| Ferrotec Corporation (6890) |
|
||||||||
Company |
Ferrotec Corporation |
||
Code No. |
6890 |
||
Exchange |
JASDAQ |
||
Industry |
Electric Equipment (Manufacturing) |
||
President |
Akira Yamamura |
||
HQ Address |
Nihonbashi Plaza Building, Nihonbashi 2-3-4, Chuo-ku, Tokyo |
||
Year-end |
March |
||
URL |
|||
* Share price as of closing on December 8, 2014. Number of shares issued at the end of the most recent quarter excluding treasury shares.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
* Estimates are those of the Company.
|
|
| Key Points |
 |
| Company Overview |
|
Ferrotec was born as a company with highly unique technologies including thermoelectric modules with uses in thermal elements and vacuum technologies that respond to magnetic fluids that were born from the NASA space program in the 1980s. Over the course of its 30 year history of operations, the Company has developed a wide range of diverse technologies with applications in the automobile, electronics, next generation energy and other industries. And as a transnational company, Ferrotec deploys its businesses in Japan, Europe, the Americas, China, and Asia, and boasts of marketing, development, manufacturing, sales, and management capabilities in various countries and regions. <Business Segments>
Ferrotec's operations can be divided between the equipment related business segment, where vacuum feedthroughs, quarts products, and other ceramic products used in semiconductor, FPD, and LED related manufacturing equipment are manufactured, electronic device business segment, where thermoelectric module application products are made, and photovoltaic business segment, where silicon crystal, PV wafers, and crucibles used in crystal manufacturing devices are produced. In fiscal year March 2014, sales of the equipment related business, electronic device, and photovoltaic related business segments accounted for 48.3%, 14.8% and 29.5% of total sales respectively, while saw blades, equipment part cleansing, machine tool, and other products not included in reported segments accounted for 7.4%.
 Equipment Related Business
Ferrotec places a strong emphasis upon and provides total engineering services in the Equipment Related Business business segment. In addition, the Company provides equipment parts, consumables, spare parts and equipment cleaning services (50% share in China). The main product of vacuum feedthroughs boasts of top market share in the world, and is a functional part that insulates the interior of manufacturing equipment from gas and dust contamination while supporting rotating action of the equipment. This part is critical in manufacture of semiconductor, FPD, LED and photovoltaic manufacturing equipment. This product uses magnetic fluid (Fluids that respond to magnetic fields), which has been a core technology of Ferrotec since its founding. Because of instability in these applications arising from their link with corporate capital investments cycles, the Company focuses its marketing efforts upon expanding sales to applications for which demand is more stable, including transportation equipment, precision robots, and general industry usages. In addition, Ferrotec has also focused its efforts upon assuming consigned manufacture of vacuum chambers that use vacuum feedthroughs and gate valves (Both use vacuum related equipment).At the same time, quartz products and ceramic products are critical elements in the process of semiconductor manufacturing. Quartz products are able to resist high temperature conditions that exist in the semiconductor manufacturing process, and are a high purity silica glass product that protects semiconductors from undergoing chemical reaction by preventing it from activating with gas. Ferrotec boasts of a high share of products purchased by LED manufacturers, in addition to high share of quartz crucibles (Photovoltaic related business) used in the photovoltaic cell manufacturing process. This technology is also being used to cultivate high purity crucibles for use in semiconductor applications. The Company boasts of semiconductor manufacturing equipment manufacturers as their clients in Japan and overseas that purchase ceramic products that are Ferrotec's core material and technology. At the same time, sales of semiconductor inspection tools for machinable ceramics to flash memory applications are growing. In addition, Ferrotec has achieved 300,000 units per month of small wafer processing (Ingot slicing) for discrete semiconductor applications, and its contribution are becoming significant. Electronic Device Business
Thermal element "thermoelectric modules" are products that can instantly raise or lower temperatures to a highly precise degree and are a core product of this business. Thermoelectric modules are used primarily in hearted automobile seats, and also in a wide range of other applications including genetic analysis equipment, optical communications, and consumer electronics. Ferrotec is also devoting efforts to expanding the range of applications for this product by improving product quality, introducing automated manufacturing lines to reduce costs, and developing new products that are high in functionality. Sales of magnetic fluids, including applications currently being developed for use in fishing reels (Water protecting internal seals) and speakers for 4K televisions, are also conducted in this segment.
