Bridge Report:(7776)CellSeed First Half of Fiscal Year December 2019
 Setsuko Hashimoto, President &CEO | CellSeed Inc.(7776) |
 |
Company Information
Market | JASDAQ |
Industry | Precision Instrument (Manufacturing) |
President | Setsuko Hashimoto, Ph.D. |
HQ Address | Telecom Center Building, Aomi 2-5-10, Koto-ku, Tokyo |
Year-end | December |
Homepage |
Stock Information
Share Price | Number of shares issued (excluding treasury shares) | Total market cap | ROE Act. | Trading Unit | |
¥502 | 11,459,265 shares | ¥5,753 million | 9.8% | 100 shares | |
DPS Est. | Dividend yield Est. | EPS Est. | PER Est. | BPS Act. | PBR Act. |
- | - | - | - | 92.91 | 5.4 x |
*Stock price as of closing on August 27, 2019. Number of shares at the end of the most recent quarter excluding treasury shares. ROE is the actual values of the previous term. BPS is the actual values of 1H
Earnings Trend
Fiscal Year | Sales | Operating Profit | Current Profit | Net Profit | EPS | DPS |
December 2015 | 193 | -568 | -531 | -535 | - | - |
December 2016 | 100 | -1,413 | -1,415 | -1,414 | - | - |
December 2017 | 85 | -956 | -964 | -966 | - | - |
December 2018 | 1,026 | 140 | 140 | 129 | 11.35 | - |
December 2019 Est. | 300 | -1,100 | -1,100 | -1,100 | - | - |
* Estimates are those of the company (Unit: million yen, yen).
This Bridge Report presents the first half of the fiscal year ending December 2019 earnings results and the future outlook of CellSeed Inc.
Table of Contents
Key Points
1. Company Overview
2. First Half of Fiscal Year ending December 2019 Earnings Results and the Future Outlook
3. Mid-term Business Plan(Fiscal Year 2019 to 2021)
4. Conclusions
<Reference: Regarding Corporate Governance>
Key Points
- The sales for the 2nd quarter of the term ending December 2019 (cumulative total) were 162 million yen, down 53.3% year on year, and operating loss was 321 million yen (40 million yen in the same period of the previous year). In the regenerative medicine supporting business, the company posted sales of 57 million yen from the first regenerative medicine project the company undertook. In the cell sheet regenerative medicine business, the company posted sales of 105 million yen from the alliance with MetaTech in Taiwan (in the same period of the previous year, sales of 325 million yen were posted due to the partial provision of study data to MetaTech). As for profit and loss, SG&A expenses augmented due to the increases in the outsourcing of development (research and development expenses) and expenses for maintaining Cell Processing Facility, while sales declined.
- There is no revision to the full-year earnings forecast, and it is estimated that sales will be 300 million yen, down 70.8% year on year and operating loss will be 1.1 billion yen (an operating income of 140 million yen posted in the previous term). In both the regenerative medicine supporting business and the cell sheet regenerative medicine business, the company is projected to post sales of 150 million yen (in the previous term, the company posted sales of 960 million yen in the cell sheet regenerative medicine business, due to the revenue from the contract on exclusive business alliance in Taiwan).
- The efficacy of the epithelial cell sheet for esophageal regeneration has not been verified, and it is necessary to conduct additional clinical trials. However, the company is not pessimistic because this does not mean that its efficacy is doubtful. As for the regenerated cartilage sheets, the treatment with autologous cell sheets was approved as advanced medicine. Once advanced medicine starts, the contracted manufacturing of regenerated cartilage sheets will contribute to revenue and the company will advance significantly toward the approval for the manufacturing and sale of autologous cell sheets. In 1Q, Cell Processing Facility started the contracted manufacturing of cell sheets. Outside Japan, MetaTech submitted a notification on the clinical trial for the epithelial cell sheet for esophageal regeneration in Taiwan at the end of the previous term. After many twists and turns, several buds of revenue are steadily growing. The company is developing the structure of a regenerative medicine maker. We would like to pay attention to the progress of the mid-term business plan aimed at moving into the black in fiscal 2021.
