Bridge Report:(6890)Ferrotec he first half of the fiscal year March 2020
 Akira Yamamura, President | Ferrotec Holdings Corporation (6890) |
 |
Company Information
Exchange | JASDAQ |
Industry | Electric Equipment (Manufacturing) |
President | Akira Yamamura |
HQ Address | Nihonbashi Plaza Building, Nihonbashi 2-3-4, Chuo-ku, Tokyo |
Year-end | March |
Website |
Stock Information
Share Price | Shares Outstanding | Market Cap. | ROE (Act.) | Trading Unit | |
¥951 | 37,110,134shares | ¥35,292million | 5.7% | 100shares | |
DPS (Est.) | Dividend Yield (Est.) | EPS (Est.) | PER (Est.) | BPS (Act.) | PBR (Act.) |
¥24.00 | 2.5% | ¥67.45 | 14.1x | ¥ 1,310.69 | 0.7x |
*Share price as of closing on December 19, 2019. The number of shares issued at the end of the latest quarter excludes its treasury shares. ROE is based on the result of the previous term.
*BPS is taken from the financial briefing report of the second quarter of FY March 2020.
Consolidated Earnings Trends
Fiscal Year | Sales | Operating Income | Ordinary Income | Net Income | EPS (¥) | DPS (¥) |
March 2016 (Act.) | 69,463 | 4,024 | 3,822 | 2,162 | 70.18 | 10.00 |
March 2017 (Act.) | 73,847 | 5,678 | 5,675 | 3,256 | 105.67 | 18.00 |
March 2018 (Act.) | 90,597 | 8,437 | 7,157 | 2,678 | 77.08 | 24.00 |
March 2019 (Act.) | 89,478 | 8,782 | 8,060 | 2,845 | 76.90 | 24.00 |
March 2020 (Est.) | 85,000 | 6,500 | 4,500 | 2,500 | 67.45 | 24.00 |
* Estimates are those of the Company.
*Unit: million yen.
This Bridge Report reviews the overview of Ferrotec’s earnings results of the first half of the fiscal year March 2020 and earnings estimates for fiscal year March 2020.
Table of Contents
Key Points
1.Company Overview
2.First Half of Fiscal Year ending March 2020 Earnings Results
3.Fiscal Year ending March 2020 Earnings Forecasts
4. Medium to Long Term Management Objectives
5. Conclusions
Reference: Regarding corporate governance
Key Points
- For the first half of the term ending March 2020, sales and operating income decreased 7.5% and 29.6%, respectively, year on year. Although the downsizing of the Photovoltaic Business caused significant effects, the sales of the Electronic Device Business grew 18.9% year on year thanks to the good performance of substrates for power semiconductors, etc. and the sales of the Semiconductor and Other Equipment Related Business were nearly unchanged (down 1.4%) year on year. As for profit, the company saw the augmentation of the allowance for doubtful accounts and R&D costs at the Chinese subsidiary and the increase in expenses due to the full-scale operation of the subsidiary, while sales declined.
- As for the full-year forecast, it is estimated that sales and operating income will decrease 5.0% and 26.0%, respectively, year on year. It is forecasted that inventory adjustment will be continued in the second half and the facility operation rates of device manufacturers will be stagnant, so the estimated sales and profit for the second half have been revised downwardly. In the full year, the sales of the Electronic Device Business are estimated to grow, but the downturn of the Semiconductor and Other Equipment Related Business will produce negative effects. As for profit, gross profit rate is projected to rise slightly, but the augmentation of SGA will become a burden. The company plans to pay a term-end dividend of 12 yen/share. When combined with an interim dividend at the end of 2Q, the annual total of dividends will be 24 yen/share.
- As the semiconductor market is entering the correction phase, the company continues aggressive business operation by investing in equipment and procuring funds actively, but it had to revise the earnings forecast for the term ending March 2020. Not a few people may have thought the company has a rocky road ahead, as the forecast has been revised downwardly in the first fiscal year of the mid-term plan, but they do not need to be pessimistic, when considering the expected recovery in the next term ending March 2021 and the mid/long-term growth potential. In the Chinese market, the investment by leading device manufacturers is getting active, and especially in the memory manufacturing field, the performance of all manufacturers is reportedly recovering. Above all, China is promoting the domestic production of semiconductors as a national policy. Under these circumstances, the company possesses the advantage of producing products from good-quality ingots in China and the advanced technological level for 8-inch and 12-inch wafers.
1. Company Overview
Ferrotec Holdings Corporation conducts business mainly on the basis of the following two segments: the Equipment Related Business, in which it offers parts for semiconductors and fine panel display (FPD) manufacturing equipment, consumable materials and wafers used in the process of manufacturing semiconductors, and semiconductors for equipment offering cleaning services of equipment parts, and the Electronic Device Business that focuses on the thermal element “thermoelectric modules,” with 48 companies serving as Ferrotec’s subsidiaries (42 consolidated subsidiaries and 6 non-consolidated affiliated companies accounted for by the equity method and other related companies).
Ferrotec was born as a company with highly unique technologies including thermoelectric modules with uses in thermal elements and vacuum technologies that respond to magnetic fluids that were born from the NASA space program in the 1980s. Over the course of its 40 years history of operations, the Company has developed a wide range of diverse technologies with applications in the automobile, electronics, next generation energy and other industries. As a transnational company, Ferrotec deploys its businesses in Japan, Europe, the Americas, China, and Asia, and boasts of marketing, development, manufacturing, sales, and management capabilities in various countries and regions. A holding company structure was implemented from April 2017.
【Corporate Philosophy】
Bringing Satisfaction to Customers
Caring About the Environment
Providing Dreams and Vitality to the World
From a global perspective, Ferrotec operates in harmony with international and local communities, acting in good faith as a company that provides products and services that contribute to everyday life of people. Ferrotec’s corporate philosophy is to earn satisfaction and trust from the customers, contribute to solving global environmental problems, and be devoted to serving society through manufacturing.
1-1.Business Segments
Ferrotec’s operations includes semiconductor seal related products such as vacuum seal, quartz products, ceramic products, etc. used in manufacturing equipment of semiconductor, FPD, LED etc., electronic device business centering on thermo modules, silicon crystal, PV wafer, crystal manufacturing equipment. Other businesses, which handle saw blades, machine tools, surface treatment, silicon products for solar cells, etc.
The reported segments of the company have been “Semiconductor and Other Equipment Related Business,” “Photovoltaic Business,” and “Electronic Device Business,” but the quantitative importance of “Photovoltaic Business” degraded. So, it was excluded from segments to be reported in the term ending March 2020, and included in “Other Businesses” (“Quartz crucibles” handled as products in “Photovoltaic Business” are now included in “Equipment Related Business” because the purpose of use and buyers changed.)