Photovoltaic Related Business
Ferrotec entered the photovoltaic related business in 2005, and has manufactured and sold silicon crystal manufacturing equipment, consumable products including quartz crucibles, and silicon products. Based upon the current needs of the market, the Company is conducting manufacture and sales of silicon use multiple crystal crystal vessels (Manufactured using quartz processing technologies), single crystal crucibles manufactured when making ingots, and consigned manufacturing of silicon crystal ingots and wafers used in photovoltaic substrates. With regards to consumable products like crucibles, Ferrotec boasts of a high market share due to its wide ranging lineup of products and ability to manufacture customized products.
<New Endeavors>
Over the medium term, Ferrotec is expected to implement measures that leverage its strengths in vacuum and precision processing technologies to expand the realm of industries to which is provides products to include the food, water, energy, communications and medical fields. Within the medical field, negotiation for sales of vacuum chambers, seals, and other parts used in CT scan and MRI equipment are being conducted with Chinese manufacturers. At the same time, negotiations for sales of power semiconductor boards used by European power device manufacturers are also being promoted.Ferrotec will also leverage the long life and highly accurate temperature control functions of its thermoelectric modules used in DNA and PCR analysis equipment that have allowed it to achieve market share of over 90%. 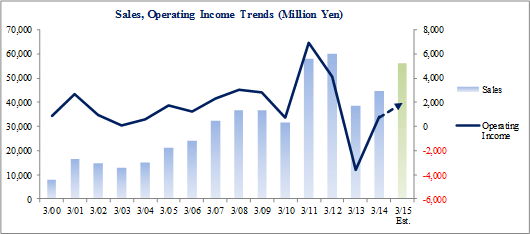 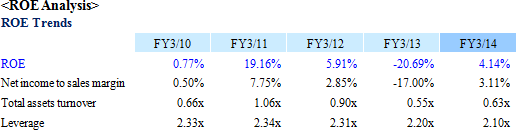 Large amounts of capital investments were conducted for the photovoltaic related business around this time as well. The net outflow of investing cash flow in fiscal year March 2010 expanded from ¥1.5 billion to ¥4.4 billion in fiscal year March 2011, and then nearly doubled to ¥8.5 billion in fiscal year March 2012. As a result, total asset turnover declined to 0.55 times in fiscal year March 2013 due to the decrease in sales and increase in assets. In November 2012, Ferrotec started restructuring its businesses and focused on expanding its engineering services by leveraging its core competence in the vacuum technology and precision processing realms. At the same time, management reforms that include a strategy of "selection and concentration", which entails retreat from unprofitable businesses and strict analysis of all business from the standpoint of profitability, were undertaken. Subsequent to these efforts, fiscal year March 2014 earnings returned to profits with an operating income of ¥800 million being recorded. Moreover, sale of marketable securities totaling to ¥1.360 billion allowed extraordinary income of ¥1.378 billion to be recorded and contributed to the improvement in net income to a profit of just under ¥1.4 billion, exceeding operating income. However, total asset turnover remained at 0.63 times and pointed to conditions of excessive facilities. 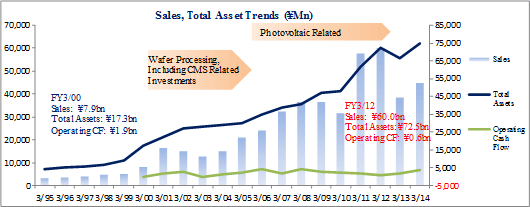 |
| First Half of Fiscal Year March 2015 Earnings Results |
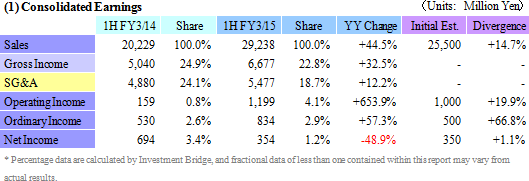 Sales and Ordinary Income Rose by 44.5% and 57.3%
