Bridge Report:(6890)Ferrotec the Cumulative Second Quarter of the Fiscal Year ending March 2026
 President He Xian Han | Ferrotec Corporation (6890) |
 |
Company Information
Exchange | TSE Standard Market |
Industry | Electric Equipment (Manufacturing) |
President | He Xian Han |
HQ Address | Nihonbashi Plaza Building, Nihonbashi 2-3-4, Chuo-ku, Tokyo |
Year-end | March |
Website |
Stock Information
Share Price | Shares Outstanding (Term end) | Market Cap. | ROE (Act.) | Trading Unit | |
¥4,890 | 46,838,347 shares | 229,040 million | 7.1% | 100 shares | |
DPS (Est.) | Dividend Yield (Est.) | EPS (Est.) | PER (Est.) | BPS (Act.) | PBR (Act.) |
¥148.00 | 3.0% | ¥341.73 | 14.3x | ¥4,734.00 | 1.0x |
*Share price as of closing on December 19. Shares outstanding (Excluding Treasury Shares), DPS, EPS, and BPS are taken from the summary of financial results of the second quarter of the fiscal year ending March 2026. ROE is the actual value for the previous fiscal year.
Consolidated Earnings Trends
Fiscal Year | Sales | Operating Income | Ordinary Income | Net Income | EPS (¥) | DPS (¥) |
March 2022 (Act.) | 133,821 | 22,600 | 25,994 | 26,659 | 668.06 | 50.00 |
March 2023 (Act.) | 210,810 | 35,042 | 42,448 | 29,702 | 644.81 | 105.00 |
March 2024 (Act.) | 222,430 | 24,872 | 26,537 | 15,154 | 322.65 | 100.00 |
March 2025 (Act.) | 274,390 | 24,089 | 25,558 | 15,692 | 334.13 | 141.00 |
March 2026 (Est) | 285,000 | 30,000 | 28,000 | 16,000 | 341.73 | 148.00 |
*The forecast is from the company. Unit: million-yen, yen. The dividend for fiscal year ended March 2022 includes a special dividend of 9.00 yen/share. Net income is net income attributed to parent shareholders. The same shall apply hereafter.
This Bridge Report reviews the overview of Ferrotec’s earnings results for the second quarter of the fiscal year ending March 2026.
*Ferrotec Holdings performed an absorption-type merger with Ferrotec Material Technologies Corporation, a Japanese subsidiary, on July 1, 2025, and changed the company name to “Ferrotec Corporation.”
Table of Contents
Key Points
1. Company Overview
2. Earnings Results for the Cumulative Second Quarter of the Fiscal Year ending March 2026
3. Full-Year Earnings Estimates for the Fiscal Year ending March 2026
4. Conclusions
<Reference 1: New Mid-Term Management Plan>
<Reference 2: Measures for Achieving Management Conscious of Capital Costs and Stock Price>
<Reference 3: Regarding Corporate Governance>
Key Points
- In the cumulative second quarter of the fiscal year ending March 2026, sales grew 4.3% year on year to 140,980 million yen, and operating income rose 0.6% year on year to 14,333 million yen. As the product lineup and profitability in the semiconductor equipment-related business were favorable, the company revised its full-year operating income and ordinary income forecasts upwardly. In addition to successfully capitalizing on the tailwind of robust semiconductor investment and production demand within China, its effective response to the “Ex-China” trends among its U.S. clients contributed to their healthy performance.
- The semiconductor equipment-related business saw a 5% year-on-year increase in sales, with a 2% year-on-year decrease in operating income. Ceramics among semiconductor materials drove the segment's performance. Sales of quartz products and silicon parts were sluggish due to the impact of inventory. The equipment parts cleaning business continued to grow. Although sales of quartz crucibles for PV systems decreased, profitability improved.
- The sales and operating income in the electronic device business increased 22% and 46% year on year, respectively. Shipments of micro modules for optical transceivers among thermos-electric modules continued to be robust due to a significant investment in generative AI servers.
- In the automotive-related business, sales increased 12% year on year and operating income rose 10% year on year. The sales of power semiconductor substrates for automotive applications were sluggish due to the slow growth in demand for EVs. Furthermore, thermos-electric modules saw a revenue decline, partly due to the deteriorating market conditions.
- The company has revised its full-year operating income and ordinary income targets upwardly for the fiscal year ending March 2026, while taking into account the results of its semiconductor equipment-related business in the first half and recent performance. The revised corporate plan projects sales of 285 billion yen (+ 4% YoY), an EBITDA of 55 billion yen (+ 15% YoY), an operating income of 30 billion yen (+ 25% YoY), and an ordinary income of 28 billion yen (+ 10% YoY). The company raised its exchange rate assumptions (average during the fiscal year) from 146 yen to 148 yen (the actual rate in FY 3/2025: 152.24 yen) for the US dollar and kept it at 20 yen for the Chinese yuan (the actual rate in FY 3/2025: 21.12 yen). The estimated capital investment of 65 billion yen (the actual rate in FY 3/2025: 51.77 billion yen) remains unchanged.
- The progress rates were 49.5% for sales and 47.8% for operating income against the full-year forecast (after the upward revision) for the results in the first half. Although there are differences in fundamentals by product, it is fair to say that overall performance has been solid due to the success of portfolio management. At the financial results briefing, the company stated that “the year 2025 was a fairly good year.” While the company expressed high confidence in achieving its targets for the fiscal year ending March 2026, it also indicated that it is considering aggressive investment for the fiscal year ending March 2027 onwards and is aware of challenges ahead.
- The share price of the company has been rising since bottoming out in April 2025 and has finally reached a PBR of 1.0x. In addition to macro factors, such as rising expectations for a recovery in demand for semiconductor materials and equipment, it can be considered that the logical implementation of improvement plans in response to PBR falling below 1.0x contributed to the rise in share price. Favorable external conditions will be needed to provide a tailwind for share price to continue to rise. However, the company needs to achieve stable growth in sales and profits based on the investments for growth so far, improve ROE, and enhance shareholder returns. In this regard, the company has launched a solid capital policy, including a minimum DOE of 3.5% and a total return ratio of 50%.
1. Company Overview
Ferrotec Corporation develops, manufactures, and sells silicon products, magnetic fluid, sensors, and products to which such items are applied, as well as Vacuum Feedthroughs that are used in equipment for manufacturing semiconductors and flat panel displays (FPDs), quartz products, ceramics products, CVD-SiC products, silicon parts, crucibles, and thermo-electric modules used in temperature controllers.