Semiconductor equipment related business
Ferrotec provides total engineering services in the Equipment Related business segment, including the manufacture and sale of Vacuum Feedthrough of equipment parts for solar power, semiconductor, FPD and LED applications, consumable products used in manufacturing of devices, quartz products, ceramic products, CVD-SiC products, quartz crucibles, silicon wafer processing and equipment cleaning services.
Its vacuum seal boasts of top market share in the world, and is a functional part that insulates the interior of manufacturing equipment from gas and dust contamination while supporting rotating action of the above-mentioned equipment. These Vacuum Feedthrough use magnetic fluids (Fluids that respond to magnetic fields), which has been a core technology of Ferrotec since its founding. Because of instability in these applications arising from their link with corporate capital investments cycles, the Company focuses its marketing efforts upon expanding sales to applications for which demand is more stable, including transportation equipment, precision robots, and general industry usages. In addition, Ferrotec has also focused its efforts upon assuming consigned manufacture of vacuum chambers that use Vacuum Feedthrough and gate valves (Both use vacuum related equipment). At the same time, quartz, ceramic, and CVD-SiC products are critical elements in the process of semiconductor manufacturing. Quartz products are able to resist high temperature conditions that exist in the semiconductor manufacturing process, and are a high purity silica glass product that protects semiconductors from undergoing chemical reaction by preventing it from activating with gas. The Company boasts of semiconductor manufacturing equipment manufacturers as their main clients in Japan and overseas who purchase ceramic products, which are Ferrotec’s core material and technology. At the same time, semiconductor inspection tools for machinable ceramics and fine ceramics used in semiconductor manufacturing equipment are two main products in this CVD-SiC.
*CVD-SiC products are the term used to describe SiC products manufactured by "CVD method (Chemical Vapor Deposition method)" (created from compounds of silicon and carbon gas). Currently, semiconductor equipment and structural parts are provided, and research and development for products used in aeronautics and space (Turbine, mirrors), automobile (Power semiconductors), energy (Nuclear power related), information technology (Semiconductor manufacturing equipment parts) and other applications are also being conducted.
Ferrotec is expanding its strengths and capabilities in processing six-inch wafers (diameter) into eight-inch wafers, and has taken the largest share in the equipment part cleaning services market in China.

(From the company website)
Electronic Device Business
Thermal element “thermoelectric modules” are products that can instantly raise or lower temperatures to a highly precise degree and are a core product of this business. Thermoelectric modules are used primarily in heated automobile seats, and also in a wide range of other applications including heated wafers in semiconductor manufacturing equipment, genetic analysis equipment, optical communications, and consumer electronics and power semiconductor substrates that is sold as unitized products. Ferrotec is also working on developing new demand and expanding further applications through cost reduction and quality improvement through development of new products using high performance materials and introduction of automated lines. Earnings of magnetic fluids, including applications currently being developed for use in linear vibration motors for smartphones and speakers for 4K televisions, are also conducted.
(From the company website)
Other business

(From the company website)
Business Segment Trends
| FY 3/15 | FY 3/16 | FY 3/17 | FY 3/18 | FY 3/19 |
Equipment Related | 26,566 | 31,405 | 32,243 | 46,661 | 55,953 |
Electronic Device | 9,679 | 13,328 | 12,627 | 12,701 | 12,897 |
Photovoltaic | 17,948 | 18,505 | 18,773 | 20,938 | 8,082 |
Others | 4,883 | 6,224 | 10,204 | 10,296 | 12,544 |
Total Sales | 59,078 | 69,463 | 73,847 | 90,597 | 89,478 |
Equipment Related | 1,523 | 3,148 | 4,234 | 7,497 | 9,186 |
Electronic Device | 1,459 | 2,467 | 2,594 | 3,006 | 2,365 |
Photovoltaic | -1,272 | -1,692 | -1,184 | -1,592 | -1,659 |
Others | 10 | 143 | 244 | -429 | -311 |
Adjustments | -50 | -42 | -210 | -44 | -798 |
Total Operating Income | 1,671 | 4,024 | 5,678 | 8,437 | 8,782 |
*Unit: million yen
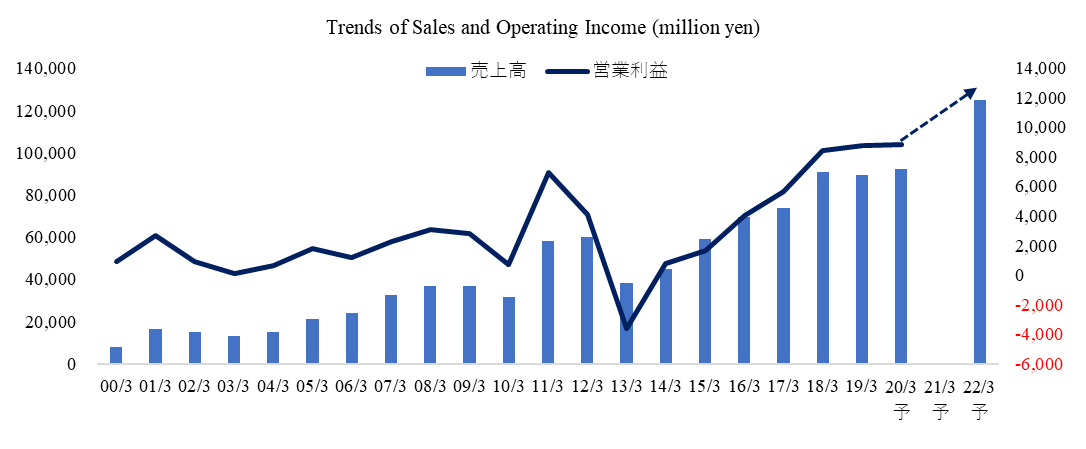
2.First Half of Fiscal Year ending March 2020 Earnings Results
2-1.Consolidated Earnings
| 1H of FY 3/19 | Ratio to sales | 1H of FY 3/20 | Ratio to sales | YoY | Initial Est. | Difference from the forecasts |
Sales | 45,230 | 100.0% | 41,849 | 100.0% | -7.5% | 45,000 | -7.0% |
Gross Income | 13,877 | 30.7% | 13,907 | 33.2% | +0.2% | 13,661 | +1.8% |
SG&A | 8,808 | 19.5% | 10,341 | 24.7% | +17.4% | 9,339 | +10.7% |
Operating Income | 5,069 | 11.2% | 3,566 | 8.5% | -29.6% | 4,322 | -17.5% |
Ordinary Income | 4,866 | 10.8% | 2,472 | 5.9% | -49.2% | 4,000 | -38.2% |
Net Income | 2,825 | 6.2% | 1,539 | 3.7% | -45.5% | 2,300 | -33.1% |
*Unit: million yen
Sales and operating income dropped 7.5% and 29.6%, respectively, year on year.