Sales rose by 44.5% year-over-year to ¥29.238 billion on the back of increases in sales of all business segments. Photovoltaic use silicon manufactured on an OEM basis contributed to the strong 78.7% year-over-year growth in sales of the photovoltaic related business. Also, sales of the electronic device business rose by 48.6% year-over-year to on the back of strong demand for thermoelectric modules used in automobile seat automated heating applications. At the same time, sales of eequipment related business rose by 27.1% year-over-year due to increases in investments in semiconductor and FPD, and increased production activities.With regards to profits, cost of sales margin rose by 2.1% points due to changes sales composition, and increases of subsidiaries' sales, general, and administrative expenses caused by the weaker yen (Business restructuring plan contributed to reductions in fixed costs, and declines in sales, general, and administrative expenses margin). However higher sales allowed operating income to rise to ¥1.199 billion year-over-year from ¥159 million. However, at the end of the first half of the current term (Subsidiaries' first half end in June), a translation loss on yen based liabilities held by subsidiaries (A foreign exchange translation loss of ¥106 million was booked during the previous first half) arising from the strengthening of the yen relative to the Chinese yuan from the end of the previous fiscal year contributed to a deterioration in non-operating income. The disappearance of profits derived from sales of investment securities (An extraordinary profit of ¥645 million) booked in the previous first half contributed to a 48.9% year-over-year decline in net income to ¥354 million. Moreover, the fact that net income remained only in line with initial estimates is attributed to larger than expected increases in tax burdens of subsidiaries resulting from improvements in their earnings. In addition, capital investments focused upon Chinese subsidiaries in Shanghai, Hangzhou, and Yinchuan declined by 19.9% year-over-year to ¥1.314 billion (¥1.640 billion in the previous first half) and depreciation declined by 4.1% to ¥1.899 billion (¥1.981 billion in the previous first half). The average exchange rates were ¥102.23 per United States dollar (¥95.90 in the previous first half), and ¥16.56 per Chinese yuan (¥15.53 in the previous first half). 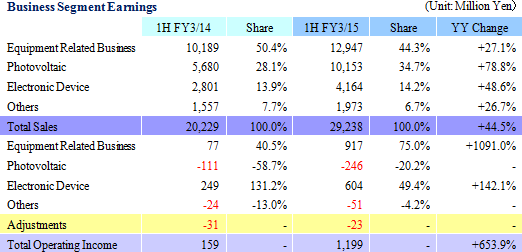 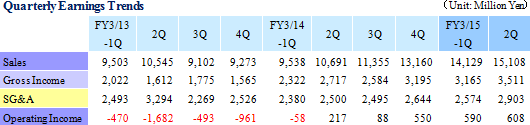 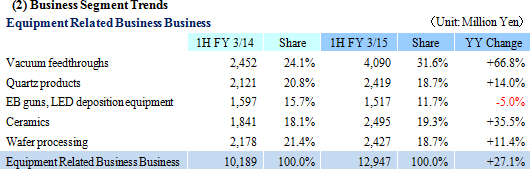 Moreover, device maker applications rose on the back of favorable demand arising from investments in three dimensional semiconductors and miniaturization, small to medium sized liquid crystal displays for cellular handset terminals and organic EL manufacturing equipment, and automobile applications. Demand for consigned manufacturing from semiconductor manufacturing equipment applications trended favorably. With regards to profits, increases in sales allowed profit to rise, and improvements in profitability led increases in profit margins above expectations. 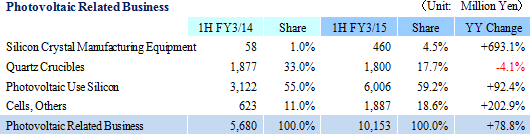 With regards to profits, continued stagnant pricing of multiple crystal square tanks and strong customer demands to reduce photovoltaic cell use silicon costs were apparent. And despite the reduction of and retreat from unprofitable businesses, fixed costs including depreciation weighed heavy and contributed to larger than expected declines in profit margins. 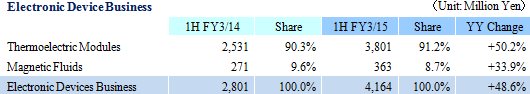 With regards to profits, operating income margin rose from 8.9% to 14.5%, marking a recovery to the same levels seen before the Lehman Shock. 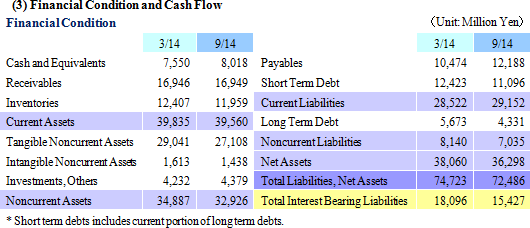 Moreover, the need to acquire ample liquidity for the China subsidiaries due to uncertainties surrounding the financial policies of China is a reason for the increase in cash and equivalents to ¥8.0 billion (Net interest bearing liabilities of ¥7.4 billion). At the same time, fortification of tax policies toward traded processed materials by China led to the one off frontloading of materials, which in turn contributed to temporary rise in accounts payables (The impact upon operating cash flow is large). 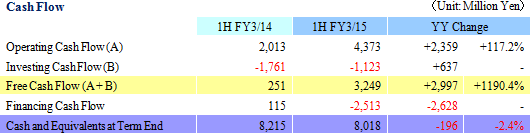 |