1. Company Overview
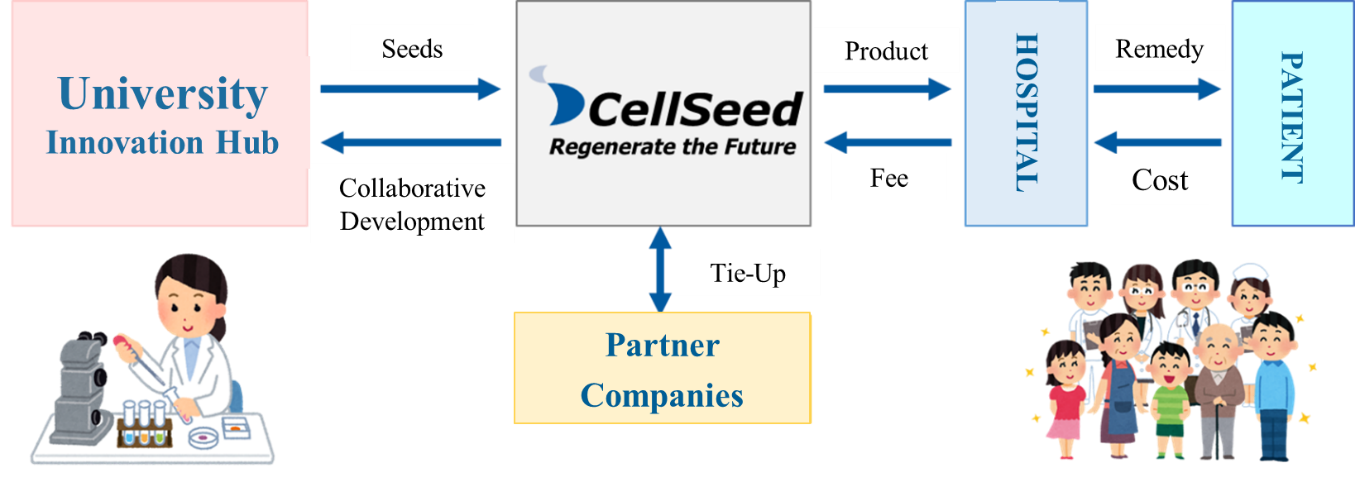
Regenerative medicine is a new kind of medicine for regenerating and curing lost, damaged or deteriorated tissues. CellSeed uses the fundamental technologies of “cell sheet engineering” developed in Japan by Professor Okano of the Tokyo Women’s Medical University in its “cell sheet regenerative medicine” that employs “cell sheets” for the cell regenerative medicine business, and the regenerative medicine support business, where temperature responsive cell cultureware used to fabricate cell sheets are developed and sold and the regenerative medicine consignment services, which support for research and development and commercialization of regenerative medicine, is provided.
Mission: We take the initiative of contributing to global health care in the valuable and innovative field of regenerative medicine.
Using the outcomes of research at universities as seeds, the company conducts clinical trials and develop regenerative medicine products, with the aim of contributing to medicine around the world.
(Source: the company)
1-1.Business Description
Cell sheet regenerative medicine business
Commercialization through the cultivation of new businesses is being conducted in joint clinical research efforts with universities. The current development pipeline consists of the two main realms of “epithelial cell sheet for esophageal regeneration” based upon the fundamental technology of “regenerative cell sheet engineering”, and “regenerated cartilage sheet” of knee osteoarthritis.
A clinical trial of the “epithelial cell sheet for esophageal regeneration” was completed in the first quarter of fiscal 2019 in Japan; however, the company has been required to perform another clinical test, and thus it will submit a clinical trial notification for the additional trial during fiscal 2019 with the aim of applying for approval for manufacturing and sale in fiscal 2022. As for business in overseas nations, CellSeed entered into a business alliance with MetaTech (AP) Inc. (hereinafter referred to as MetaTech) in Taiwan in April of fiscal 2017 and the company submitted a clinical trial notification at the end of December 2018.
Meanwhile, the “regenerated cartilage sheet,” for which Tokai University Hospital had submitted an application for approval, was approved as advanced medicine in January 2019, allowing the company to prepare for starting to offer the medical treatment at the university hospital. Furthermore, CellSeed has licensed out the product to MetaTech, and MetaTech is putting forth efforts to commercialize it in Taiwan. Application of regenerative medicine products using the “cell sheet engineering” technology is not limited to the esophagus or knee cartilage. Clinical research is being propelled forward with regard to treatment of various tissues. The company is now considering and selecting the third development pipeline and geographic region and will embark on product development once all the necessary arrangements have been made, such as contracts with research institutions.