Sales were 41,849 million yen, down 7.5% year on year. The downsizing of Photovoltaic Business (included in Other Businesses from the term ending March 2020) affected the business performance significantly, but the sales of Electronic Device Business grew 18.9% year on year due to the favorable performance of substrates for power semiconductors, and the sales of Semiconductor and Other Equipment Related Business were nearly unchanged (down 1.4%) year on year, as the decrease in sales of vacuum seals, etc. was offset by those of quartz products, wafer processing, and parts cleaning.
Operating income was 3,566 million yen, down 29.6% year on year. Due to the drop in sales, cost ratios of core products, including vacuum seals and ceramic products, increased, but consolidated cost ratio increased 2.5 points to 66.8%, due to the recoil from the posting of impairment loss in the Photovoltaic Business in the same period of the previous year. While sales declined, gross profit rose 0.2% year on year to 13,907 million yen, but could not offset the augmentation of SGA, which was caused by the increases in allowance for doubtful accounts (up 435 million yen) and R&D cost (up 566 million yen) in the Chinese subsidiary, the full-scale operation of the subsidiary, etc.
Ordinary income dropped 49.2% year on year to 2,472 million yen. The revenue from subsidies increased from 47 million yen to 358 million yen, but non-operating income/loss worsened because investment gain on equity method decreased from 294 million yen to 181 million yen, interest expense augmented from 335 million yen to 540 million yen, exchange gain/loss worsened from 96 million yen to negative 984 million yen. The worsening of exchange gain/loss was caused mainly by the valuation of yen-denominated debts of the Chinese subsidiary. A 1% fluctuation in the yuan against the yen would generate an exchange gain/loss of about 300 million yen.
The average exchange rates in the term were 1 US dollar = 109.97 yen (110.36 yen in the same period of the previous year) and 1 yuan = 16.23 yen (16.64 yen in the same period of the previous year). Equipment investment increased 59.0% year on year from 12,030 million yen to 19,123 million yen, and depreciation rose 29.5% year on year from 2,651 million yen to 3,434 million yen.
Comparison with the initial estimates
The sales of the Electronic Device Business were almost in line with the estimate, but the Semiconductor and Other Equipment Related Business saw the sales of products and services other than vacuum seals falling below the estimates. As for profit, the company posted allowance for doubtful accounts and exchange loss, which were not assumed at the beginning of the term, while sales declined.
Business Segment Trends
| 1H of FY 3/19 | Ratio to sales Profit margin | 1H of FY 3/20 | Ratio to sales Profit margin | YoY | Initial Est. | Difference from the forecasts |
Equipment Related | 27,580 | 61.0% | 27,182 | 65.0% | -1.4% | 29,000 | -6.3% |
Electronic Device | 5,879 | 13.0% | 6,991 | 16.7% | +18.9% | 7,100 | -1.5% |
Others | 11,771 | 26.0% | 7,675 | 18.3% | -34.8% | 8,900 | -13.8% |
Total Sales | 45,230 | 100.0% | 41,849 | 100.0% | -7.5% | 45,000 | -7.0% |
Equipment Related | 5,054 | 18.3% | 2,680 | 9.9% | -47.0% |
|
|
Electronic Device | 1,231 | 20.9% | 1,320 | 18.9% | +7.2% |
|
|
Others | -1,194 | - | 190 | 2.5% | - |
|
|
Adjustments | -22 | - | -625 | - | - |
|
|
Total Operating Income | 5,069 | 11.2% | 3,566 | 8.5% | -29.6% | 4,322 | -17.5% |
*Unit: million yen
2-2.Business Segment Earnings Trends
Semiconductor related business
| 1H of FY 3/19 | Ratio to sales | 1H of FY 3/20 | Ratio to sales | YoY | Initial Est. | Difference from the forecasts |
Vacuum Feedthroughs | 6,704 | 14.8% | 4,031 | 9.6% | -39.9% | 4,000 | +0.8% |
Quartz Products | 7,300 | 16.1% | 8,189 | 19.6% | +12.2% | 8,300 | -1.3% |
Ceramic Products | 5,302 | 11.7% | 4,603 | 11.0% | -13.2% | 5,000 | -7.9% |
CVD-Sick | 1,291 | 2.9% | 1,218 | 2.9% | -5.7% | 1,300 | -6.3% |
EB guns and LED Deposition Equipment | 2,458 | 5.4% | 1,720 | 4.1% | -30.0% | 1,900 | -9.5% |
Wafer Processing | 2,360 | 5.2% | 4,502 | 10.8% | +90.8% | 4,700 | -4.2% |
manufacturing equipment cleaning | 1,615 | 3.6% | 2,375 | 5.7% | +47.1% | 3,000 | -20.8% |
Quartz crucibles | 550 | 1.2% | 544 | 1.3% | -1.1% | 800 | -32.0% |
Sales | 27,580 | 61.0% | 27,182 | 65.0% | -1.4% | 29,000 | -6.3% |
*Unit: million yen
Vacuum seals are used for equipment for manufacturing semiconductors (accounting for 36% of sales), LEDs (11%), FPDs (11%), solar cells (19%), etc. and others (23%). In the first half of this term, sales dropped 39.9% year on year. The sales of vacuum seals for semiconductor manufacturing equipment for memories dropped considerably due to the decrease in equipment investment. The sales for LEDs and FPDs, too, decreased, but there is a sign of recovery in the demand for vacuum seals for FPDs for organic EL. In addition, the company undertakes the processing of vacuum seals, but its sales decreased due to the sluggish sales for semiconductors.
As for quartz products, OEM accounts for 70% of total sales. In the first half, sales grew 12.2% year on year. The sales of quartz products for equipment for manufacturing memories (DRAM and 3D-NAND) decreased, but the company saw the growth of sales of silicon boards for the high-temperature microfabrication process and silicon parts for vacuum etchers. OEM was partially approved in 2 facilities established in 2018 in China (Changshan and Dongtai) and the development facility in Yamagata.
As for the sales composition of ceramic products, the fine ceramics of parts of semiconductor manufacturing equipment account for 68% (54% outside Japan, 14% inside Japan), the machinable ceramics “Photoveel” mainly for jigs for inspecting semiconductors 24%, and the other fine ceramics 8%. In the first half of this term, sales dropped 13.2% year on year. The sales of the machinable ceramics “Photoveel” for jigs for inspecting semiconductors and components of medical apparatus increased, but the sales of fine ceramics declined inside and outside Japan.
The sales of CVD-SiC products declined 5.7% year on year. The sales of high-purity heat-resistant parts for SiC epitaxial wafers increased mainly for manufacturers of semiconductor manufacturing equipment, but the sales of parts for semiconductor manufacturing equipment decreased due to the postponement of investment in equipment and inventory adjustment.