| Fiscal Year March 2015 Earnings Estimates |
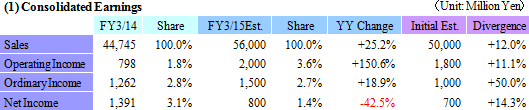 Sales and Operating Income to Rise 25.2% and 18.9%
Earnings estimates for the full fiscal year were revised upwards on the back of the first half earnings performance and the outlook for business conditions during the second half. Equipment Related Business business is expected to see a 16.3% year-over-year increase in its sales, along with 39.1% and 26.6% year-over-year increases in sales of photovoltaic related and electronic device businesses respectivelyHowever, a slowing during the second half of the fiscal year is anticipated because of the outlook for an adjustment of wafer processing for FPD applications is anticipated within the Equipment Related Business business, uncertainties in the photovoltaic related business, and weakness in the recovery in overall pricing. Estimates for sales have been revised upwards to a 9.2% year-over-year increase and operating income has been left unchanged. Consequently, full year estimates call for sales and operating income to rise by 9.2% and 25.3% year-over-year to ¥26.761 and ¥0.8 billion, and ordinary and net incomes to decline by 9.0% and 36.2% year-over-year to ¥665 and ¥445 million respectively. There are no large scale capital investments planned for the second half, and on a cash flow basis full year capital investments taking outstanding payments into consideration is expected to be ¥3.0 billion (Down 21.6% year-over-year), and depreciation ¥4.0 billion (Up 1.5% year-over-year). The assumption for foreign exchange is ¥105.00 per United States dollar (¥97.90 in the previous term) and ¥17.00 per Chinese yuan (¥15.97 in the previous term). Dividend payment is expected to be raised by ¥2 to ¥8 per share at the end of the fiscal year March 2015. 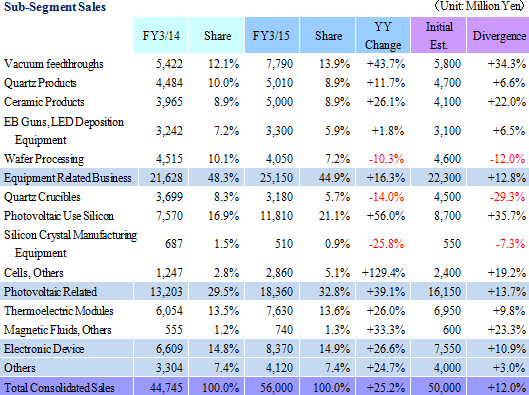 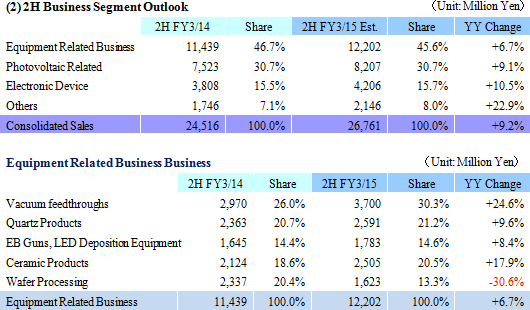 Vacuum feedthroughs used in semiconductor applications are expected to continue to grow gradually, and LED use metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) for automobile applications is expected to begin growing. At the same time, while Chinese manufacturers in FPD applications maintain plans to conduct new capital investments, the potential for slowing in demand due to declines in small to medium sized panel pricing exists. In addition to efforts to strengthen marketing for the overhaul business and other businesses in the Taiwan market, Ferrotec will endeavor to capture consigned manufacturing projects for medical and food related equipment. Furthermore, efforts to cultivate the China market will be made by forming alliances with Japanese companies entering China. Quartz products manufactured on an OEM basis for major clients in the United States are expected to continue to trend favorably, along with renewed growth in sales of OEM products sold to major clients within Japan, after having peaked out temporarily. Aside from OEM applications, favorable demand from semiconductor applications within Japan and Asia is expected to contribute to continued high capacity utilization rates. Sales