Regenerative medicine supporting business
Consigned regenerative medicine services for the comprehensive support regarding regenerative medicine and development, manufacture, and sales of temperature responsive cell cultureware are being conducted. The main services provided within the consigned regenerative medicine services include regenerative cell sheet product manufacturing method development, consigned manufacturing, operational and application support, cell culturing technician training and others.
 | UpCell® Temperature-responsive cell cultureware for collecting cell sheets
|
 | RepCell ™ Temperature-responsive cell cultureware for collecting cells |
 | HydroCell ™ The ultralow adhesion cell cultureware |
|
|
(Source: the company)
Development of Manufacturing Methods for Cell Sheet Products and Contract Manufacturing
CellSeed develops and manufactures mainly cell sheet products on consignment from pharmaceutical companies and research institutions. The company has hired clinical cultivatists certified by the Japanese Society for Regenerative Medicine, and its staff with extensive experience in cell culture develop manufacturing methods for regenerative medicine products using high-quality cell sheet, etc. and manufacture such products at the Cell Processing Facility (CPF) approved for manufacturing and processing specified cell products. As for the regenerated cartilage sheet that is being researched and developed in the cell sheet regenerative medicine business, Tokai University applied for the approval as Advanced Medicine B, and it was approved in January 2019. The cell sheets used for this advanced medicine are scheduled to be cultured at Cell Processing Facility (processing entrusted by Tokai University).
Management of Facilities and Support for the Application
“The Act on Safety of Regenerative Medicine” stipulates operation of buildings and facilities, and cell processing, requiring submitting notification and approval application to the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare for each Cell Processing Facility. CellSeed provides support services of submission of notification and preparation of application forms for manufacturing and processing specified cell products, and preparation of documents necessary for operation. It also assists clients with administrative procedures required, such as preparation of documents for consultation with the authorities concerned that will be necessary for submitting application, including clinical trial notification, and preparation of application forms.
Training and Education in Cell Culturing Technology
CellSeed trains and educates cell culturing engineers who have little or no experience in manufacturing or processing cell sheets about various matters, including the procedures for culturing and exfoliating cell sheets.
1-2. Cell Processing Facility (CPF)
This Cell Processing Facility boasts of 763 square meters of floor space, and has an automated monitoring system to control cleanliness, room pressure, temperature and humidity, Operational status of equipment (Incubator, Reagent stocker etc.) and a surveillance camera system throughout the entire facility. In addition, this facility is only 20 minutes drive from Haneda International Airport. In March 2017, “manufacture and process specified cell products ” in accordance with Article 35, paragraph 1 of the Act on Safety of Regenerative Medicine was granted by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Consequently, CellSeed is able to provide consigned processing business for cell sheets.

(Source: the company)
2. First Half of Fiscal Year ending December 2019 Earnings Results and Full-Year Estimates
2-1 Consolidated Earnings of First Half
| 1H FY 12/ 18 | Share | 1H FY 12/ 19 | Share | YY Change | Initial Est. | Divergence |
Sales | 347 | 100.0% | 162 | 100.0% | -53.3% | 180 | -9.8% |
Gross Income | 337 | 97.1% | 133 | 82.3% | -60.5% | - | - |
SG&A | 378 | - | 454 | - | +20.1% | - | - |
Operating Income | -40 | - | -321 | - | - | -450 | - |
Ordinary Income | -40 | - | -320 | - | - | -450 | - |
Net Income | -41 | - | -319 | - | - | -450 | - |
* unit: million yen
Sales were 162 million yen, down 53.3% year on year, and operating loss was 321 million yen (40 million yen in the same period of the previous year).
Sales were 162 million yen, down 53.3% year on year. The sales from the regenerative medicine supporting business were 57 million yen (22 million yen in the same period of the previous year). In the service of undertaking regenerative medicine projects based on Cell Processing Facility, the company posted sales from the first case of the first project entrusted by Tokyo Women's Medical University in the first quarter, and sales from the second and third cases in the second quarter.
On the other hand, the sales of the cell sheet regenerative medicine business declined 67.7% year on year to 105 million yen. The company posted sales from some business activities based on the exclusive business alliance with MetaTech regarding the cell sheet regenerative medicine business in Taiwan (in the same period of the previous year, the company posted sales of 325 million yen from the partial provision of development data to MetaTech).
As for profit and loss, SG&A expenses augmented 20.1% year on year, due to the increases in the cost for outsourcing development tasks and expenses for maintaining Cell Processing Facility, while gross income declined 60.5% year on year due to the drop in sales. Research and development expenses rose 31.6% year on year to 208 million yen. The reason why the loss fell below the initial estimate is that the cost for outsourcing development tasks and expenses for maintaining Cell Processing Facility were lower than the initial estimates.