These products are categorized roughly into either the “semiconductor equipment-related business,” “the electronic device business,” or “the automotive-related business.” The core products and the major companies in each segment are as follows:
| Segment | Core products | Major companies | |
| Semiconductor equipment-related business | Vacuum Feedthroughs | Development, manufacturing, sale | Ferrotec Material Technologies CorporationFerrotec (USA) Corporation |
| Development, sale | Hangzhou Dahe Thermo-Magnetics Co., Ltd. (FTH)Ferrotec Taiwan CO., LTD.KSM FerroTec Co., Ltd. | ||
| Sale | FERROTEC CORPORATION SINGAPORE PTE LTD | ||
| Quartz products | Development, sale | Hangzhou Dahe Thermo-Magnetics Co., Ltd. (FTH) Ferrotec (Zhejiang) Quartz Technology Co., Ltd.Aliontek Corporation. | |
| Sale | Ferrotec Material Technologies Corporation Ferrotec (USA) CorporationFERROTEC CORPORATION SINGAPORE PTE LTDFerrotec Taiwan CO., LTD. | ||
| Ceramics products | Development, manufacturing, sale | Ferrotec Material Technologies CorporationHangzhou Dahe New Material Technology Co., Ltd.Ferrotec (Zhejiang) Semiconductor Material Technology Co., Ltd. | |
| Sale | Ferrotec (USA) CorporationFERROTEC CORPORATION SINGAPORE PTE LTD | ||
| CVD-SiC products | Development, manufacturing, sale | Ferrotec Material Technologies Corporation | |
| Equipment parts cleaners | Development, sale | Ferrotec (Anhui) Technology Development Co., Ltd. | |
| Silicon parts | Development, sale | Hangzhou Dunyuan Juxin Semiconductor Technology Co., Ltd. (FTHS)Zhejiang Dunyuan Juxin Semiconductor Technology Co., Ltd. | |
| Quartz crucibles | Development, manufacturing, sale | Ningxia Dunyuan Juxin Semiconductor Technology Corporation (FTNC) | |
| Others | Development, sale | Ferrotec (USA) Corporation Ferrotec Europe GmbHHangzhou Dahe Thermo-Magnetics Co., Ltd. (FTH)Anhui Changjiang Reclaim Semiconductor Material Co., Ltd.Hangzhou Semiconductor Wafer Co., Ltd. (CCMC) | |
| Electronic device business | Thermo-electric modules | Development, sale | Ferrotec Material Technologies CorporationFerrotec (USA) Corporation Ferrotec Nord Corporation |
| Sale | Ferrotec Europe GmbH | ||
| Manufacturing | Hangzhou Dahe Thermo-Magnetics Co., Ltd. (FTH)Shanghai Shenhe Investment Co., Ltd. (FTS) | ||
| Power semiconductor substrates | Development, manufacturing, sale | Jiangsu Ferrotec Semiconductor Technology Co., Ltd. (FLH)Ferrotec (Sichuan) Semiconductor Technology Co., Ltd. (FLHC) | |
| Magnetic fluid | Development, manufacturing, sale | Ferrotec Material Technologies CorporationFerrotec (USA) Corporation | |
| Sale | Shanghai Shenhe Investment Co., Ltd. (FTS)FERROTEC CORPORATION SINGAPORE PTE LTD | ||
| Sensors | Development, manufacturing, sale | OHIZUMI MFG. CO., LTD.Ferrotec (Zhejiang) Sensor Technology Co., Ltd. | |
| Others | Development, manufacturing, sale | Ferrotec (USA) CorporationShanghai Shenhe Investment Co., Ltd. (FTS)Shanghai Hanhong Precision Machinery Co., Ltd.Hong Kong First Semiconductor Technology Co., Ltd.Ningxia Shenhe New Material Technology Co., Ltd. MES Ferrotec China Co., Ltd. | |
(Excerpt from the company’s Annual Securities Report for FY 3/24)
*The electronic device business was divided into the electronic device business and the automotive-related business in FY 3/25. The chart above is based on the classification used until FY 3/24.
Ferrotec was born as a company with highly unique technologies including thermo-electric modules with uses in thermal elements and vacuum technologies that respond to magnetic fluids that were born from the NASA space program in 1980. A wide range of diverse technologies cultivated over more than 40 years were applied in the electronics, automobile, next generation energy, and other industries. As a transnational company, Ferrotec deploys its businesses in Japan, Europe, the Americas, China, and Asia, and involves in marketing, development, manufacturing, sales, and management while taking advantage of the strengths of each country and region. A holding company structure was implemented from April 2017. In April 2022, due to market reorganization, the company got listed on the Standard Market of TSE.
1-1 Business Segments
Ferrotec’s operations includes semiconductor seal related products such as Vacuum Feedthrough, quartz products, ceramic products, etc. used in manufacturing equipment of semiconductor, FPD, LED etc., electronic device business centering on thermo-electric modules, “the automotive-related business,” which handles mainly thermos-electric modules for in-vehicle systems, substrates for power semiconductors, and sensors, and business segments that are not included in the reportable segments. Other businesses, which handle silicon crystal and solar cell wafers, saw blades, machine tools, surface treatment, industrial washing machines etc.
Semiconductor Equipment-related Business
Ferrotec provides total engineering services in the Equipment Related business segment, including the manufacture and sale of Vacuum Feedthrough of equipment parts for solar power, semiconductor, FPD and LED applications, consumable products used in manufacturing of devices, quartz products, ceramic products, CVD-SiC products, quartz crucibles, silicon wafer processing and equipment cleaning services.
Vacuum Feedthroughs, which are the company’s mainstay products, are functional parts that transmit rotational motion to the inside of manufacturing equipment while preventing foreign substances, including gas and dust, from entering the inside of equipment. This Vacuum Feedthrough boasts the top market share in the world. These Vacuum Feedthrough use magnetic fluids (Fluids that respond to magnetic fields), which has been a core technology of Ferrotec since its founding. All of the business fields, however, are easily affected by capital investment, and the company focuses also on entering general fields with relatively stable demand, including conveyers and precision robots. In addition, Ferrotec has also focused its efforts upon assuming consigned manufacture of vacuum chambers that use Vacuum Feedthrough and gate valves (Both use vacuum related equipment).
At the same time, quartz products, ceramic products, CVD-SiC products, and quartz crucibles are critical elements in the process of semiconductor manufacturing. Quartz products are able to resist high temperature conditions that exist in the semiconductor manufacturing process and are a high purity silica glass product that protects semiconductors from undergoing chemical reaction by preventing it from activating with gas. The Company boasts of semiconductor manufacturing equipment manufacturers as their main clients in Japan and overseas who purchase ceramic products, which are Ferrotec’s core material and technology. At the same time, semiconductor inspection tools for machinable ceramics and fine ceramics used in semiconductor manufacturing equipment are two main products in this CVD-SiC. CVD-SiC products are the term used to describe SiC products manufactured by "CVD method (Chemical Vapor Deposition method)" (created from compounds of silicon and carbon gas). Currently, semiconductor equipment and structural parts are provided, and research and development for products used in aeronautics and space (Turbine, mirrors), automobile (Power semiconductors), energy (Nuclear power related), information technology (Semiconductor manufacturing equipment parts) and other applications are also being conducted. With regard to silicon wafer processing, the company manufactures wafers in sizes of 6 inches (diameter), 8 inches, and 12 inches. It has a large market share accounting for more than half of the manufacturing equipment cleaning market in China.

(From the company’s materials)
Electronic Device Business
Thermal element “thermo-electric modules” are products that can instantly raise or lower temperatures to a highly precise degree and are a core product of this business.
Thermo-electric modules are mainly used for automotive temperature control seats and many other purposes, including wafer temperature control in semiconductor manufacturing equipment, genetic testing apparatus, optical communications, home appliances, and other application products such as power semiconductor substrates. The company has the largest share in the global market of thermo-electric modules. By developing new products using high-performance materials and reducing costs and improving quality by adopting automated manufacturing lines, the company is stirring new demand and diversifying purposes of use of its products.
The company has the biggest share in the global market of magnetic fluid, which is increasingly used for such newly developed applications as linear vibration motors for smartphones, speakers for 4K-resolution televisions and automobiles, and high-sound-quality headphones. Furthermore, OHIZUMI MFG. CO., LTD., one of its consolidated subsidiaries, engages in a business of temperature sensors.