The sales from wafer processing grew 90.8% year on year. Due to the demand regulation for industrial equipment, etc., the sales of 8-inch wafers were sluggish, but the sales of 6-inch wafers increased 36% year on year, although demand weakened slightly from the second half of the term ended March 2019.
The sales from equipment part cleaning increased 47.1% year on year, thanks to the contribution of the new factory in Tongling City, Anhui Province and the new second factory in Neijiang City, Sichuan Province. As these two factories started operation, the company has established a structure constituted by 5 strongholds and 6 factories.
Electronic Device Business
| 1H of FY 3/19 | Ratio to sales | 1H of FY 3/20 | Ratio to sales | YoY | Initial Est. | Difference from the forecasts |
Thermoelectric Modules | 5,451 | 12.1% | 6,651 | 15.9% | +22.0% | 6,500 | +2.3% |
Magnetic Fluids, Others | 428 | 0.9% | 340 | 0.8% | -20.6% | 600 | -43.3% |
Sales | 5,879 | 13.0% | 6,991 | 16.7% | +18.9% | 7,100 | -1.5% |
*Unit: million yen
The sales of power semiconductor substrates increased 2.1 times year on year, due to the enhancement of the production capacity of the new foothold. As for thermo modules, the sales of products for temperature adjustment sheets for automobiles decreased 9% year on year, but the trial production and marketing for temperature adjustment for next-generation automobiles produced some results. As for the performance of products for other industries, the sales of products for Chinese communications devices grew considerably, and the performance of products for the bio industry was healthy.
2-3.Financial Condition and Cash Flow
Balance Sheet Summary
| 3/19 | 9/19 |
| 3/19 | 9/19 |
Cash | 31,555 | 28,086 | Payables | 20,887 | 17,986 |
Receivables | 21,460 | 19,699 | ST Interest-Bearing Liabilities (Lease obligations) | 20,345 | 25,572 |
Inventories | 16,276 | 17,989 | Current liabilities | 60,180 | 63,923 |
Current Assets | 77,271 | 76,282 | LT Interest-Bearing Liabilities (Lease obligations) | 40,730 | 50,734 |
Tangible Assets | 76,133 | 100,785 | Noncurrent liabilities | 53,069 | 71,100 |
Intangible Assets | 3,557 | 791 | Net Assets | 49,848 | 48,953 |
Investments and Others | 6,136 | 6,118 | Total Liabilities and Net Assets | 163,098 | 183,978 |
Noncurrent Assets | 85,827 | 107,695 | Total Interest-Bearing Liabilities (Lease obligations) | 61,076 | 76,307 |
*Unit: million yen
The total assets as of the end of the second quarter were 183,978 million yen, up 20,879 million yen from the end of the previous term. On the debit side, cash and deposits decreased through the investment in equipment for large-diameter wafers. On the other hand, tangible assets increased, due to the rise in the construction-in-progress account for machinery through the investment in equipment for large-diameter wafers, the posting of leased assets (about 5 billion yen) in the Chinese subsidiary through the application of IFRS16, the land use right (including the transfer of about 3 billion yen) that had been posted in intangible assets until the previous term, etc. Intangible assets declined, through the transfer of the land use right (about 3 billion yen) to lease assets. Capital-to-asset ratio was 26.4% (30.3% at the end of the previous term).
Cash Flow
| 1H of FY 3/19 | 1H of FY 3/20 | YOY | |
Operating cash flow(A) | 5,403 | 933 | -4,470 | -82.7% |
Investing cash flow (B) | -12,251 | -19,229 | -6,977 | - |
Free Cash Flow (A + B) | -6,848 | -18,295 | -11,447 | - |
Financing cash flow | 20,679 | 14,909 | -5,770 | -27.9% |
Cash and Equivalents at the end of term | 36,720 | 28,086 | -8,633 | -23.5% |
*Unit: million yen
The company secured an operating CF of 933 million yen, as pretax profit was 2,527 million yen (4,731 million yen in the same period of the previous year), depreciation was 3,435 million yen (2,652 million yen in the same period of the previous year), the increase in inventory assets was negative 2,131 million yen (negative 182 million yen in the same period of the previous year), the decrease in accounts payable was negative 2,768 million yen (negative 215 million yen in the same period of the previous year), etc. Investing CF is mainly due to the equipment investment for large-diameter wafers amounting to 14.6 billion yen. Financing CF is due to the accumulation of short and long-term debts and the issuance of corporate bonds.
3.Fiscal Year ending March 2020 Earnings Forecasts
3-1.Full year Consolidated Earnings
| FY 3/19 Act. | Ratio to sales | FY 3/20 Est. | Ratio to sales | YoY | Initial Est. | Difference from the forecasts |
Sales | 89,478 | 100.0% | 85,000 | 100.0% | -5.0% | 92,000 | -7.6% |
Gross profit | 27,137 | 30.3% | 27,405 | 32.2% | +1.0% | 28,062 | -2.3% |
SG&A | 18,354 | 20.5% | 20,880 | 24.6% | +13.8% | 19,262 | +8.4% |
Operating Income | 8,782 | 9.8% | 6,500 | 7.6% | -26.0% | 8,800 | -26.1% |
Ordinary Income | 8,060 | 9.0% | 4,500 | 5.3% | -44.2% | 8,100 | -44.4% |
Net Income | 2,845 | 3.2% | 2,500 | 2.9% | -12.1% | 4,700 | -46.8% |
*Unit: million yen
Sales and operating income are estimated to decrease 5.0% and 26.0%, respectively, year on year.
It is forecasted that inventory adjustment will be continued in the second half and the facility operation rates of device manufacturers will be stagnant, so the estimated sales and profit for the second half have been revised downwardly. In the full year, the sales of the Electronic Device Business are estimated to grow, but consolidated sales are projected to decline 5.0% to 85 billion yen, as the drop in sales from the Semiconductor and Other Equipment Related Business will not be offset. As for profit, gross profit rate is projected to rise slightly as the augmentation of depreciation due to the mass production of 8-inch wafers will be offset by the effect of withdrawal from the Photovoltaic Business, but operating income is estimated to drop 26.0% to 6.5 billion yen, due to the augmentation of SGA.
The assumed average exchange rates in the term are 1 US dollar = 110.00 yen (110.36 yen in the previous term) and 1 yuan = 16.00 yen (16.64 yen in the previous term). Equipment investment is forecasted to rise 11.3% year on year from 35,953 million yen to 40 billion yen and depreciation is projected to augment 21.6% year on year from 5,755 million yen to 7 billion yen.
