles | 1,671 | 72.0% | -1.5% |
Shock absorbers for motorcycles | 282 | 12.2% | -2.8% |
Hydraulic equipment for automobiles | 321 | 13.8% | -23.8% |
Others | 47 | 2.0% | -7.2% |
Total | 2,321 | 100.0% | -5.6% |
* unit: 100 million yen
Region | Sales | Composition ratio | YoY |
Japan | 660 | 28.4% | -9.1% |
Europe | 554 | 23.9% | -5.6% |
America | 280 | 12.1% | -0.7% |
China | 150 | 6.5% | -16.7% |
Southeast Asia | 142 | 6.1% | -50.7% |
Others | 404 | 17.4% | +2.0% |
Total | 2,321 | 100.0% | -5.6% |
* unit: 100 million yen
As the profitability of the shock absorbers for automobiles (OEM) improved and fixed costs were reduced, profit increased while sales decreased.
② HC Business
Products | Sales | Composition ratio | YoY |
Hydraulic equipment for industrial use | 1,170 | 93.4% | -11.5% |
Others | 83 | 6.6% | -0.3% |
Total | 1,253 | 100.0% | -10.9% |
* unit: 100 million yen
Region | Sales | Composition ratio | YoY |
Japan | 849 | 67.8% | -7.2% |
Europe | 72 | 5.7% | -11.1% |
America | 60 | 4.8% | -20.0% |
China | 171 | 13.6% | -22.6% |
Southeast Asia | 23 | 1.8% | -20.7% |
Others | 79 | 6.3% | -8.1% |
Total | 1,253 | 100.0% | -10.9% |
* unit: 100 million yen
The reduction of fixed costs did not compensate for the decrease of orders from major clients, so sales and profit declined.
(3) Financial standing and cash flows
◎ Major BS
| End of Mar. 2019 | End of Mar. 2020 |
| End of Mar. 2019 | End of Mar. 2020 |
Current assets | 235,105 | 216,635 | Current liabilities | 206,979 | 237,931 |
Cash, etc. | 56,092 | 50,423 | Trade payables | 87,189 | 69,661 |
Trade receivables | 107,426 | 95,547 | Debts | 54,255 | 88,714 |
Inventories | 59,591 | 56,252 | Noncurrent liabilities | 78,451 | 92,707 |
Noncurrent assets | 205,969 | 193,818 | Debts | 44,046 | 33,268 |
Property, plant and equipment | 161,368 | 165,825 | Total liabilities | 285,430 | 330,639 |
Intangible assets | 7,532 | 4,874 | Net assets | 155,643 | 79,815 |
Other financial assets | 22,983 | 14,230 | Retained earnings | 86,536 | 19,617 |
Total assets | 441,074 | 410,454 | Total liabilities and net assets | 441,074 | 410,454 |
* unit: million yen. “Cash, etc.” means cash and cash equivalents. “Trade receivables” means trade receivables and other receivables. “Trade payables” mean trade payables and other payables
Current assets decreased 18.5 billion yen from the end of the previous term due to the decline in cash, trade receivables, etc. Noncurrent assets decreased 12.2 billion yen from the end of the previous term, due to the decline in other financial assets, and total assets were 410.5 billion yen, down 30.6 billion yen from the end of the previous term.
Total liabilities increased 45.2 billion yen to 330.6 billion yen from the end of the previous term due to the increase in debts. Net asset was 79.8 billion yen, down 75.8 billion yen from the end of the previous term due to the decrease in retained earnings, etc. As a result, the ratio of equity attributable to owners of parent declined from 33.9% at the end of the previous term to 18.1%.
◎ Cash Flow
| FY 3/19 | FY 3/20 | Increase/decrease |
Operating CF | 17,047 | -4,999 | -22,046 |
Investing CF | -13,616 | -21,505 | -7,889 |
Free CF | 3,431 | -26,504 | -29,935 |
Financing CF | 10,418 | 22,576 | +12,158 |
Cash and equivalents | 56,092 | 50,423 | -5,669 |
* unit: million yen
Due to the increase in pretax loss, operating CF and free CF turned negative.