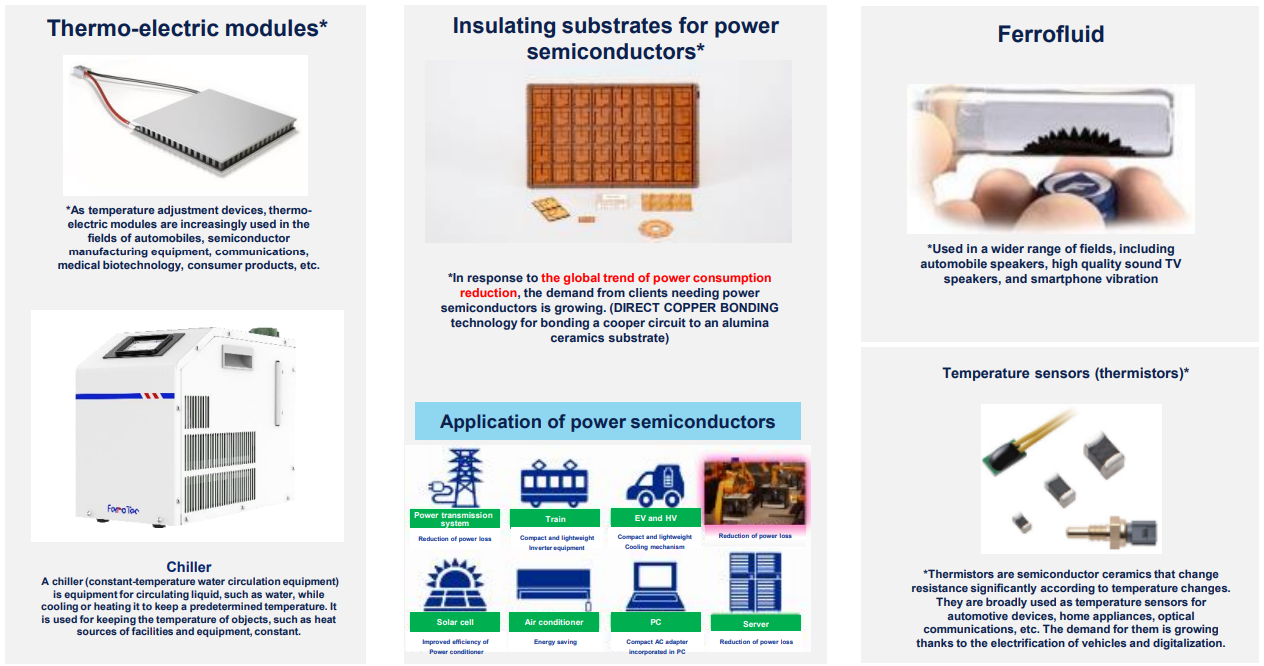
(From the company’s materials)
Automotive-related Business
Thermo-electric modules, power semiconductor substrates and sensors for in-vehicle systems, which used to be included in the electronic device business, have been disclosed as an automotive-related business since the first quarter of the fiscal year ended March 2025.
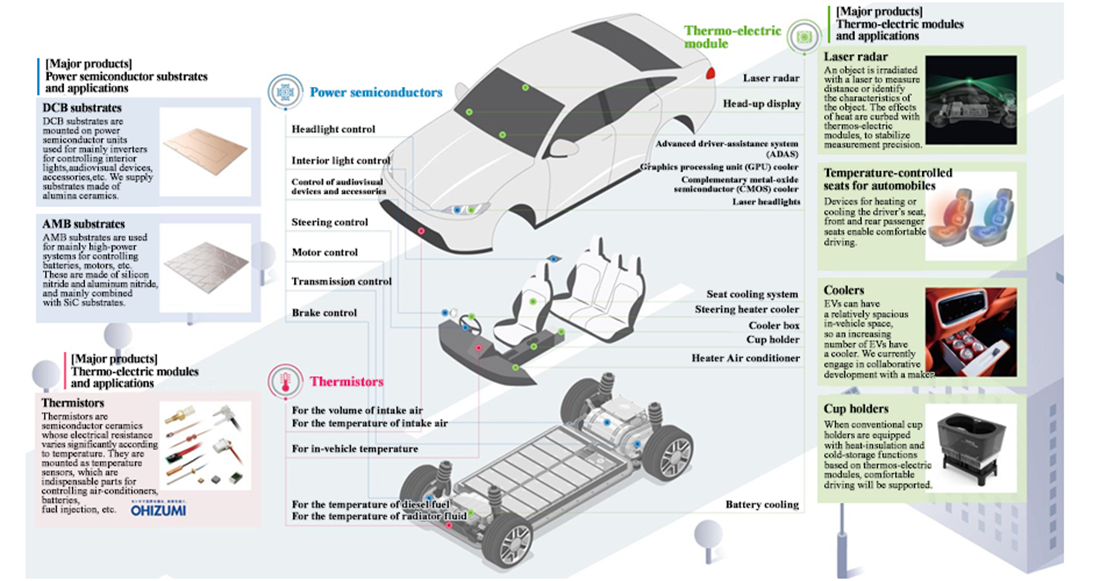
(From the company’s materials)
2. Earnings Results for the Second Quarter of the Fiscal Year ending March 2026
2-1 Consolidated Earnings
| FY 3/25 2Q Cumulative | Ratio to sales | FY 3/26 2Q Cumulative | Ratio to sales | YoY |
Sales | 135,157 | 100.0% | 140,980 | 100.0% | +4.3% |
Gross Income | 38,111 | 28.2% | 40,780 | 28.9% | +7.0% |
SG&A | 23,859 | 17.7% | 26,446 | 18.8% | +10.8% |
Operating Income | 14,251 | 10.5% | 14,333 | 10.2% | +0.6% |
Ordinary Income | 15,470 | 11.4% | 12,923 | 9.2% | -16.5% |
Interim Net Income | 9,190 | 6.8% | 6,308 | 4.5% | -31.4% |
*Unit: million yen.
Sales grew 4.3% year on year and operating income rose 0.6% year on year
In the cumulative second quarter of the fiscal year ending March 2026, sales grew 4.3% year on year to 140,980 million yen, and operating income rose 0.6% year on year to 14,333 million yen. While operating income declined year on year in the first quarter, gross profit margin rose to 29.6% in the second quarter (26.8% in the previous 2Q, 28.2% in 1Q of the current fiscal year), enabling the company to recover, increasing operating income in the cumulative second quarter.
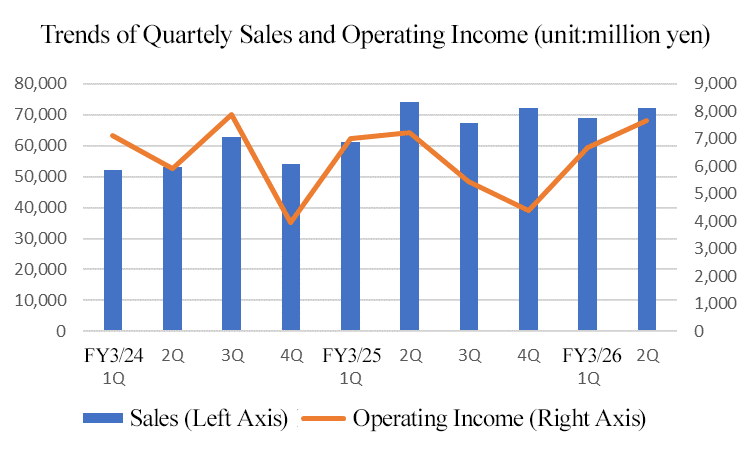
2-2 Business Segment Trends
Business Segment Sales and Profits
| FY 3/25 2Q Cumulative | Composition ratio Profit margin | FY 3/26 2Q Cumulative | Composition ratio Profit margin | YoY |
Semiconductor Equipment-related | 84,042 | 62.2% | 88,378 | 62.7% | +5.2% |
Electronic Device | 23,085 | 17.1% | 28,090 | 19.9% | +21.7% |
Automotive-related | 14,304 | 10.6% | 15,991 | 11.3% | +11.8% |
Others | 13,723 | 10.2% | 8,520 | 6.0% | -37.9% |
Consolidated Sales | 135,157 | 100.0% | 140,980 | 100.0% | +4.3% |
Semiconductor Equipment-related | 8,363 | 10.0% | 8,190 | 9.3% | -2.1% |
Electronic Device | 3,992 | 17.3% | 5,823 | 20.7% | +45.9% |
Automotive–related | 1,323 | 9.2% | 1,454 | 9.1% | +9.9% |
Others | 793 | 5.8% | -301 | -3.5% | - |
Adjustments | -220 | - | -833 | - | - |
Consolidated Operating Income | 14,251 | 10.5% | 14,333 | 10.2% | +0.6% |
*Unit: million yen.