of LED applications are expected to rise on the back of increases in demand from smartphone applications. In addition to reducing costs by concentrating production at facilities in China, efforts will be made to cultivate demand from Taiwanese manufacturers by leveraging responses that boast of short delivery times, stable quality levels, and customization. Furthermore, Ferrotec plans to enter the silicon parts for next generation equipment and other processing equipment realms. Large orders for machinable ceramics have been booked from Taiwanese and Korean manufacturers for use in new smartphone applications (Subsidiary ends its fiscal year in December) during the summer season in the ceramic products realm. While some segments experienced adjustments from fall onwards, the overall trends remain unchanged. Orders and sales within and outside of Japan are expected to grow due to favorable trends in new equipment applications and against the backdrop of aggressive investments for miniaturization and production capacity expansion in the realm of fine ceramics. Moreover, marketing activities will be continued to develop new clients and new applications for both machinable and fine ceramics. Aside from the above mentioned realms, the LED market applications for EB guns and LED deposition equipment are expected to recover due to expansion in communication chips for smartphones. In addition to focusing marketing activities upon the optical market applications, efforts to overcome uncertainties in the realm of EB guns in Europe will also be implemented. At the same time, wafer processing are expected to benefit from continued favorable demand for in-house branded products and the production adjustments of OEM clients has already been factored into the company's strategy. A shift of ingot manufacturing to the inland facilities in Yinchuan, China is being implemented to reduce costs, and restructuring of the service structure for technology and product quality are also being conducted. 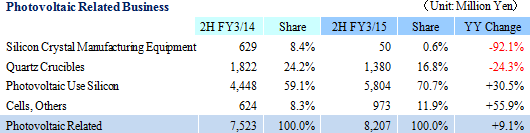 Amidst these trends, efforts to reduce costs by shifting production to the Yinchuan plant and efforts to fortify pricing of long life products are being implemented to improve profitability of quartz crucibles. In addition, other efforts to expand customers by improving the performance of N type single crystals, promoting responses for fixed abrasive grain thin wafers, improvements in profitability by shifting production of silicon crystal manufacturing process from Shanghai to the Yinchuan plant and concentration of manufacturing are being implemented. At the same time, efforts to sell small diameter quartz crucibles for semiconductor applications and acquire certification of Japanese semiconductor manufacturers will also be conducted. 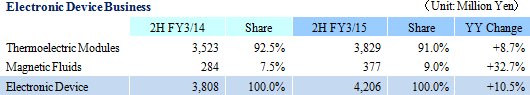 Start of mass production of power device boards and launch of new module products for new applications are planned. Ferrotec will endeavor to raise customer satisfaction by using proposal based marketing and fortifying support for the launch of new applications of thermoelectric modules. |
| Conclusions |
|