The surplus of financing CF increased thanks to the increase in debts. Also, no payment of dividends was required. The cash position declined.
3.Fiscal Year ending March 2021 Earnings Estimates
(1) Regarding the earnings forecast
Due to the uncertainties owing to the spread of COVID-19, the forecast for the term ending March 2021 as well as the dividend forecast are still to be determined. The company will promptly disclose the forecast when it becomes possible to estimate results.
(2) Reflecting on the 2017 Mid-term Management Plan
According to the “2017 Mid-term Management Plan,” which was announced in May 2017, the company aimed for sales of 398 billion yen, a segment profit of 26 billion yen, and ROE of 10% for the term ended March 2020. However, unfortunately, all of them were unachieved.
The main reason for failing to achieve the targets is the nonconforming acts in the non-core business and the delay in reforming the structure of unprofitable businesses, both of which are issues that need to be reflected on. However, the company has confirmed other achievements such as releasing value-added products for automobiles, estimating the timing for transferring and integrating product lines for construction machinery, and making some progress in the reconstruction of unprofitable bases.
As for the next mid-term management plan, it is currently difficult to set a plan due to the uncertainty of the COVID-19 effects; the company will pay attention to the situation and will design and announce a plan accordingly.
4. Current management issues
(1) Quickly adapt seismic isolation/mitigation oil dampers
(Overview)
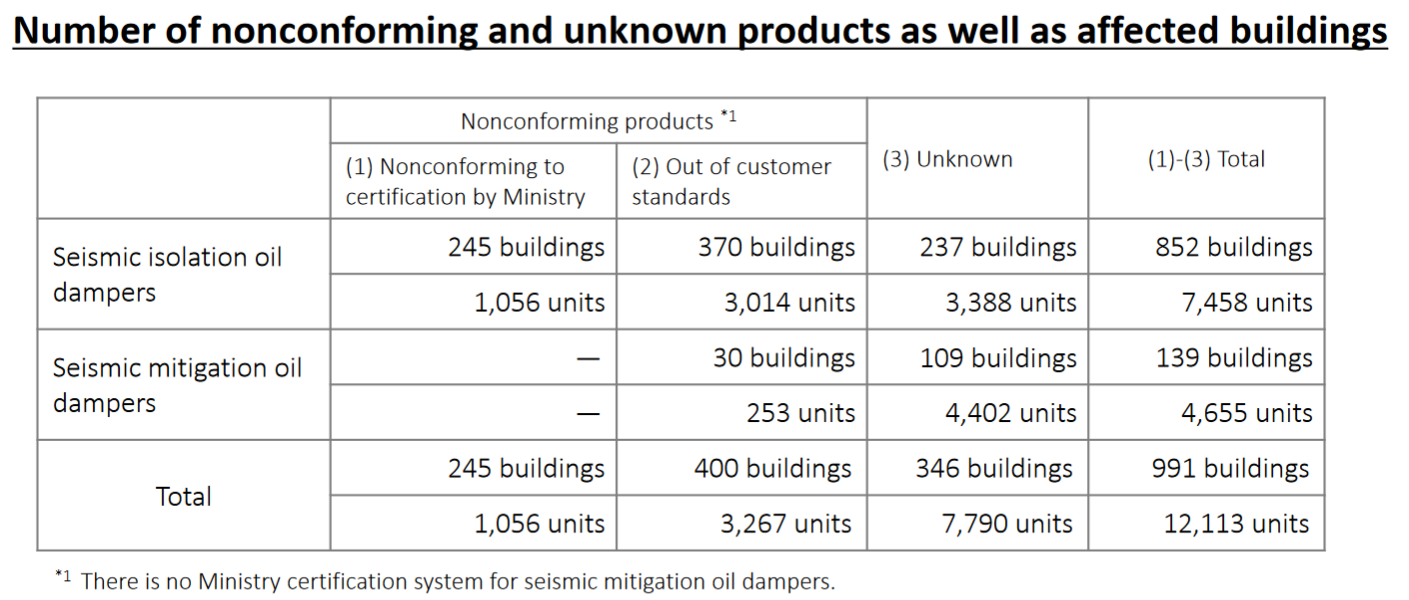
In October 2018, it was revealed that the performance inspection records for seismic isolation/mitigation oil dampers products, which are manufactured and sold by KYB and its subsidiary named Kayaba System Machinery Co., Ltd., were falsified and then the products that do not comply with the criteria approved by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT) or clients’ specs were attached to buildings.