(1) Semiconductor Equipment-related Business
Sales in the semiconductor equipment-related business increased 5.2% year on year to 88,378 million yen, while operating income decreased 2.1% year on year to 8,190 million yen. Among semiconductor materials, ceramic products have driven the growth by capturing strong demand in the U.S. and China. Meanwhile, the sales of quartz products and silicon parts remained sluggish due to the lingering impact of customers' inventory levels. In addition, the equipment parts cleaning business steadily captured growing demand in China, and sales of quartz crucibles for PV systems decreased.
The profit margin in this segment declined 0.7 points to 9.3%. Higher depreciation and other start-up costs for the new plant continued to weigh on profits. However, it is important to note that profit margin has bottomed out, having hit a low of 3.5% in the previous fourth quarter.
(2) Electronic Device Business
Sales in the electronic device business increased 21.7% year on year to 28,090 million yen and operating income rose 45.9% year on year to 5,823 million yen. The profit margin in this segment rose 3.4 points to 20.7%. In the thermo-electric modules business, shipments of micro modules for optical transceivers continued to be strong against the backdrop of significant investment in generative AI servers. In the business of power semiconductor substrates, the company has secured a 15.2% year-on-year growth in sales, despite intensifying competition due to sluggish demand. Sensors performed well, mainly for air conditioners, in addition to the impact of a change in the accounting period of OHIZUMI MFG. CO., LTD., a consolidated subsidiary of the company, resulting in the recording of profits from the second quarter of the fiscal year ending March 2025.
(3) Automotive-related Business
Sales of the automotive-related business increased 11.8% year on year to 15,991 million yen, while operating income increased 9.9% year on year to 1,454 million yen. The profit margin in this segment decreased 0.1 points to 9.1%. Regarding power semiconductor substrates, sales increased 3.5% year on year despite sluggish demand due to slow growth in the demand for EVs and intensifying price competition. Regarding thermo-electric modules, sales remained sluggish, mainly for temperature control seats, partly due to the impact of deteriorating market conditions. Like the electronic devices segment, no profits from sensors were recorded in the first quarter of the fiscal year ending March 2025 due to the change in the accounting period of OHIZUMI MFG. CO., LTD., a consolidated subsidiary of the company. However, profit was recorded this quarter, resulting in a net increase.
(4) Other Businesses
Sales in the other business segment decreased 37.9% year on year to 8,520 million yen, while operating income became a deficit. Sales decreased significantly due to a continued decline in shipments of silicon products for solar cells coupled with a reactionary decline in sales of machine tools, which had increased shipments in the same period of the previous fiscal year.
2-3 Financial Condition
| Mar, 25 | Sep, 25 | Increase Decrease |
| Mar, 25 | Sep, 25 | Increase Decrease |
Current Assets | 295,367 | 296,468 | +1,101 | Current Liabilities | 151,750 | 150,376 | -1,374 |
Cash | 117,727 | 115,700 | -2,027 | Payable | 59,591 | 52,602 | -6,990 |
Receivable | 92,608 | 88,909 | -3,698 | St Interest-Bearing Liabilities | 59,074 | 65,655 | +6,581 |
Inventory | 72,077 | 77,119 | +5,040 | Noncurrent Liabilities | 125,292 | 135,616 | +10,323 |
Noncurrent Assets | 305,226 | 303,095 | -2,131 | Lt Interest-Bearing Liabilities | 103,222 | 114,094 | +10,872 |
Tangible Asses | 245,064 | 242,351 | -2,712 | Total Liabilities | 277,043 | 285,993 | +8,949 |
Intangible Assets | 6,166 | 5,496 | -669 | Net Assets | 323,549 | 313,570 | -9,979 |
Investments and Other Assets | 53,996 | 55,247 | +1,250 | Retained Earnings | 90,435 | 92,717 | +2,282 |
Total Asset | 600,593 | 599,563 | -1,029 | Total Liabilities and Net Assets | 600,593 | 599,563 | -1,029 |
*Unit: million yen. Interest-bearing liabilities do not include lease obligations.
Total assets decreased 1,029 million yen from the end of the previous fiscal year to 599,563 million yen. Although merchandise/finished goods (inventories) and investments and other assets increased, receivables, machine/transport equipment, and construction in progress (tangible assets) decreased.
Total liabilities increased 8,949 million yen to 285,993 million yen. While receivables decreased, both short- and long-term interest-bearing liabilities increased.
Net assets decreased 9,979 million yen to 313,570 million yen. Although retained earnings increased 2,282 million yen, a decrease of 18,070 million yen in foreign currency translation adjustment produced a significant effect.
2-4 Cash Flow
| FY 3/25 2Q Cumulative | FY 3/26 2Q Cumulative | Increase Decrease |
Operating Cash Flow | 4,151 | 12,405 | +8,254 |
Investing Cash Flow | -17,736 | -32,596 | -14,860 |
Free Cash Flow | -13,585 | -20,191 | -6,606 |
Financing Cash Flow | 12,169 | 25,061 | +12,892 |
Cash and Equivalents at the end of term | 104,368 | 108,302 | +3,934 |
The cash flow from operating activities was 12,405 million yen. This was mainly due to a year-on-year decrease in the increase of receivables. Regarding the cash flow from investing activities, expenditures for acquiring tangible fixed assets and shares in the affiliate company CCMC. Meanwhile, the cash flow from financing activities increased significantly, mainly due to an increase in payment from non-controlling shareholders (capital increase of the cleaning subsidiary FTSVA). As a result, the balance at the end of the second quarter of the fiscal year ending March 2026 stood at 108,302 million yen, up 3,934 million yen year on year.
The breakdown of expenditures for acquisition of tangible fixed assets totaling 27,225 million yen is as follows: 2.6 billion yen for the former FTHD (Kumamoto Plant/parts cleaning, etc.), 4.5 billion yen for the former FTMT (Ishikawa Plant No. 3/ceramics, etc.), 2.4 billion yen for Changshan (ceramics), 2.0 billion yen for Malaysia (power substrates), 2.1 billion yen for Changshan Phase 4 (metal processing), 2.4 billion yen for Malaysia-Kulim (quartz, ceramics, metal processing), and 2.2 billion yen for Yeosu (sensors).
2-5 Topics
◎ Response to Ex-CHINA
<Malaysia>
Kulim Factory No.1 has steadily increased production volume since the mass production began and achieved profitability on a monthly basis at a faster pace than expected. The company expects to improve its capacity to supply products to customers and focus on acquiring new customers by further promoting certification.