Sales and Operating Income by Segment
| 1H FY12/18 (Cumulative total) | Share | 1H FY12/19 (Cumulative total) | Share | YY Change |
Regenerative medicine supporting business | 22 | 6.6% | 57 | 35.3% | +150.4% |
Cell sheet regenerative medicine business | 325 | 93.4% | 105 | 64.7% | -67.7% |
Sales, Total | 347 | 100.0% | 162 | 100.0% | -53.3% |
Regenerative medicine supporting business | -42 | - | -20 | - | - |
Cell sheet regenerative medicine business | 152 | - | -127 | - | - |
Adjustments | -150 | - | -173 | - | - |
Operating Income, Total | -40 | - | -321 | - | - |
*Unit: million yen
Financial Conditions
| Dec. 18 | May. 19 |
| Dec. 18 | May. 19 |
Cash | 1,057 | 987 | Accounts Payable | 56 | 57 |
Inventories | 57 | 53 | Advances received | 64 | 15 |
Current Assets | 1,505 | 1,116 | Total Interest-Bearing Liabilities | - | - |
Tangible Assets | 19 | 26 | Liabilities | 174 | 116 |
Investments and Others | 61 | 61 | Net Assets | 1,411 | 1,088 |
Noncurrent Assets | 81 | 88 | Total Liabilities and Net Assets | 1,586 | 1,205 |
*Unit: million yen
Cash Flow(CF)
| 1H FY12/18 (Cumulative total) | 1H FY12/19 (Cumulative total) | YY Change | |
Operating Cash Flow(A) | -102 | -58 | +44 | - |
Investing Cash Flow (B) | 0 | -7 | -6 | - |
Free Cash Flow(A+B) | -103 | -66 | +37 | - |
Financing Cash Flow | 3 | - | - | - |
Cash and Equivalents at the end of term | 1,240 | 987 | -253 | -20.4% |
* Unit: million yen
2-2 Consolidated Financial Estimates
| FY 12/ 18 Act. | Ratio to sales | FY 12/ 19 Est. | Ratio to sales | YoY |
Sales | 1,026 | 100.0% | 300 | 100.0% | -70.8% |
Operating Income | 140 | 13.6% | -1,100 | - | - |
Ordinary Income | 140 | 13.6% | -1,100 | - | - |
Net Income | 129 | 12.6% | -1,100 | - | - |
*Unit: million yen
Research and development expenses will augment in the second half.
In both the regenerative medicine supporting business and the cell sheet regenerative medicine business, the company is projected to post sales of 150 million yen respectively (in the previous term, the company posted sales of 960 million yen in the cell sheet regenerative medicine business, due to the revenue from the contract for exclusive business alliance in Taiwan). Operating loss is estimated to increase to 1.1 billion yen, due to the decline in sales and the augmentation of research and development expenses.
3. Mid-term Business Plan(Fiscal Year 2019 to 2021)
3-1 Basic policies
・ | To apply for the approval for the manufacturing and sale of the epithelial cell sheet for esophageal regeneration (2022) |
・ | To accelerate development for starting clinical trials for the regenerated cartilage sheets in 2021 |
・ | To work on the development of products for the next phase (development of periodontal ligament cell sheets: commencement of discussions with Tokyo Medical and Dental University) |
・ | To develop organizational structures and infrastructure |
・ | To seize more earning opportunities by developing new products for supporting regenerative medicine and promoting contract manufacturing |
・ | To form business alliance for global business expansion (establishment of a joint venture with MetaTech: conclusion of a memorandum of understanding) |
3-2 Activities for completing the mid-term business plan
As for the epithelial cell sheet for esophageal regeneration, the company aims to apply for the approval for manufacturing and sale as soon as possible, and for the regenerated cartilage sheet, it will prepare for the contract manufacturing after the start of Advanced Medicine B with the regenerated autologous cartilage sheet, while accelerating the development of allogeneic cartilage regeneration sheets. After the epithelial cell sheet for esophageal regeneration and the regenerated cartilage sheet, the company plans to develop periodontal ligament cell sheets and commenced discussions with Tokyo Medical and Dental University. It will also work on the development of organizational structures and infrastructure. In the regenerative medicine supporting business, the company will proceed with the development of new products for supporting regenerative medicine and expand sales, while aiming to seize more earning opportunities in the business of undertaking tasks. To make CellSeed recognized, it hosted and held the first cell sheet engineering innovation forum in July. There were around 160 participants from academia and enterprises.
In order to expand made-in-Japan cell sheet engineering around the world, the company plans to form business alliance with overseas enterprises actively. As part of this activity, it concluded a memorandum of understanding for establishing a joint venture company with MetaTech in Taiwan.