As a result of the investigation, 991 non-conforming products and 12,113 products that cannot be judged were found as of March 31, 2020.
(Correspondence and Progress)
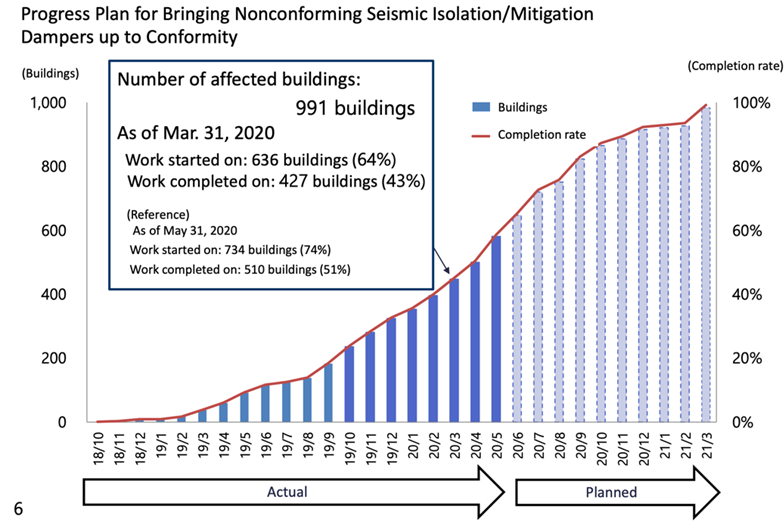
Aiming to complete work by the end of March 2021.
(Measures to prevent recurrence)
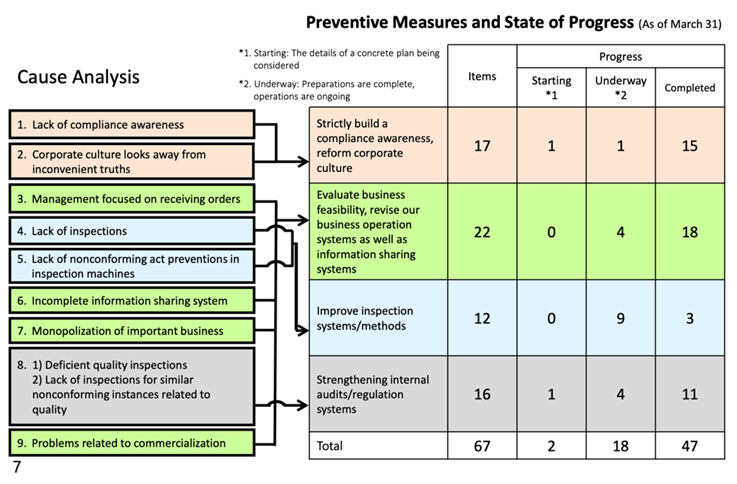
In the report, 9 causes including “lack of awareness of the rules,” “corporate culture in which staff avoid facing the truth,” and “factories which are operated assuming that orders are received,” are stated, and “enhancing the awareness of the rules and reforming corporate culture,” “Evaluation of business feasibility and review of business operation and information sharing systems,” “improvement of inspection system and method,” and “fortification of internal audit and control systems” are listed as starting points for the measures to prevent recurrence.
Then, the company started announcing the progress of measures for preventing recurrence every 3 months.