The construction of Kulim Factory No. 2 is progressing on schedule toward completion in the second half of 2026. Specifically, after beginning construction in June 2025, foundation work was completed, and the project has now moved into the building construction phase. A ridgepole raising ceremony is scheduled to be held in December.
<Japan>
In the fiscal year ending March 2026, the company will complete the construction of production bases in Japan (Ishikawa Factory No. 3 and Kumamoto Factory) under the keyword of “reshoring to Japan.” Fine ceramics and machinable ceramics are the main products manufactured at Ishikawa Factory No. 3 (building area 13,000 square meters), while semiconductor manufacturing equipment, components, and precision products are recycled at Kumamoto Factory (building area: 13,000 square meters). The company plans to step up efforts to capture demand from customers in Japan as well as in Europe and the U.S. Furthermore, Kumamoto Factory reportedly has room for expansion on adjacent land.
◎ Activities of Chinese Subsidiaries
Ferrotec (Anhui) Technology Development Co., Ltd. (FTSVA), a listed subsidiary in China, made Jiangsu Ferrotech Semiconductor Technology Co., Ltd. (FLH), a subsidiary that manufactures power semiconductor substrates, a subsidiary through a share exchange. In addition, it conducted a third-party allocation of new shares of 780 million yuan (approximately 16.1 billion yen) for the purpose of developing power semiconductor substrates, etc.
Hangzhou Semiconductor Wafer Co., Ltd., an equity-method affiliate engaged in the semiconductor wafer business, has been listed as an over-the-counter company on China's New Third Board (National Equities Exchange and Quotations, China's over-the-counter market) and began trading on October 22. The company also raised 610 million yuan (about 12.9 billion yen) through a third-party allotment for the purpose of purchasing fixed assets and repaying interest-bearing debt.
3. Full-Year Earnings Estimates for the Fiscal Year ending March 2026
3-1 Full Year Consolidated Earnings
| FY 3/25 | Ratio to sales | FY 3/26 Previous forecast | FY 3/26 Revised forecast | Ratio to sales | YoY | Progress rate |
Sales | 274,390 | 100.0% | 285,000 | 285,000 | 100.0% | +3.9% | 49.5% |
Operating Income | 24,089 | 8.8% | 28,000 | 30,000 | 10.5% | +24.5% | 47.8% |
Ordinary Income | 25,558 | 9.3% | 26,000 | 28,000 | 9.8% | +9.6% | 46.2% |
Net Income | 15,692 | 5.7% | 16,000 | 16,000 | 5.6% | +2.0% | 39.4% |
*Unit: million yen
Revised the full-year operating income and ordinary income targets upwardly while considering the recent performance in the semiconductor equipment-related business and other segments
In the full-year corporate plan announced at the beginning of the fiscal year ending March 2026, the forecasts of sales of 285 billion yen (+ 4% YoY) and EBITDA of 55 billion yen (+ 15% YoY) were left unchanged, while the forecasts of operating income and ordinary income were revised upwardly. The exchange rate assumptions (average during the fiscal year) are 148 yen for the U.S. dollar (initial plan: 146 yen, actual for FY 3/2025: 152.24 yen) and 20 yen for the Chinese yuan (unchanged from the initial plan, actual for FY 3/2025: 21.12 yen). The estimated capital investment of 65 billion yen (actual for FY 3/2025: 51.77 billion yen) remains unchanged.
The upward revision was driven by a favorable product lineup and profitability in the semiconductor and other equipment-related businesses. However, the company incurred a loss of 493 million yen on the disposal of fixed assets in the first half due to the relocation of production equipment from Kansai Factory to Ishikawa Factory. As a result, the company's initial net income projections remained unchanged.
| FY 3/26 1H | YoY | FY 3/26 2H | YoY | FY 3/26 Full Year | YoY |
Vacuum Feedthroughs | 22,557 | +16.6% | 29,274 | +47.5% | 51,831 | +32.2% |
Quartz products | 16,440 | +1.9% | 16,500 | +4.5% | 32,940 | +3.2% |
Silicon parts | 6,713 | -6.4% | 6,407 | -1.6% | 13,121 | -4.1% |
Ceramics products | 19,099 | +23.6% | 19,100 | +7.9% | 38,199 | +15.2% |
CVD-SiC products | 4,639 | +16.2% | 3,125 | -25.6% | 7,764 | -5.2% |
EB-Gun, LED deposition equipment | 3,932 | -3.5% | 2,103 | -49.5% | 6,036 | -26.8% |
Recycled wafers | 2,216 | +77.2% | 2,581 | +60.9% | 4,798 | +68.0% |
Equipment parts cleaning | 8,294 | +17.5% | 8,832 | +7.1% | 17,126 | +11.9% |
Quartz crucibles | 4,484 | -53.0% | 4,196 | +34.5% | 8,681 | -31.5% |
Semiconductor Equipment-related Business | 88,378 | +5.2% | 92,122 | +13.4% | 180,500 | +9.2% |
Thermo-electric modules | 14,639 | +17.8% | 16,244 | +9.8% | 30,884 | +13.4% |
Power semiconductor substrates | 10,009 | +15.2% | 9,080 | -4.0% | 19,090 | +5.2% |
Ferrofluid, Others | 616 | +7.1% | 677 | +20.5% | 1,293 | +13.7% |
Sensors | 2,825 | +103.7% | 3,681 | +42.5% | 6,506 | +63.8% |
Electronic Device Business | 28,090 | +21.7% | 29,684 | +8.3% | 57,774 | +14.4% |
Thermo-electric modules | 2,639 | -15.1% | 2,253 | -31.8% | 4,892 | -23.7% |
Power semiconductor substrates | 9,961 | +3.5% | 6,949 | -27.8% | 16,911 | -12.2% |
Sensors | 3,390 | +116.2% | 4,173 | +29.0% | 7,563 | +57.5% |
Sales of Automotive-related Business | 15,991 | +11.8% | 13,376 | -17.2% | 29,367 | -3.6% |
*Unit: million yen
4. Conclusions
The progress rates were 49.5% for sales and 47.8% for operating income against the full-year forecast (after the upward revision) for the results in the first half. Although there are differences in fundamentals by product, it is fair to say that overall performance has been solid due to the success of portfolio management. At the financial results briefing, the company stated that “the year 2025 was a fairly good year.” While the company expressed high confidence in achieving its targets for the fiscal year ending March 2026, it also indicated that it is considering aggressive investment for the fiscal year ending March 2027 onwards and is aware of challenges ahead.
The share price of the company has been rising since bottoming out in April 2025 and has finally reached a PBR of 1.0x. In addition to macro factors, such as rising expectations for a recovery in demand for semiconductor materials and equipment, it can be considered that the logical implementation of improvement plans in response to PBR falling below 1.0x contributed to the rise in share price. Favorable external conditions will be needed to provide a tailwind for share price to continue to rise. However, the company needs to achieve stable growth in sales and profits based on the investments for growth so far, improve ROE, and enhance shareholder returns. In this regard, the company has launched a solid capital policy, including a minimum DOE of 3.5% and a total return ratio of 50%.