Business Segment Earnings Trends
| FY 3/19 Act. | Ratio to sales | FY 3/20 Est. | Ratio to sales | YoY | Initial Est. | Difference from the forecasts |
Vacuum Feedthroughs | 11,889 | 13.3% | 8,055 | 9.5% | -32.2% | 8,500 | -5.2% |
Quartz Products | 15,590 | 17.4% | 16,050 | 18.9% | +3.0% | 16,800 | -4.5% |
Ceramic Products | 10,221 | 11.4% | 8,800 | 10.4% | -13.9% | 10,200 | -13.7% |
CVD-SiC | 2,800 | 3.1% | 2,100 | 2.5% | -25.0% | 2,600 | -19.2% |
EB guns and LED Deposition Equipment | 4,750 | 5.3% | 3,880 | 4.6% | -18.3% | 3,800 | +2.1% |
Wafer Processing | 7,236 | 8.1% | 8,100 | 9.5% | +11.9% | 10,500 | -22.9% |
manufacturing equipment cleaning | 3,468 | 3.9% | 6,400 | 7.5% | +84.5% | 6,600 | -3.0% |
Quartz crucibles | 1,072 | 1.2% | 1,100 | 1.3% | +2.6% | 1,800 | -38.9% |
Total of Equipment Related Business | 57,026 | 63.7% | 54,485 | 64.1% | -4.5% | 60,800 | -10.4% |
Thermoelectric Modules | 11,930 | 13.3% | 12,600 | 14.8% | +5.6% | 13,700 | -8.0% |
Magnetic Fluids, Others | 967 | 1.1% | 700 | 0.8% | -27.6% | 1,200 | -41.7% |
Total of Electronic Device Business | 12,897 | 14.4% | 13,300 | 15.6% | +3.1% | 14,900 | -10.7% |
*Unit: million yen
3-2. Estimates of the second half by segments
Equipment Related Business
| FY 3/19 Act. | Ratio to sales | FY 3/20 Est. | Ratio to sales | YoY | Initial Est. | Difference from the forecasts |
Vacuum Feedthroughs | 5,185 | 11.7% | 4,024 | 9.3% | -22.4% | 4,500 | -10.6% |
Quartz Products | 8,290 | 18.7% | 7,861 | 18.2% | -5.2% | 8,500 | -7.5% |
Ceramic Products | 4,919 | 11.1% | 4,197 | 9.7% | -14.7% | 5,200 | -19.3% |
CVD-SiC | 1,509 | 3.4% | 882 | 2.0% | -41.6% | 1,300 | -32.2% |
EB guns and LED Deposition Equipment | 2,292 | 5.2% | 2,160 | 5.0% | -5.8% | 1,900 | +13.7% |
Wafer Processing | 4,876 | 11.0% | 3,598 | 8.3% | -26.2% | 5,800 | -38.0% |
manufacturing equipment cleaning | 1,853 | 4.2% | 4,025 | 9.3% | +117.2% | 3,600 | +11.8% |
Quartz crucibles | 518 | 1.2% | 556 | 1.3% | +7.3% | 1,000 | -44.4% |
Total of Equipment Related Business | 28,924 | 65.4% | 27,303 | 63.3% | -7.3% | 31,800 | -14.1% |
*Unit: million yen
The sales of vacuum seals are estimated to decrease 22.4% year on year. Full-scale recovery is expected in the first half of the next term or later, but the sales of vacuum seals for equipment for manufacturing semiconductors and organic EL will be on a recovery track until the end of the term. The business environment surrounding the entrusted processing is estimated to be stringent, and the company will strive to keep its factories in operation by undertaking the processing tasks for products other than semiconductors. By taking advantage of the existing channels and brands of companies of the corporate group, the company will enhance marketing in the Chinese market and continue collaborative development with manufacturers of semiconductor manufacturing equipment. The investment in large-scale processing machinery will be continued.
The sales of quartz products are estimated to decline 5.2% year on year. As the products of Ferrotec will be adopted for semiconductor manufacturing equipment in China, the sales of Si parts will grow and the sales of Si boards targeted at Chinese IC manufacturers will increase, but the performance of products for semiconductor manufacturing equipment for memory manufacturers will be sluggish. In the late second half, leading IC manufacturers in South Korea, Taiwan, and China will start equipment investment. Before the growth of demand for OEM from leading companies, the company will prepare for the increase in output at Changshan Factory and Dongtai Factory in China, and enhance the development of products for the next and following generations at the development foothold in Japan (in Yamagata). In May 2019, the factory for next-generation products started operation, and will proceed to the mass-production stage on a full-scale basis in the next term or later.
The sales of ceramic products are estimated to decrease 14.7% year on year. The sales of the machinable ceramics “Photoveel” are estimated to grow, as it will be used as the material for semiconductor inspection jigs inside and outside Japan and for the components of medical apparatus outside Japan, but the sales of fine ceramics are projected to decline especially for the components of overseas etching devices. For the machinable ceramics “Photoveel,” the company will concentrate on the sales of new inspection jigs, for which the company receives an increasing number of inquiries as they have been downsized, and the sales promotion of machinable ceramics, which are characterized by high physical properties. The sales of fine ceramics for coating equipment in Japan are on a recovery track, and the demand for parts has emerged. The company will expand the clients to the manufacturers of the parts of general industrial machinery, etc.
The sales of CVD-SiC parts are estimated to decrease 41.6% year on year. The sales of high-purity heat-resistant materials for SiC epitaxial equipment will remain healthy in the second half, but the performance of the parts for semiconductor manufacturing equipment will remain sluggish. For business expansion, the company will expand the sales for semiconductor etching devices and LED manufacturing equipment, and develop its production system. In addition, the company will strengthen the system for the development and trial production of SiC semiconductors.
The sales from wafer processing are forecasted to drop 26.2% year on year. As the demand for 6-inch and 8-inch wafers will decline, sales are estimated to decrease. As for 8-inch wafers, the equipment will be installed in the new factory in Hangzhou, and mass production will begin in the first quarter of the next term. The mass production in Hangzhou will be started stepwise according to demand, and the company aims to establish a system for producing 450,000 wafers per month, combined with 100,000 wafers from Shanghai Factory.
The sales from equipment parts cleaning are estimated to rise 117.2% year on year. Thanks to the expansion of production output by semiconductor device manufacturers and FPD manufacturers in China, the sales are projected to keep growing significantly in the second half, too. For the parts cleaning business, the company will restructure Ferrotec (Anhui) Technology Co., Ltd., which operates Tongling Factory in Anhui, as the central sub-subsidiary of the business, establish an analysis center in Shanghai, and develop a system for incorporating the cutting-edge technology in a timely manner.
As for Ferrotec (Anhui) Technology Co., Ltd., the company will increase its capital and reorganize its organization from a limited company under the Chinese company act to a joint-stock company in December 2019.