The progress overview as of March 31, 2020 is as belo
(Effects on business performance)
Regarding the expenses for this incident, the company posted 35.1 billion yen as provision of reserve for product warranties and 6 billion yen as measures for product warranties, respectively, for FY 2018, which amount to 41.1 billion yen, and posted 22.5 billion yen and 12.2 billion yen, respectively, for FY 2019, which amount to 34.7 billion yen. The total for the two terms is 75.8 billion yen.
As for the effect on cash, the company posted 6 billion yen as measures for product warranties in FY 2018; for FY 2019, it posted 11.8 billion yen as reverse of provision for product warranties, and 12.2 billion yen as measures for product warranties, which amount to 24 billion yen. The total cash outflow for the two terms was 30 billion yen.
Thus, the company will prepare enough provisions for debts mainly.
(2) Response to COVID-19 (as of June 5, 2020)
① The current situation, etc.
◎AC Business
The sales decline peaked around April to May and production adjustments were made in each region.
The company views that the key is how much the willingness to purchase automobiles, which are expensive durable consumer goods, will recover.
◎HC Business
Although the performance in China recovered quickly from the slump, the performance in developed countries remains sluggish. The company will pay attention to the resumption of infrastructure investments after the lifting of transportation restrictions and business-stimulating measures in all countries.
② Countermeasures
The company adopted countermeasures against the infection prioritizing the safety of all stakeholders and responded as follows:
◎Structural reform and thoroughgoing cost reduction
In the AC Business, the reorganization of bases was complete, while in the HC Business, the sales to local Chinese manufactures expanded. The company aims to speed up selection and concentration, etc.
Moreover, for the drastic reduction in fixed costs, the company started to rationalize indirect departments and production personnel for the reduction in volume. Additionally, it promotes a manufacturing system aimed at reducing costs, etc., in the entire company, based on the policy of thoroughly eliminating waste called KPS (Kayaba Production System).
◎Improving the cash flow
In order to improve the cash flow, the company will continue the investment necessary for growth in the future, however, will postpone or cancel capital investments.
Further, the company is working towards securing cash on hand by improving the accuracy of demand estimates and reconsidering inventory levels, which are necessary for improving inventory management and reducing the working capital.
◎Reorganization of unprofitable businesses and bases
The company will integrate and restructure the mainstay bases and secure competitiveness in accordance with the ongoing shift of areas of customer demand.
* AC Business
The company will restructure the SA bases in the European region and shift from Western Europe to Eastern Europe.
As for the EPS production, it will proceed with the restructuring that is focused on China.
Further, it will shut down the PV base in Spain.
Regarding motorcycles, the company will restructure the production bases in Asia.
* HC Business
The company will focus its efforts in China, which is the largest market for shovels.
It will develop a low-cost model.
It will complete the domestic restructuring for integrating the manufacturing of motor products.
(3) Measures considering the post-pandemic society
KYB thinks that the AC Business and the HC Business, which are the 2 core businesses, will take full advantage of the company’s strengths and as the COVID-19 pandemic changes values all over the world, the company aims to evolve into a company that will be chosen by the society.
Below are the keywords and measures to achieve this purpose:
Keyword | Goal/measure |
Selection and concentration | To shift to growing markets and fields. For the AC Business, the company will focus on expanding sales for the top 3 German luxury car brands. In the HC Business, the company will work on developing a low-cost model focused on the Chinese base. |
Automation and labor-saving | To promote innovative manufacturing. To improve the automation level of production lines and pursue unmanned operations. |
Improvement of core technologies | To create high added-value products. For the AC Business, the company will make the core technology for shock absorbers, which are the mainstay products, more sophisticated. For the HC Business, the company will develop electronically controlled hydraulic systems. |
For promoting innovative manufacturing, the company plans to introduce automated or unmanned operations domestically and abroad for production lines so that by the final term it will reduce the processing costs by 30%.
(4) Measures to regain trust: ESG measure
The company, in which trust was lost due to nonconforming acts during the inspection of seismic isolation/mitigation oil dampers, will establish normative consciousness as a foundation and strive to recover again as a company that will never cause societal trouble ever again.