<Reference 1: New Mid-Term Management Plan (FY3/26 to FY3/28)>
1 Basic policies of the new mid-term management plan
The basic policies of the new mid-term management plan are as follows:
Business growth | ➣Expand semiconductor related, electronic device and automobile related businesses to pursue growth ➣Focus on capturing semiconductor-related needs in China while reinforcing production outside China, such as in Malaysia, responding to needs for manufacturing outside China (Ex-China), brought about by the friction between the U.S. and China |
Enhancement of productivity and improvement of production efficiency | ➣Raise return rate by boosting production and improving efficiency at Factorys in Malaysia (Kulim, Johor) ➣Pursue the improvement of production efficiency and the enhancement of competitiveness by working on digitalization, automatization, and adoption of AI ➣Promote and enhance the development of new products and new technologies, continuing rigorous quality control under the philosophy of “what matters is quality.” |
Human resources and corporate culture | ➣Promote the recruitment and training of personnel, viewing the emphasis on human resources as an important management strategy ➣Continue activities for diffusing the policy of “respecting clients, respecting employees, paying respect to diligence and trust, and taking steady action to pursue innovation,” as corporate culture is the cornerstone of a company |
Financial and shareholder returns | ➣Consider ways of utilizing market value of shares, which is projected to increase upon the integration of FTSVA, a cleaning business subsidiary, and FLH, a subsidiary for power semiconductor substrates, which are listed on the Chinese market ➣Policy to adopt DOE and flexibly consider treasury stock acquisition in accordance with the new shareholder return policy |
(Produced by Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. with reference to disclosed material.)
2 Numerical Targets of Mid-term Management Plan
(million yen) | Mid-term management plan (FY 3/25 – FY 3/27) | |||
FY 3/25 (Act.) | FY 3/26 (Est.) | FY 3/27 (Est.) | FY3/28 (Est.) | |
Sales | 274,390 | 285,000 | 340,000 | 400,000 |
Operating income | 24,089 | 30,000 | 35,000 | 47,000 |
Operating income margin | 8.8% | 10.5% | 10.3% | 11.8% |
Net income | 15,692 | 16,000 | 20,000 | 29,000 |
ROE | 7.1% |
| 15.0% | |
ROIC | 3.9% |
| 8.0% | |
Shareholder’s equity ratio | 39.4% | 40% | 40% | 40% |
Investment amount | 51,777 | 65,000 | 45,000 | 30,000 |
Dividend per share (yen) | 141.0 | 148.0 | Lower limit for DOE at 3.5% Total return ratio of 50% | |
*ROIC = Net income attributable to owners of the parent / (interest-bearing liabilities + net assets); Net assets do not include share acquisition rights or non-controlling shareholders’ equity.
(Produced by Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. with reference to disclosed material.)
Regarding CAGR for the three terms from the fiscal year ended March 2025, the company forecasts an increase of 13% for sales and an increase of 25% for operating income. Despite negative growth in 2023, the semiconductor market has recovered by 2024 and is projected to grow 11% year on year in 2025 (as announced by WSTS). It is assumed that it could reach a scale of 1 trillion dollars by 2030 (presuming an annual growth rate of 7.5%). The market scale is projected to grow 1.7 times from 2024. The Wafer Fab Equipment (WFE), the growth of which has been flat recently due to a decrease in export to China, is also projected to get on a growth track after bottoming out in 2025 (company’s assumption).
Taking such external environment into account, the company intends to keep expanding their business and pursuing growth. They are planning to focus especially on capturing semiconductor-related needs in China while enhancing production outside China, such as in Malaysia, to address needs for manufacturing outside China brought about by the friction between the U.S. and China. Raising the return rate by boosting production and elevating efficiency at the two factories in Malaysia (Kulim and Johor) is likely to become an important point of the medium-term management plan.
The Kulim Factory, completed in January 2024, achieved profitability in terms of monthly profit and loss in the first quarter of 2025, also owing to the steady progress in client certification. The company intends to further work on boosting production and elevating efficiency, forecasting a possible raise from the current production capacity of 15 billion yen to the maximum production capacity of 19 billion yen. They have also decided to construct a second factory as they received requests for enhancing production from clients in the U.S., etc. as a result of the friction concerning semiconductors between the U.S. and China. The second factory is expected to start operation between 2026 and 2027, and reach the maximum production capacity of 24 billion yen. Regarding Johor Factory, which will produce power semiconductor substrates, the company started to install equipment in the fourth quarter of 2024, and started trial production in January 2025 (first shipment in March of the same year).


(Excerpt from the company’s materials)
3 Details of major factories newly established and increases in principal manufacturing capacities
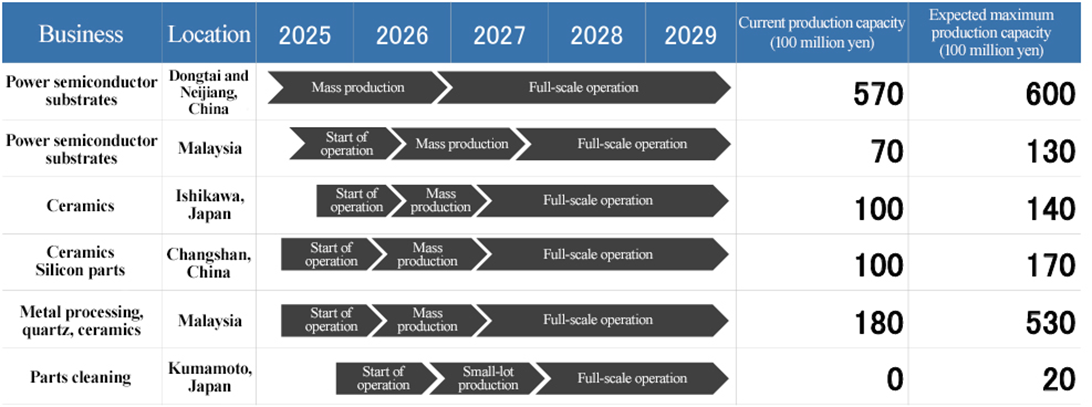
(From the company’s materials)
◎ Long-term goals
The company has not revised its numerical goals set in the long-term vision, that is, sales of 500 billion yen and a net income of 50 billion yen in fiscal year ending March 2031.
<Reference 2: Measures for Achieving Management Conscious of Capital Costs and Stock Price>
On July 31, 2024, the company disclosed its initiative on "Measures for Achieving Management Conscious of Capital Costs and Stock Price." The gist of the medium-term management plan, which was disclosed this time, remains unchanged, except the change in the shareholder return policy from “focusing on a payout ratio of 20-30%” to “3.5% for the lower limit of DOE and 50% for total return ratio.” Key points are as follows.
The company has defined its shareholder equity cost at 8.62% for FY 3/24, calculated using the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM). The assumptions for this calculation include a risk-free rate of 1.735% (20-year government bond yield), a β of 1.043 (for the semiconductor manufacturing equipment industry), and an equity risk premium of 6.60%. The company's ROE for FY 3/24 was 7.8%, falling below its shareholder equity cost, which is considered as the primary reason for its PBR (Price-to-Book Ratio) remaining below 1. Recognizing the urgent need to enhance profitability above its shareholder equity cost, the company has set a target of achieving an ROE of 15%. To reach this goal, it plans to drive business and profit growth, strengthen profitability, implement effective ROIC management, focus on business selection and concentration to improve total asset turnover, and optimize financial leverage. Additionally, the company aims to improve its PER (Price-to-Earnings Ratio) through enhanced shareholder return policies and the further strengthening of non-financial strategies. The specific initiatives to achieve these goals are outlined below.