Electronic Device Business
| FY 3/19 Act. | Ratio to sales | FY 3/20 Est. | Ratio to sales | YoY | Initial Est. | Difference from the forecasts |
Thermoelectric Modules | 6,479 | 14.6% | 5,949 | 13.8% | -8.2% | 7,200 | -17.4% |
Magnetic Fluids, Others | 539 | 1.2% | 360 | 0.8% | -33.2% | 600 | -40.0% |
Sales | 7,018 | 15.8% | 6,309 | 14.6% | -10.1% | 7,800 | -19.1% |
*Unit: million yen.
In the second half, too, the demand of temperature control sheets for automobiles is estimated to be weak. For cultivating the market of apps, the company will enhance sales and marketing while focusing on promising projects. For the other industries, the sales of products for 5G-related communications devices, new wearable devices, etc. are expected to increase. On the other hand, the sales of power semiconductor substrates are projected to decline, through the adjustment for industrial equipment and home appliances. The company will conduct global sales promotion for sub-assembly items for thermo modules, and cultivate the market of apps for automobiles with the aim of realizing mass production in 3 to 5 years. As for power semiconductor substrates, the company will enhance the cultivation of the market of silicon nitride (AMB substrates) for automobiles.
4. Medium to Long Term Management Objectives
4-1 Summary
Strategic business
The strategic business handles semiconductor materials (quartz, ceramic, silicon, CVD-SiC), semiconductor wafers, equipment parts cleaning, and power semiconductor substrates, and the company aims to grow this business further. Regarding semiconductor wafers, the company seeks to start mass production of medium to large diameter wafers at an early stage and build a production structure that produces 880,000 units monthly. As for the term ending March 2022, the costs for launching the business of semiconductor wafers will need to be covered by the earnings from the other strategic businesses; but the company sees it as a period for strengthening its footing in order to achieve a leap of growth.
Business streamlining and the medium to long term strategy
The company withdrew from the unprofitable solar cell business. On the other hand, the company will try to use thermo modules and magnetic fluids for in-vehicle applications as core products for the Automotive Project and aspires to nurture it into a core business in the future.
KPI targets
The company sets the targets for the last fiscal year of the mid term plan (FY March 2022), which are to achieve 125 billion yen in consolidated sales, an operating income of 12.5 billion yen (operating income margin: 10%), an ROE of 10% or more, an ROIC of 6% or more, and a capital adequacy ratio of 40% or more.
4-2 Strategic Products and Services
Technologies such as IoT, AI, automated driving, and big data have drastically evolved and the demand for semiconductors, which is the linchpin for these technologies, is expected to substantially increase. The semiconductor manufacturing equipment market remains unpredictable due to the US-China trade friction. However, the Semiconductor Equipment and Materials International (SEMI) predicts that it will hit the bottom in the second half of 2019, and it will get back on a growth track in 2020 or later. Looking at each country, the decline in sales in China due to the US-China trade friction is expected to recover in 2020 or later and will exceed the sales in Taiwan making China the largest customer.
The US-China trade friction is causing a stir regarding the semiconductor market in China, but, according to “Made in China 2025,” Chinese manufacturers continue to make capital investments in order to increase their self-sufficiency rate and they are progressing with the reform of the supply chain. The company had expanded in China from an early stage and it currently owns a base in the major industrial area. The company is making good progress on the increase of Chinese customers. For example, the company's market share of ceramic circuit boards for power semiconductors in China exceeds 90%. Additionally, it has good relations with the Chinese government. For instance, it succeeded in acquiring subsidies from the Chinese government in some areas (Hangzhou, etc.). In the future, there is a chance that semiconductor companies will receive corporation tax benefits.
As for the US-China trade friction, the results are not positive in the short term, but, the company considers this “a chance to expand its market share in China for the medium to long term,” and plans to continue expanding its business in China proactively.

(From the company website)
Semiconductor materials are divided into products proportional to capital investments and consumables proportional to the operation of semiconductor manufacturing equipment. The company does not only handle products (vacuum seals) that are linked to capital investments, but also consumables (semiconductor materials) and services (equipment parts cleaning) which are linked to the manufacturing of semiconductors. Thus, stable revenues can be secured even if capital investment is in a transitional period.
According to the company’s data, the WFE (Wafer Fab Equipment) market bottomed out in 2019 and will recover from 2020 onwards. By 2021, it will exceed the record high achieved in 2018 and approach its peak in 2022. In other words, capital investments in semiconductors are in an adjustment phase, but the period for recovery after hitting the bottom is not far. On the other hand, the sales of consumable semiconductor materials are favorable and the company will expand production capacity by expanding production lines.
Merging domestic subsidiaries
In January 2020, the ceramics business subsidiary, Ferrotec Ceramics Corporation (Chuo-ku, Tokyo), and the CVD-Sic business subsidiary, ADMAP Inc. (Tamano, Okayama prefecture), have merged and were reestablished as Ferrotec Material Technologies Corporation. Merging the two companies, which were expected to achieve synergy for consumable materials and jigs used in semiconductor manufacturing equipment, will enhance the development of fine ceramics (FC), machinable ceramics (MC), and CVD-SiC products and will strengthen the company's ability to respond to customers’ needs.
Currently, Ferrotec Ceramics Corporation separately conducts the trial manufacturing of FC in Amagasaki Plant (Hyogo Prefecture), and the mass production of FC in Hangzhou, China, while it conducts the trial manufacturing and mass production of MC in Ishikawa Plant in Ishikawa Prefecture. On the other hand, ADMAP Inc. conducts the trial manufacturing and mass production of CVD-SiC in Okayama Plant in Okayama Prefecture.
Semiconductor wafers
In anticipation of medium to long term needs, the company has invested approximately 43.6 billion yen in equipment for wafers and plans to establish a structure that can produce approximately 880,000 small, medium, and large diameter wafers per month by the term ending March 2022.
On November 22, 2019, a completion ceremony was held for the new wafer plant in Hangzhou, and during the “China semiconductor industry forum” as the afternoon session, intellectuals exchanged opinions about the trend, etc. of start of domestic production in China. Nevertheless, though the market is showing a general trend of recovery, the prices of wafers are dropping, and the company is reconsidering the early commencement of the mass production of 350 thousand units per month for the wafer manufacturing business in Hangzhou and plans to start mass production, depending on supply and demand. As for sales, the company enlisted cooperation of Global Wafers Co., Ltd., a major semiconductor company in Taiwan, and proceeded with the establishment of its own independent sales structure.