Epithelial Cell Sheet for Esophageal Regeneration
22,000 patients within Japan are diagnosed with esophageal cancer every year (90% of the esophageal cancer cases diagnosed within Japan are squamous cell carcinoma), with 11,500 patients dying every year. In addition, the rate of occurrence and death related to esophageal cancer in male patients is five times that of female patients, with five year survival rates for males and females said to be 36% and 44%, respectively. The endoscopic resection surgery (ESD) was posted in the drug price list from 2008 and is on the rise, but its side effect of esophageal stricture after surgery has been recognized as a problem.
The company strives to put the epithelial cell sheet for esophageal regeneration into practice, aiming to improve patients’ quality of life by reducing the frequency of occurrence of esophageal strictures.
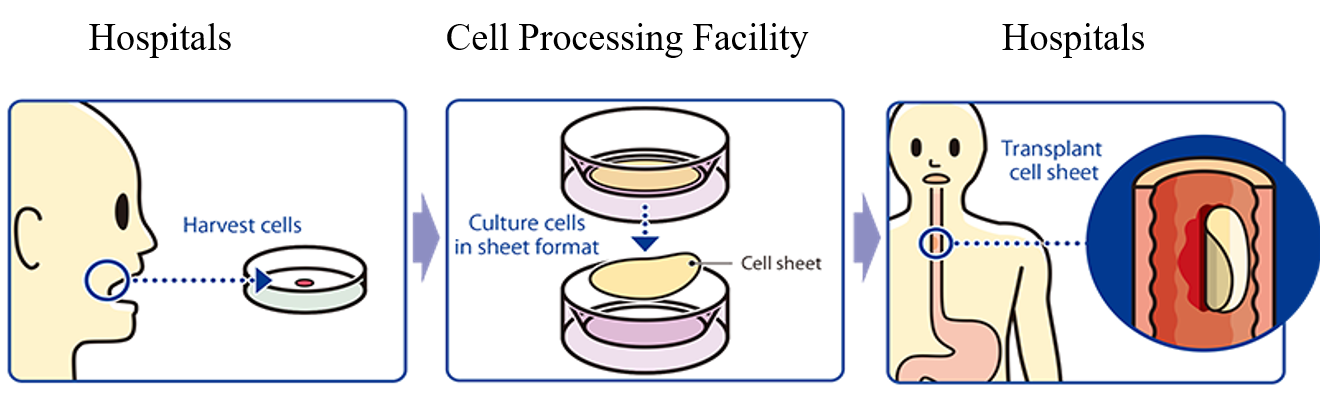
Treatment with “the epithelial cell sheet for esophageal regeneration”
The treatment with “the epithelial cell sheet for esophageal regeneration” was developed by Tokyo Women's Medical University, in order to solve the problem with the regenerative medical treatment against esophageal cancer (treatment of esophageal tear and prevention of stenosis). Cells taken from the oral mucosa of a patient are cultured for about 2 weeks using the temperature-responsive cell cultureware to produce cell sheets. In conjunction with the process of culturing cell sheets, an endoscopic surgery for esophageal cancer excision is performed and the cell sheets are transplanted to the part of an esophageal tumor in the patient.
(Source: the company)
Efforts to obtain approval inside and outside Japan
There have been 30 clinical cases from 2008 to 2014, 10 cases at TWMU, 10 cases at TWMU and Nagasaki University (Long-distance transportation test: Collect cells at Nagasaki University, Culture at TWMU, Transplant at Nagasaki University), and 10 cases at Karolinska University Hospital (Sweden). CellSeed has concluded Basic Agreement for Development with TWMU and has taken over the research results.
In Japan, the company finished with case registration in the second quarter of fiscal 2018 and completed the clinical trials in the first quarter of fiscal 2019. No side effect was reported in the clinical trials, meaning that no safety issues were confirmed; on the other hand, the efficacy rate of the “effectiveness of stricture prevention 8 weeks after endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD)” (rate of cases of non-stenosis), which was an important evaluation item, was only 12.5%, which did not prove the statistical superiority to the threshold response rate (the rate of cases of non-stenosis in patients who did not receive any treatment after ESD). Accordingly, it is necessary to conduct an additional clinical trial, and the company plans to submit a notification on the clinical trial by the end of this term. The additional clinical trial is scheduled to end in fiscal 2021, and the company plans to apply for the approval for manufacturing and sale in fiscal 2022.
Outside Japan, the company signed a contract for business alliance with MetaTech in the first quarter (April.) of fiscal 2017 and submitted a notification on a clinical trial at the end of December 2018. In Europe, it had discussions with European Medicines Agency (EMA) in fiscal 2016, to obtain approval.