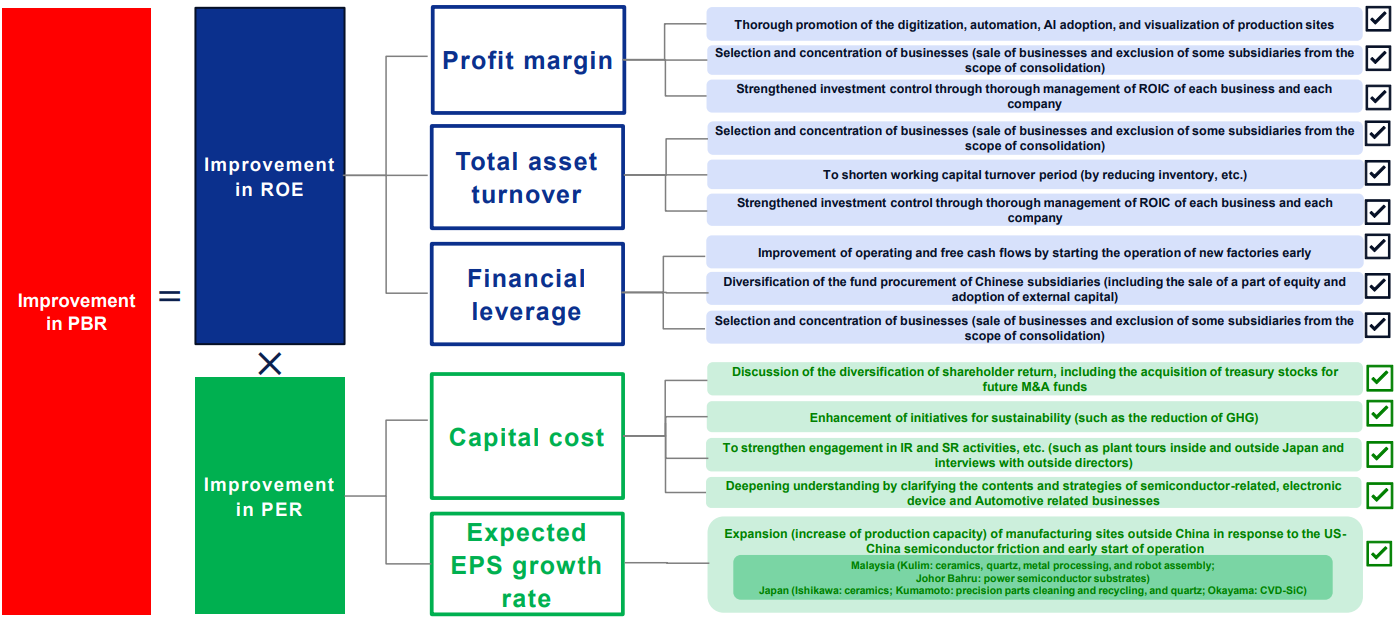
(From the company’s materials)
As achieving the medium-term management plan is essential to meeting these targets, the company has also announced a transition to a performance-linked compensation system, which strengthens both short-term and medium-to-long-term incentives, further aligning executive remuneration with business performance.
<Reference 3: Regarding Corporate Governance>
◎ Organization type, and the composition of directors and auditors
Organization type | Company with auditors |
Directors | 9 directors, including outside ones 3 (including 3 independent executives) |
Auditors | 3 auditors, including outside ones 2 (including 2 independent executives) |
◎ Corporate Governance Report (Updated on July 17, 2025)
Basic policy
While pursuing our corporate principles: “Strong commitment to our customers,” “Excellence in engineering precision solutions,” and “Delivering superior quality, value and service,” our corporate group has drawn up a code of conduct as follows: From a global perspective, Ferrotec always operates in harmony with the international community and acts in good faith with unwavering corporate ethics and social decency, as well as in compliance with the laws of each country as a company that provides products and services that contribute to everyday life of the people all over the world who are related to us; Ferrotec earns customer trust and satisfies our customers by proposing high-quality products and services and providing cost-competitive products and services mainly in the new energy and electronics industries; Considering proactive eco-friendly activities to be one of our high-profile business issues, Ferrotec contributes to solving global environmental problems by adapting ourselves to the requirements of the latest environmental regulations one by one and developing materials and products that can be used in the new energy industry; and Ferrotec contributes to society through manufacturing based on our core technology, continues to be a company whose stakeholders, including customers, shareholders, employees, business partners, and local communities, are looking forward to seeing it grow, and engages in business activities based on social decency, such as laws, social order, and international rules.
Our company not only proactively promotes environmental preservation activities and our corporate group’s governance pursuant to the aforementioned corporate principles and code of conduct, but also strives to continue being a company whose stakeholders look forward to its growth. We have also formulated a quality philosophy saying that we focus on developing new materials and production technologies, such as semiconductor materials, and pursue customer satisfaction improvement by giving top priority to quality, and are moving forward with automation, digitalization, and standardization of our production processes. Our basic business policies are to increase our share in the global market and form a corporate group with a stable profit structure.
Based on the above corporate principles, code of conduct, and basic management policy, the company considers that it is important to improve its corporate value, emphasize the soundness of its business administration to become an enterprise that will be trusted and supported by stakeholders, including shareholders, customers, business partners, and local communities, and also establish a managerial system responding the rapid changes to the business environment swiftly and accurately.
<Main Reasons for Non-compliance with the Principles of the Corporate Governance Code (Excerpt)>
<Supplementary Principle 1-1-1: Analysis of Reasons Behind a Considerable Number of Opposing Votes at a General Shareholders’ Meeting>
While our company has not set the criterion for a “considerable number” in case a considerable number of opposing votes was cast at a general shareholders’ meeting, we shall consider defining the criterion from now on. In case a considerable number of opposing votes was cast, we shall swiftly analyze the reasons behind the opposition and the cause for the increase of opposing votes and present our view of the issue, such as making a press release of the analysis results.
<Supplementary Principle 2-4-1: Ensuring diversity in promotion to core human resources>
As a basic policy for human capital, the group operates under two major policies regarding organizations and human resources.
The first is to create a company and organization, in which each employee, regardless of their attributes, can act autonomously and with ambition and have a sense of fulfillment in their work. The second is to localize management, make decisions quickly, and manage the business and the organization according to the characteristics of each region.
While our business is expanding on a global basis, our corporate group drastically strengthens our human resources and organization and proactively employs women, foreign nationals, and mid-career workers with extensive skills and experience to raise our corporate value in the medium/long term. In addition, we actively promote women, foreign nationals, and mid-career hires to managerial positions by comprehensively considering and evaluating such factors as their skills and valuable experience cultivated in companies outside of our corporate group.
・Voluntary and Measurable Targets for Ensuring Diversity
A talented human resource strategy and diversity are important, and the company aims to increase the ratio of female recruits to 25% or more by the fiscal year ending March 2028. As of the end of March 2025, the ratio was 22.2%.
・Human Resource Development Policy and Internal Environment Improvement Policy to Ensure Diversity, and their Status
In order to develop an environment in which employees can work with peace of mind, the company aims to increase the retention rate of new graduates and mid-career recruits after three years to 80% or more by the fiscal year ending March 2028. As of the end of March 2025, the rate stood at 77.78%.
Going forward, the company will earnestly consider disclosing its human resource development policy and internal environment improvement policy from a medium- to long-term perspective, including the promotion of women, foreign nationals, and mid-career recruits to management positions, as well as the progress and achievement status of these policies.
<Supplementary Principle 3-1-3: Disclosure of initiatives on sustainability and business strategies, such as investment in human capital and intellectual property>
Following our corporate principles: “Strong commitment to our customers, excellence in engineering precision solutions, and delivering superior quality, value and service,” our company has framed a basic policy on materiality and sustainability in 2021 because we consider ESG (Environment, Social, and Governance) to be extremely important for medium- and long-term improvement of our corporate value. We will build an organizational structure, enlighten our employees, and set quantitative goals for promoting ESG. Regarding investment in human capital and intellectual property, our Japanese subsidiaries proactively promote young employees to the position of executive officer and flatten their organizations. Meanwhile, our Chinese subsidiaries actively invest in intellectual property by, as necessary, founding research institutes related to semiconductors, employ a greater number of human resources who have degrees equivalent to doctor’s degrees, and granting their employees awards and rewards for superb patent applications. We will monitor quantitative goals that we set and announce our progress with them via our website, IR material, and other means.