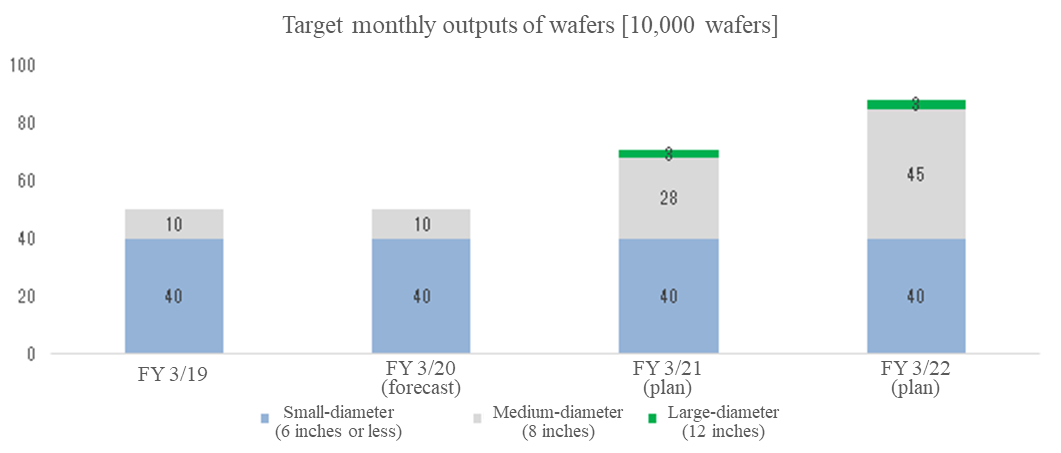
(According to company data)
Entering the wafer recycling business
As China promoted the domestic production of semiconductors, the demand for the recycling of monitor wafers (for usage before starting mass production) is rapidly increasing. Therefore, the company is preparing for its entry into the monitor wafers recycling business, which is a business that utilizes the company's resources of the wafer business and its know-how in the cleaning business and will contribute to the improvement of the services for the wafer business. This September, the company established Ferrotec (Anhui) Changjiang Semiconductor Material Co., Ltd. in Anhui through a joint investment between the company’s subsidiary and the investment fund of Tongling People's Government of Anhui, China (the shareholding ratio is 7:3). They aim to construct a plant and start mass production during FY 2020, and the amount of investment is being examined. They expect the monthly production output to be about 150 thousand units.
Equipment parts cleaning
The company has established its parts cleaning business based on 5 bases and 6 plants, and it established its position as the largest vendor in the precision recycling and cleaning market in China. The company has a 60% market share in China, where most of the leading semiconductor device manufacturers and foundries are the customers of the company. At the end of this July, the company reformed the structure to position Ferrotec Technology (Anhui) Co., Ltd. (Tongling, Anhui Province) at the top of the equipment parts cleaning business. In addition, the company will receive a contribution from the investment fund financed by the Tongling government as the company aims to further strengthen the business base in China by enhancing the cooperative relationships with Tongling, where Ferrotec Technology (Anhui) Co., Ltd. is located. As a main recurring-revenue business, the company plans to expand the business in China and considers expanding the business outside China.
Power semiconductor substrates
According to a market research firm, the global power semiconductor market, which was worth 2.9 trillion yen in 2018, is estimated to grow by 45% to 4.2 trillion yen by 2030. In practice, the demand for power semiconductors in the fields of machine tools and automobiles, where the company has competitive advantage, has increased. The company has established a production structure in the Shanghai and Hangzhou plants that produce 600 thousand DCB (Direct Copper Bonding: alumina ceramics material) substrates per month. It is also increasing the production capacity of the new plant in Dongtai, Jiangsu province, which was completed in the term ended March 2019. In addition to the DCB substrates, the company plans to produce the AMB (Active Metal Brazing: made of silicon nitride) substrates.

(From the company website)

(From the company website)
4-3. Products Related to Electronic Devices
In addition to power semiconductor substrates, the company deals in thermo modules and magnetic fluids in the Electronic Device Business. The demand for thermo modules is increasing before the full-scale operation of 5G and its usage is expanding to the consumer markets, etc. For example, wearable devices (clothes, etc.), which flexibly adapt to each country’s regional characteristics and seasons, are considered promising. By adapting to various usages, it will diversify its revenue sources.

(From the company website)
Strengthening the Automotive Manufacturing Domain
The company owns various products, including thermo modules, magnetic fluids, and power semiconductor substrates, which are expected to see growth in demand due to the next-generation automobiles. Thus, it is providing various manufacturers with proposals for in-vehicle parts. In the next 3 years, the company plans to expand consolidated sales in the automotive field to the 20 billion yen; furthermore, it is considering making the in-vehicle segment independent from the electronic devices business and establish it as the “in-vehicle segment,” around the period from FY2021 onwards.
Examples of the thermal module applications (examples of products for EV/ADAS)
Thermal module type battery cooler/heater | Heat transfer from the heat pump. Temperature management (cooling/heating) of lithium-ion batteries for low power consumption EVs. |
Thermal module type ADAS camera cooler | Heat radiation of CMOS image sensors used in ADAS (advanced driver-assistance systems) cameras (temperature management to enable a correct view of far objects) |
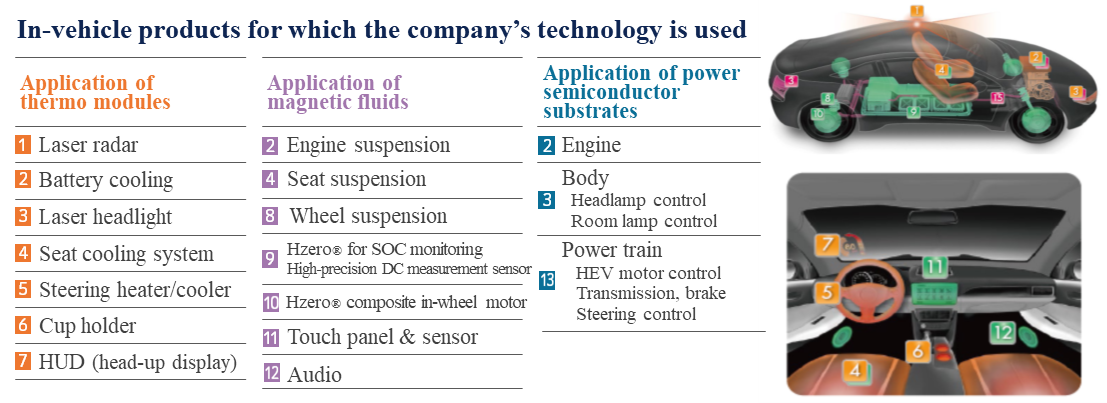
(From the company website)
4-4. Numerical plans and efforts in the Semiconductor and Other Equipment Related Business
Sales plan
| FY 3/ 18 | FY 3/ 19 | FY 3/ 20 Est. | FY 3/ 21 Forecast | FY 3/ 22 Forecast |
Sales | 90,598 | 89,478 | 85,000 | 105,000~115,000 | 120,000~130,000 |
Operating Income | 8,437 | 8,783 | 6,500 | 9,200 | 12,000~13,000 |
*Unit: million yen
The initial earnings forecast for the term ending March 2020 has been revised downwardly, considering the situation of the semiconductor market in the first half. The performance in the second half is estimated to be sluggish, but the market is expected to recover in the next term or later. In the term ending March 2022, which is the final fiscal year, the company plans to earn sales of 125 billion yen (average) and an operating income of 12.5 billion yen (average), hitting a record high for both sales and operating income.