Regenerated Cartilage Sheet (Indication: knee osteoarthritis)
Knee osteoarthritis is refractory articular cartilage degeneration that progresses slowly. The number of its patients (aged 40 years or older) in Japan is estimated to be 25.3 million, and the number of patients suffering from symptoms is estimated to be 8 million (a survey by the 22nd Century Medical & Research Center, the University of Tokyo Hospital). In addition, it is forecasted that the number of patients will increase due to the aging population, and it is considered imperative to cope with this disease from the viewpoints of the healthy life expectancy of citizens, nursing care and medical costs.
According to Comprehensive Survey of Living Conditions by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare in 2013, locomotor disabilities accounted for 25% of the reasons why people became in need of support or nursing care.
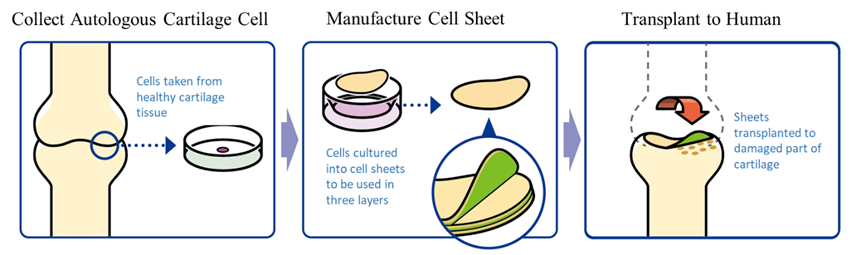
Treatment with “Regenerated Cartilage Sheet”
(Source: the company)
The company researched the “regenerated cartilage sheet” with Professor Masato Sato of Department of Orthopaedics, Tokai University. Its indications are cartilage defects and osteoarthritis caused by sport injury and aging. As of now, there are no methods to cure the injury completely, but the collaborative research with Professor Sato is aimed at regenerating the cartilage surface radically. The cartilage of the knee is called hyaline cartilage, which is hard and excellent in cushioning and abrasion resistance properties, differing from the cartilages of the ear, nose, etc., and it is difficult to regenerate. However, it was confirmed in clinical research that the “regenerated cartilage sheet,” which is being researched collaboratively with the professor, can regenerate the cartilage of the knee as hyaline cartilage.
Prosthetic joints can be used for curing the knee osteoarthritis, but they have a service life of 15 to 20 years, so the treatment with prosthetic joints cannot be said to be radical. Compared with other companies’ regenerative medicine for knee joints, CellSeed’s treatment with cell sheets is excellent in settling into the defective cartilage, so that it can regenerate the cartilage surely.
Treatment with Autologous Cell Sheets
Professor Masato Sato started clinical research into autologous cartilage sheets in 2010 and has completed the study of 8 cases. In January 2019, “the cartilage regeneration treatment with autologous cell sheets” proposed by Tokai University Hospital was approved as Advanced Medicine B at “the 71st advanced medical care meeting” hosted by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare.
In collaboration with Professor Masato Sato, the company has searched for factors that determine the efficacy of cartilage cell sheets for curing the knee osteoarthritis and conducted research for the treatment with regenerated allogeneic cartilage sheets, through the project of Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED). The company undertakes the manufacturing of the regenerated cartilage sheets, for the cartilage regeneration treatment with autologous cell sheets, which was approved as advanced medicine.
Advanced Medicine B means the treatments using advanced medical technologies and the medical technologies whose efficacy and safety have satisfied certain criteria although the approval for sale is still to be obtained. Since the company has not yet obtained the approval for sale, patients need to pay the treatment fee all by themselves, but they can combine this treatment with the ones covered by public health insurance unlike the case of treatments not covered by public health insurance. (In principle, treatments not covered by public health insurance cannot be combined with treatments covered by public health insurance.)
Treatment with allogeneic cartilage sheets
As for the treatment with allogeneic cartilage sheets, Professor Masato Sato started clinical research (transplantation of allogeneic cartilage cell sheets) in Feb. 2017, and studied the first case. In 3 years until March 2020, he plans to study 10 cases, and in 2021, enterprise-led clinical trials are scheduled to be conducted. In parallel with clinical research, they plan to develop a cell bank and automate the manufacturing of cell sheets.
In the treatment with allogeneic cartilage sheets, cartilage tissue is taken from a polydactyly patient, and cultured for 2 to 3 weeks to produce cell sheets, and the cell sheets are transplanted (the cartilage cells of the finger cut from an infant who had 6 fingers congenitally, and used after obtaining consent). The treatment with allogeneic cartilage sheets has been adopted in the project for developing evaluation methods, etc. for the industrialization of regenerative medicine (support for acceleration of development of regenerative medicine seeds) of AMED (project period: Oct. 2018 to Mar. 2021).