To achieve this, it is necessary to establish trusting relationships with all stakeholders, thus, all staff will join hands to reform the corporate culture, manage products’ safety and quality, and address environmental issues.
5. Conclusions
The current term’s forecasts are undetermined due to the effects of COVID-19 and investors will have to wait until a quarterly announcement; we expect to have some qualitative information about the current situation if possible.
The main measures against the post-pandemic world have been taken before COVID-19 has spread, while recognizing it as a serious issue. The business environment is harsh and we will pay attention to whether the company will overcome issues with the AC Business and the HC Business, which should be addressed swiftly.
<Reference : Regarding Corporate Governance>
◎ Organization type and the composition of directors and auditors
Organization type | Company with an audit and supervisory board |
Directors | 6 directors, including 2 outside ones |
Auditors | 4 auditors, including 2 outside ones |
◎ Corporate Governance Report
Last update date: March. 9, 2020
<Basic approach>
In order to respond to the expectations of the stakeholders through realization of sustainable growth and corporate value improvement as well as fulfill the corporate social responsibility of contributing to society, it is our basic approach to pursue the development of a rapid and efficient management structure centered on the Board of Directors and establishment of fair and transparent management supervision functions and work on strengthening and enhancing corporate governance based on the following management philosophy and basic policies.
(Management philosophy)
“KYB group contributes to the society, by serving technologies and products that make people’s life safe and comfortable.”
1.Handle all matters with sincerity while adhering to the normative consciousness.
2.We shall build a corporate culture that holds high goals and full of vitality.
3.We shall maintain kindness and sincerity, cherish nature and care for the environment.
4.We shall constantly pursue creativity and contribute to the prosperity of customers, shareholders, business partners and society.
(Basic policies)
1.We shall respect the rights of shareholders and ensure their equality.
2.We shall take the benefits of stakeholders including our shareholders into consideration and endeavor to appropriately collaborate with those stakeholders.
3.We shall disclose not only the information in compliance with the relevant laws and regulations, but also actively provide the important and/or useful information to the stakeholders for their well-informed decision making.
4.The Board of Directors shall be aware of its fiduciary responsibility and accountability to the shareholders and shall appropriately fulfill its roles and responsibilities in order to promote sustainable and stable corporate growth and increase corporate value, profitability and capital efficiency.
5.We shall engage in constructive dialogue with the shareholders and make efforts to obtain their support regarding the company’s business policies and also reflect their opinions in the improvement of management.
To regain trust
As we announced in 2018, regarding nonconforming acts in the inspection process for seismic isolation/mitigation oil dampers for buildings, and issuing invoices based on false production figures for the defense equipment by our company and our subsidiary, we give our deepest and most sincere apology for all the related parties, whom we’ve caused trouble and worry. Regarding the nonconforming acts of the seismic isolation/mitigation oil dampers, we have sincerely accepted the suggestions by the external investigation committee, designed measures to prevent recurrence in the future, and we are publicly disclosing the progress every 3 months. Eliminating the related parties’ worries and concerns as fast as possible is the management’s most important issue, which we are handling in all sincerity. Moreover, regarding the nonconforming acts related to defense equipment, we have proactively reported it to the Ministry of Defense on January 28, 2019, and on January 24, 2020, we finalized the payment of 8,033 million yen as a refund to the National Treasury.
One of the measures for preventing recurrence is that we revised the management philosophy on October 1, 2019. The management philosophy is established based on the “the spirit of creation and development,” which is inherited from the founder, Shiro Kayaba. While the revision sticks to the basic philosophy, it responds to the issues pointed out by the external investigation committee, “lack of awareness of the rules,” “corporate culture in which staff avoid facing the truth,” by adding new ideas of “compliance with norms” and “facing the truth” and we strongly expressed our firm resolve to not let any nonconforming acts happen ever again. Furthermore, as adhering to the normative consciousness by all individuals is what best supports “quality management,” which we have raised as the foundation of management from the beginning, we will take action while considering that nurturing and maintaining it as the first principle.