The estimated equipment investment amount for the term ending March 2020 has been revised from 48 billion yen to 40 billion yen, due to the delay in investment. For the term ending March 2021 (initial plan: 12 billion yen) and the term ending March 2022 (initial plan: 11 billion yen), the company is reconsidering the plan, while taking into account the launch of the recycled wafer business. As for fund procurement, the company is thinking about a variety of methods for fund procurement, including the effective use of the expanding capital in China, in addition to the borrowing from Japanese banks, etc.
5.Conclusions
As the semiconductor market is entering the correction phase, the company continues aggressive business operation by investing in equipment and procuring funds actively, but it had to revise the earnings forecast for the term ending March 2020. Not a few people may have thought the company has a rocky road ahead, as the forecast has been revised downwardly in the first fiscal year of the mid-term plan, but they do not need to be pessimistic, when considering the expected recovery in the term ending March 2021 and the mid/long-term growth potential. In the Chinese market, it is said that semiconductor device manufacturers, such as memory manufacturers (3D-NAND and DRAM) and logic foundries, are expanding investment. Especially in the memory manufacturing field, the performance of all manufacturers is recovering. In the fourth quarter (Jan. to Mar.) of the term ending March 2020 or later, the demand from manufacturers of semiconductor manufacturing equipment is also expected to start recovering. Above all, China is promoting the domestic production of semiconductors as a national policy. The company possesses the advantage of producing products from good-quality ingots in China and the advanced technological level for 8-inch and 12-inch wafers. As for 12-inch wafers, there are a few manufacturers that can supply them in China.
The expectation toward thermo modules will grow. It was mentioned in this report that the sales of thermo modules are increasing as Chinese manufacturers of communications devices demand 5G communication base stations. In the next term ending March 2021, this trend will intensify, and the sales of thermo modules for 5G are estimated to grow 1.3 to 1.5 times. The 5G base stations of Chinese manufacturers of communications devices are expected to be adopted in Africa, South America, Europe, etc., so the potential demand for thermo modules is enormous. Since thermo modules have a high profit rate, we would like to keep in mind that the sales growth of thermo modules would produce a significant impact on profit, too.
Due to the launch of the wafer recycling business, fund procurement is required more. From now on, the company plans to diversify its fund procurement scheme, by selecting capital alliance partners in each project, taking full advantage of financial support from the Chinese government, etc. It seems that the company has no plan to increase the dependence on equity while decreasing the dependence on debts.
Reference: Regarding Corporate Governance
◎ Organization type, and the composition of directors and auditors
Organization type | Company with auditors |
Directors | 8 directors, including outside ones 2 |
Auditors | 3 directors, including outside ones 3 |
◎ Corporate Governance Report(Updated on June 16, 2019)
Basic policy
The company considers that it is important to improve its corporate value, emphasize the soundness of its business administration to become an enterprise that will be trusted and supported by stakeholders, including shareholders, customers, business partners, and local communities, and also establish a managerial system responding the rapid changes to the business environment swiftly and accurately.
The organizational chart of the corporate governance of our company as of the submission date is included in “V. Others, 2. Other items regarding the corporate governance structure, etc.”
Our company’s board of directors is chaired by the representative director and president Akira Yamamura. The other 8 members (including 2 outside directors) are the representative director and vice-president Takeru Yamamura, the representative director and vice-president He Xian Han, the director Hiroo Wakaki, the director Takanori Suzuki, the director Eiji Miyanaga, the outside director Kyuzo Nakamura, and the outside director Kuniaki Yanagisawa. In addition to monthly meetings of the board of directors, we hold an extraordinary meeting of the board of directors flexibly, when there is an important matter to be discussed. The board of directors determines important items in accordance with the regulations for the board of directors in addition to laws and the articles of incorporation, and oversees the business operation of each director. All auditors attend meetings of the board of directors, to oversee the business operation of directors. The term of directors is one year, so that we can respond to changes in the management environment swiftly.
Our company adopted a system of the board of auditors, which is composed of the full-time outside auditor Takamasa Higuchi, the outside auditor Go Fujimoto, and the auditor Masaru Yoshida, that is one full-time auditor and two part-time auditors, including 2 outside auditors. It is stipulated that a meeting of the board of auditors is held 8 or more times per year, once per month in principle, and extraordinarily when necessary. Full-time auditors attend meetings of the board of directors and other important meetings, such as meetings of the board of executive officers, and express their opinions when necessary, so as to oversee the business operation of directors. They also exchange information and opinions with the internal audit division and comptrollers, and hold regular meetings, to cement cooperation and improve the auditing function.
For business operation, 9 executive officers (composed of 8 male officers and 1 female officer, including 5 male directors) serve as chiefs of respective sections, so that their roles for business operation are clarified. Monthly meetings of the board of executive officers are held, to deliberate important items, including the items to be discussed at a meeting of the board of directors.
The company receives advice about legal affairs from Goto Law Office when this is necessary for business, in accordance with a legal consultancy contract. The comptroller Ernst & Young ShinNihon LLC audits our accounting in accordance with the audit contract, and provides us with their reports, including their comments during and after audit, and tries to disclose information without delay as a company listed in the standard section of the JASDAQ market of Tokyo Stock Exchange, if an event specified in the provisions regarding disclosure occurs.
This report is intended solely for information purposes, and is not intended as a solicitation to invest in the shares of this company. The information and opinions contained within this report are based on data made publicly available by the Company, and comes from sources that we judge to be reliable. However, we cannot guarantee the accuracy or completeness of the data. This report is not a guarantee of the accuracy, completeness or validity of said information and or opinions, nor do we bear any responsibility for the same. All rights pertaining to this report belong to Investment Bridge Co., Ltd., which may change the contents thereof at any time without prior notice. All investment decisions are the responsibility of the individual and should be made only after proper consideration. Copyright(C) 2019 Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. |
To view back numbers of Bridge Reports on Ferrotec Holdings Corporation (6890) and other companies, or IR related seminars of Bridge Salon, please go to our website at the following URL.
URL:https://www.bridge-salon.jp/