Regenerative Medicine Consignment Services
The company provides a wide range of regenerative medicine services on consignment in relation to cell sheet products, including development of manufacturing methods and contract manufacturing, facility management and application support, and training and education in cell culturing technology.
The company engages in manufacturing on consignment and quality testing for cell sheet products as services of development of manufacturing methods and contract manufacturing for cell sheet products. These services are characterized by a number of staff members with extensive knowledge and experience with cell culturing practices, such as clinical cultivatists certified by the Japanese Society for Regenerative Medicine, and production of cell sheets using the company’s product UpCell® at the facility with permission for manufacturing and processing specified cell products (Facility Number.: FA3160008). CellSeed received an order in November 2018 for a project related to manufacturing of the mesenchymal stem cell sheet derived from the autologous periodontal membrane used in a research project for industrializing regenerative medicine, “Periodontal Tissue Regenerative Therapy with Periodontal Ligament-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Sheets,” by the Institute of Advanced Biomedical Engineering and Science, Tokyo Women’s Medical University (with Professor Takanori Iwata as the person in charge of this research and development project), which was adopted by AMED. The order was received in November 2018, and sales were posted in the cumulative 2nd quarter.
The company also offers facility management and application support services, such as preparation of application forms for manufacturing and processing specified cell products, application and submission, consulting for document preparation, maintenance of facility equipment and management systems, and management support. The training and education in cell culturing technology include training programs regarding culturing and exfoliation of cell sheets.
Project for developing the third product
In Aug. 2019, the company started discussions with Tokyo Medical and Dental University regarding the details about clinical development of allogeneic periodontal ligament-derived mesenchymal stem cell sheets (periodontal ligament cell sheets). They will develop a regenerative medicine product for periodontal regeneration. At Tokyo Medical and Dental University, the leading professor Takanori Iwata conducted doctor-led clinical trials, transplanting periodontal ligament cell sheets to patients of serious periodontitis that cannot be cured with the existing treatments, and evaluating its safety and efficacy. In these doctor-led clinical trials, the company undertook the manufacturing of periodontal ligament cell sheets.
Holding of a forum hosted by CellSeed
On July 19, 2019, the company held the first cell sheet engineering innovation forum at Tokyo Metropolitan Industrial Technology Research Institute (135 people in the audience and 23 poster presenters). The lecturers were to be Teruo Okano, a professor emeritus of Tokyo Women's Medical University and the director of Cell Sheet Tissue Engineering Center of the University of Utah; Masato Sato, a professor of Department of Orthopaedics, School of Medicine, Tokai University; Takanori Iwata, a senior professor of Department of Periodontology, Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences, Tokyo Medical and Dental University; Goshi Shiota, a professor of Division of Molecular and Genetic Medicine, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Tottori University; and Hidekazu Sekine, a lecturer of Institute of Advanced Biomedical Engineering and Science, Tokyo Women’s Medical University.
The themes of posters were research using “cell sheets” or “temperature-responsive cell cultureware.” Mr. Tetsuya Imamura of School of Medicine, Shinshu University received the most excellent poster award, while Mr. Takumi Takahashi of Department of Orthopaedics, School of Medicine, Tokai University and Mr. Tetsutaro Kikuchi of Institute of Advanced Biomedical Engineering and Science, Tokyo Women’s Medical University received the excellent poster award.
Promotion of Business Alliances toward Global Business Expansion
The company actively participates in exhibitions inside and outside Japan for business alliances and licensing.
DUPHAT (Feb., Dubai) | Bio International (Jun., Philadelphia) |
Bio Asia (Mar., Tokyo) | Bio Asia (Jul., Taiwan) |
Bio Europe Spring (Mar., Vienna) | Scheduled: Bio Japan (Oct., Yokohama) |
China BIO (May, Shanghai) | Scheduled: Bio Europe (Nov., Hamburg) |
Establishment of a joint venture company
The company concluded a memorandum of understanding for establishing a joint venture company with MetaTech in Taipei, Taiwan, for the purpose of developing products for regenerative medicine and treatment methods while applying cell sheet engineering based on the technologies provided by universities and research institutes in Japan or Taiwan.
Name | Cell Sheet R&D Company (provisional name) |
Location | Taipei, Taiwan |
Business description | R&D and commercialization of the cell sheet regenerative medicine business based on the technologies provided by universities, etc. in Taiwan and Japan |
Capital contribution ratio | The capital contribution ratio of the company is to be at the same level as that of MetaTech. A final decision will be made with other investors. |
Date of establishment | To be established in September 2019 |
3-3 Fund procurement: Issuance of the 18th share acquisition right (with a strike price revision clause)
By issuing the share acquisition right, the company will procure an estimated 1,567 million yen.