<Reasons for Non-compliance with the Principles of the Corporate Governance Code (Excerpts)>
Principles | Reasons for not implementing the principles |
(Supplementary principle 4-1-3 Successive plan for CEO, etc.) | Our company deems successive plans for CEO and the like as an important issue for sustainable growth and medium to long-term improvement of our corporate value. From 2016 we have established a committee of nomination formed with an internal director and an unaffiliated director so we can improve our transparency in terms of the process of nomination. From now on we will consider requirements and development policy regarding CEO and other positions, taking account of the management environment surrounding our company and the corporate culture. At the same time, we will give consideration to the supervision system by the board of directors. |
(Principle 4-11 Precondition for ensuring effectiveness of the board of directors and board of corporate auditors) | The Company does not have female directors. However, we appoint people we judge suitable for incorporating diverse values into management as directors, sufficiently considering the balance in knowledge of the whole board of directors, experience (including international experience), abilities, etc., without distinguishing them based on personal attributes such as gender, as stated in 4-11-1. |
<Disclosure Based on the Principles of the Corporate Governance Code (Excerpts)>
Principles | Disclosure contents |
Principle 1-4【So-called strategically held shares】 | (1.)Policy on strategic shareholding From the perspective of medium to long-term improvement of corporate value, our company, when judging as necessary, strategically holds shares through which the relationship of trust and the business relationship are expected to be maintained or strengthened regarding business strategies and operations after comprehensively judging the growth potential and economic rationality of such shares. With regard to strategically held shares, we check the rationality of continued holdings in consideration of whether or not the benefits of holdings are commensurate with the Company’s cost of capital, etc., at a meeting of the board of directors every year. We plan to sell shares when we consider that the rationality in holding them has weakened. (2. )Policy on exercise of voting rights Before exercising the voting rights of shares that our company strategically holds, we consider for each case whether the strategic shareholding contributes to medium to long-term improvement of our corporate value and increase in shareholder return and make judgment after giving thorough consideration to the management policies and business strategies of the company that issues relevant shares. |
Principle 5-1【Policy on constructive dialogue with shareholders】 | In our company, the global finance executive presides and the IR office of the accounting head department deals with shareholders and investors in order to encourage constructive dialogue with shareholders and the like. The IR office has established a system that allows appropriate response in collaboration with related departments of our company to enrich such dialogue. We hold financial results briefings for analysts and institutional investors, where the president and the global finance executive describe our management strategies and financial conditions, once in every half year. In addition, we carry out individual interviews as requested, and strive for proactive communication with overseas shareholders and institutional investors through attendance at conferences in and outside Japan and individual IR activities abroad. Opinions and requests obtained from shareholders and investors through our IR activities are conveyed on a regular basis to the board of directors and the management as feedback in order to share information. Our company gives meticulous attention to handling of insider information not to inflict losses on each other in dialogue with shareholders and investors. Accordingly, for a period beginning with the following day of the date of settlement and ending with the day when financial statements are announced, which is called a quiet period, our company refrains from having dialogue with shareholders and investors and endeavors to conduct thorough internal information management. |
This report is intended solely for information purposes, and is not intended as a solicitation to invest in the shares of this company. The information and opinions contained within this report are based on data made publicly available by the Company, and comes from sources that we judge to be reliable. However we cannot guarantee the accuracy or completeness of the data. This report is not a guarantee of the accuracy, completeness or validity of said information and or opinions, nor do we bear any responsibility for the same. All rights pertaining to this report belong to Investment Bridge Co., Ltd., which may change the contents thereof at any time without prior notice. All investment decisions are the responsibility of the individual and should be made only after proper consideration. Copyright(C) 2020, All Rights Reserved by Investment Bridge Co., Ltd.. |
The back number of Bridge Reports (KYB:7242) and contents of Bridge Salon (IR seminars) can be seen at www.bridge-salon.jp/