<Main Disclosure Based on the Principles of the Corporate Governance Code (Excerpt)>
<Principle 1-4, Supplementary Principle 1-4-1, Supplementary Principle 1-4-2: Strategically Held Shares>
We define and operate the policy regarding strategically held shares and the criteria for exercising the voting rights stemming from strategically held shares as follows.
1. Our policy regarding strategic shareholding
Our basic policy lies in holding no shares strategically.
However, we hold the shares of other companies only in cases where we judged that it is highly reasonable to hold the relevant shares in terms of the relationship with the issuing company, such as shares of our business partners. The president’s office regularly inspects the reasonableness of holding these shares and presents the findings to the Board of Directors. Regarding the concrete inspection method, the Board of Directors inspects whether the objective for holding the shares is appropriate or not, whether the benefits and risks stemming from holding the shares correspond with the capital cost, etc., and forges ahead with reducing strategically held shares based on the inspection results.
On a Board of Directors’ meeting held in June 2025, we decided to keep holding the shares of seven companies as a result of a careful examination.
2.Our criteria for exercising the voting rights stemming from strategically held shares
With regard to exercising voting rights, we respect the judgment of the Board of Directors of the company that issued the relevant shares as a general rule, and make affirmative judgments in voting unless the matter in question negatively impacts the relationship and transactions with our corporate group, or it can be surmised that it will clearly degrade common interests of shareholders.
3.Response to strategically held shares of our company
Apart from the aforementioned, in case a company that strategically holds our shares expresses the intention to sell these shares, we respond appropriately to the sale, etc., without making any obstructions to the sale, such as implying a reduction in transactions.
<Principle 1-5: The So-Called Anti-Takeover Measures>
We have not adopted any so-called anti-takeover measures at our company.
In case our shares are offered in a takeover bid, our Board of Directors carefully examines its objective and content, and announces our company’s opinion. In case the Board of Directors judges that it is necessary from the viewpoint of maintaining and elevating corporate value, we suggest appropriate measures while taking care so as not to unjustly hinder the right of the shareholder to accept the takeover bid.
<Principle 2-1: Formulation of Management Philosophy as the Foundation for Elevating Corporate Value in the Medium to Long Term>
We engage in business activities in accordance with the three management philosophies, which are “being trusted by customers and gaining their satisfaction,” “contributing to resolving global climate issues” and “contributing to the society through craftsmanship,” in order to pursue harmony between the global society and local societies from a global standpoint and act in a sincere way as a company offering products and services that can contribute to the lives of all kinds of people.
<Principle 2-3: Issues related to sustainability, mainly social and environmental issues>
The semiconductor manufacturing process has a significant environmental load, and solving this is a challenge for the entire industry. The company sells products such as thermo-electric modules, which are CFC-free temperature control devices, and power semiconductor substrates and ferrofluids that effectively reduce power consumption. The company also relies on clean energy, using solar panels in power generation at our factories in Japan and China. Thus, our business activities contribute to reducing greenhouse gases, leading to environmental pollution reduction. In March 2023, the "Sustainability Committee" was established as a committee under the Company's Board of Executive Officers to check the status of sustainability initiatives, review and deliberate on them, and report to the Board of Directors and other relevant bodies when necessary, in order to examine and promote sustainability on a company-wide basis. The number of university students in financial distress is increasing after the COVID-19 pandemic. Therefore, the company supports the Akira Yamamura Scholarship Foundation, which provides scholarships to engineering students to develop talented human resources who can contribute to society in the future.
<Principle 2-4: Ensuring diversity, including active participation of women>
Believing that working with employees who have different experiences and senses of values within a company is an advantage in ensuring sustainable business growth especially when companies operate globally like our company, we endeavor to ensure diversity, including active participation of women, based on our policy of entrusting each of our local subsidiaries with management of their own companies.
<Principle 5-1: Policy for Constructive Dialogue with Shareholders>
To achieve sustainable growth and improve corporate value, we will promote constructive dialogue with shareholders, explain our management policies and business conditions in an easy-to-understand manner, and strive to gain the understanding of shareholders.
- Policy for constructive dialogue with shareholders -
1. Overseeing dialogue with shareholders:
The Director in charge of Management Strategy and Special Assignments from the President, who serves as the IR Officer, has been designated as the management representative responsible for overseeing dialogue with shareholders.
2. A system of collaboration among various internal departments to support dialogue with shareholders:
The IR/Public Relations Department and the Finance and Accounting Department work together to support dialogue with shareholders.
3.Efforts to improve the means of dialogue other than individual interviews:
We utilize various means of communication, including financial results briefings, small meetings, individual investor briefings, business briefings held after the general meeting of shareholders, online meetings, and various printed materials. At financial results briefings and business briefings, the representative director personally gives explanations.
4.Management of insider information during dialogue:
We strictly manage information in accordance with our internal information management regulations.
[Actions to achieve management that is conscious of the cost of capital and stock price] [English description available]
We consider return on equity (ROE) and return on invested capital (ROIC) to be important management indicators and have set an ROE of 15% and an ROIC of 8% as one of our management targets (KPIs) for the period of our medium-term management plan (FY 3/25 to FY 3/27). The Board of Directors periodically reviews the cost of capital and weighted average cost of capital (WACC) and has calculated the cost of equity capital to be in the high-9% range and the WACC to be in the high-8% range for the fiscal year ended March 2025. In contrast, ROE and ROIC for the same consolidated fiscal year were 7.1% and 3.9%, respectively, lower than the cost of capital and WACC, mainly due to a decline in the net income margin attributable to shareholders of the parent company and an increase in tangible fixed assets caused by increased expenses associated with recent large capital investments. Therefore, we recognize that our most important management issue at hand is to stably achieve ROE and ROIC that exceed the cost of capital and WACC, respectively. In addition, our price-to-book ratio (PBR) remains below 1, at 0.53 for the fiscal year ended March 2025, and we recognize the importance of improving our ROE and price-earnings ratio (PER).
For details on the assessment of current statuses of these management issues and various measures, please refer to “Initiatives for Realizing Business Administration Conscious of Capital Cost and Share Price,” disclosed on July 31, 2024 and page 20 of the Medium-Term Management Plan (Rolling Plan) announced on May 30, 2025.
“Initiatives for Realizing Business Administration Conscious of Capital Cost and Share Price”
(Japanese) https://www.ferrotec.co.jp/php/download.php?f=jp/66b077985a236.pdf
(English) https://www.ferrotec.co.jp/php/download.php?f=en/66b0929d8d3aa.pdf
Medium-Term Management Plan (Rolling Plan)
(Japanese) https://www.ferrotec.co.jp/php/download.php?f=jp/20250602577588.pdf
This report is not intended for soliciting or promoting investment activities or offering any advice on investment or the like, but for providing information only. The information included in this report was taken from sources considered reliable by our company. Our company will not guarantee the accuracy, integrity, or appropriateness of information or opinions in this report. Our company will not assume any responsibility for expenses, damages or the like arising out of the use of this report or information obtained from this report. All kinds of rights related to this report belong to Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. The contents, etc. of this report may be revised without notice. Please make an investment decision on your own judgment. Copyright(C) Investment Bridge Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. |