Allocated t | Barclays Bank PLC |
Date of allocation | September 2, 2019 |
No. of share acquisition rights issued | 28,000 |
Issuance price | 2,884,000 yen |
Fund procurement amount | 1,567,101,000 yen (roughly estimated gross amount) |
Exercise period of the share acquisition right | 1 year (from Sep. 3, 2019 to Sep. 4, 2020) |
Purposes of use of the fund | R&D, contribution to the joint venture in Taiwan, support for development, and business operation |
3-4.Numerical goals
| FY 12/ 19 Est. | FY 12/ 20 (goal) | FY 12/ 21 (goal) |
Regenerative medicine supporting business | 150 | 225 | 300 |
Cell sheet regenerative medicine business | 150 | 125 | 1,700 |
Sales | 300 | 350 | 2,000 |
Operating Income | -1,100 | -1,300 | 300 |
Ordinary Income | -1,100 | -1,300 | 300 |
Net Income | -1,100 | -1,300 | 225 |
The regenerative medicine supporting business is expected to show steady growth thanks to the first order that the company received in November 2018 in the regenerative medicine consignment services; however, CellSeed as a whole is projected to continue making upfront investment in fiscal 2019 and 2020. The company is expected to seek opportunities for business alliances in the cell sheet regenerative medicine business to earn revenue in fiscal 2021.
4. Conclusions
The efficacy of the epithelial cell sheet for esophageal regeneration was not verified in the previous clinical trial, and it is necessary to conduct additional clinical trials, but this does not mean that its efficacy is doubtful. The reason for the failure to verify the efficacy is that many cases of patients for which a significant amount needs to be resected surgically rather than endoscopic excision (ESD) were registered. If the resection area is small, the efficacy cannot be verified by the prevention of stenosis. President Hashimoto said, “This makes it difficult to conduct clinical trials for the epithelial cell sheet for esophageal regeneration.” Accordingly, it is unnecessary to become pessimistic, although it will take time.
As for the regenerated cartilage sheets, the treatment with autologous cell sheets was approved as Advanced Medicine B. Once Advanced Medicine B starts, the contract manufacturing of the regenerated cartilage sheets will contribute to revenue and the company will advance significantly toward the approval for the manufacturing and sale of autologous cell sheets. In 1Q, Cell Processing Facility started the contract manufacturing of cell sheets. Outside Japan, MetaTech submitted a notification on the clinical trial for the epithelial cell sheet for esophageal regeneration in Taiwan at the end of the previous term. In addition, they will commence discussions about the clinical development of a periodontal ligament cell sheet, which is the third product following the esophageal and cartilage regeneration sheets. After many twists and turns, several buds of revenue are steadily growing. The company is developing a structure as a regenerative medicine maker. We would like to pay attention to the progress of the mid-term business plan aimed at moving into the black in fiscal 2021.
Reference: Regarding Corporate Governance
◎Organization type, and the composition of executive directors and auditors
Organization type | Company with company auditor(s) |
Directors | 4 directors, including 2 external ones |
Auditors | 3 corporate auditors, including 2 external ones |
◎Corporate Governance Report(Latest Update:April 9, 2019)
Basic Policy
With the missions to introduce technological innovations, to exert creativity and to contribute to people’s health and welfare by providing high-quality products and services, we are enhancing corporate governance to raise quality in all of our corporate activities.
In the future, we will increase our accountability further to improve the transparency of disclosed information and strengthen our checking system even more.
<Reasons for Non-compliance with the Principles of the Corporate Governance Code (Excerpts)>
CellSeed has stated, “Our company implements all the basic principles stipulated in the Corporate Governance Code as a JASDAQ listed company.”
This report is intended solely for information purposes and is not intended as a solicitation to invest in the shares of this company. The information and opinions contained within this report are based on data made publicly available by the company and obtained from sources that we judge to be reliable. However, we cannot guarantee the accuracy or completeness of the data. This report is not a guarantee of the accuracy, completeness or validity of said information or opinions, nor do we bear any responsibility for the same. All rights pertaining to this report belong to Investment Bridge Co., Ltd., which may change the contents thereof at any time without prior notice. All investment decisions are the responsibility of the individual and should be made only after proper consideration. Copyright(C) 2019 Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.. |
To view back numbers of Bridge Reports on CellSeed (7776) and other companies, or IR related seminars of Bridge Salon, please go to our website at the following url: www.bridge-salon.jp/