However in the electronic device business, applications of thermoelectric modules used in automobiles are expanding, and development of seven new applications is currently being undertaken. Moreover, development for mass production of new types of standard sized models with increased heat absorbing capabilities and smaller sized models heat exchange products with improved cooling capabilities is being conducted. Efforts are also being promoted to acquire certification for power device boards (Certification from Japanese and Chinese customers has been acquired, and efforts to acquire certification from Korean customers are also being conducted currently. In the future, Ferrotec will endeavor to acquire certification in Europe and North America). Thermoelectric module sales are expected to rise by 26% year-over-year to ¥7.6 billion during the current term. And within two years, sales of high power conventional products and power device boards are expected to grow to ¥15.0 billion. At the same time, efforts to expand the photovoltaic related business to include large diameter quartz crucibles used in semiconductor applications in addition to conventional small diameter crucibles will be implemented. Costs of crucibles is expected to be reduced by 20% to 30% by concentrating manufacture of quartz crucibles used in photovoltaic cell applications at the Yinchuan plant. Furthermore, production of photovoltaic cell use silicon on an OEM basis (Pulled from ingots) is steadily expanding, and cost reductions are expected to be derived from concentrated manufacturing at the Yinchuan plant (Cost reductions of over 20% are anticipated). In addition, efforts to reduce electric power costs will be implemented and a shift of production of discrete semiconductors pulled from ingots to the Yinchuan plant based upon the outlook for support of the local government (Payment of subsidies, and other preferential measures). With regards to ingot slicing, introduction of a wire saw for 80 micron diamond wire (Conventional applications are 90 microns) are expected to contribute to reductions in cost of sales. Improvements in the earnings generating structure have been confirmed by the earnings performance during the previous fiscal year and the first half of the current fiscal year. And despite various uncertainties including anti-dumping measures implemented by the United States (details will be announce later by Department of Commerce) against products manufactured in China and more stringent taxes levied against traded processed materials by China, the outlook for the electronic device and Equipment Related Business business segments is positive because of efforts to strengthen relationship with customers and development of new products and new applications. Furthermore, the efforts to reduce costs through concentration of production at the Yinchuan plant is expected to begin surfacing in the photovoltaic related business. Therefore, evidence of the successful results of all of Ferrotec's efforts to return its businesses to a growth path in the coming term should be watched closely. Disclaimer
This report is intended solely for information purposes, and is not intended as a solicitation to invest in the shares of this company. The information and opinions contained within this report are based on data made publicly available by the Company, and comes from sources that we judge to be reliable. However we cannot guarantee the accuracy or completeness of the data. This report is not a guarantee of the accuracy, completeness or validity of said information and or opinions, nor do we bear any responsibility for the same. All rights pertaining to this report belong to Investment Bridge Co., Ltd., which may change the contents thereof at any time without prior notice. All investment decisions are the responsibility of the individual and should be made only after proper consideration.
|




